Hypertrophy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
ViewingHabit (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:*+ * Photographic documentation on sexual education - Hypertrophy of breast - Nude of an elderly woman around 1870 - Photographer unknown - Public domain, since the copyright has expired;.jpg|Hypertrophy of [[breast]], c. 1870 |
File:*+ * Photographic documentation on sexual education - Hypertrophy of breast - Nude of an elderly woman around 1870 - Photographer unknown - Public domain, since the copyright has expired;.jpg|Hypertrophy of [[breast]], c. 1870 |
||
File:Hypertrophied clitoris.jpg|Hypertrophy of the [[clitoris]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
File: |
File:Feet from a case of partial hypertrophy of the foot Wellcome L0061374.jpg|Hypertrophy of the [[foot]], partial |
||
| ⚫ | |||
File:Head of a boy with hypertrophy of the ear Wellcome L0062496.jpg|Hypertrophy of the ear ([[macrotia]]) |
File:Head of a boy with hypertrophy of the ear Wellcome L0062496.jpg|Hypertrophy of the ear ([[macrotia]]) |
||
File: |
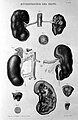
File:Kidney hypertrophy Wellcome L0005308.jpg|Kidney hypertrophy |
||
File:Lip hypertrophy.jpg|Hypertrophy of the upper lip |
|||
File:Face of man with hypertrophy of the temporal muscles Wellcome L0062508.jpg|Hypertrophy of the [[Temporalis muscle|temporal muscles]] |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
{{-plasia}} |
{{-plasia}} |
||
Revision as of 17:06, 18 December 2022
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (May 2017) |  |
| Hypertrophy | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Hypertrophy results from an increase in cell size, whereas hyperplasia stems from an increase in cell number |
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells.[1] It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number.[2] Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally-induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy.
Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart.[3] Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel).
Gallery
-
Hypertrophy of breast, c. 1870
-
Hypertrophy of the clitoris
-
Hypertrophy of the foot, partial
-
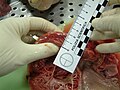
Forensic post-mortem examination of a case of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, showing thickening of the cardiac muscle
-
Hypertrophy of the ear (macrotia)
-
Kidney hypertrophy
-
Hypertrophy of the upper lip
-
Hypertrophy of the temporal muscles
| -plasia and -trophy |
|---|
|
|
See also
- Athlete's heart
- Ventricular hypertrophy (including left ventricular hypertrophy and right ventricular hypertrophy)
- Muscle hypertrophy
- List of biological development disorders
References
- ^ Hernandez, Richard; Kravitz, Len. "Skeletal muscle hypertrophy". www.unm.edu.
- ^ Updated by Linda J. Vorvick. 8/14/15.Hyperplasia
- ^ Kusumoto, F. M. (2004), Cardiovascular Pathophysiology, Hayes Barton Press, pp. 20–22, ISBN 978-1-59377-189-8