Androstenone: Difference between revisions
m need ref; tidy |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{distinguish|Androsterone|Androstenedione|5α-Androst-2-ene-17-one}} |
{{distinguish|Androsterone|Androstenedione|5α-Androst-2-ene-17-one}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date=November 2023}} |
|||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
| Verifiedfields = changed |
||
| Line 68: | Line 69: | ||
===Commercial use=== |
===Commercial use=== |
||
Some commercially available products are advertised using claims that they contain human sexual pheromones, including androstenone, and that they can act as an [[aphrodisiac]]. |
Some commercially available products are advertised using claims that they contain human sexual pheromones, including androstenone, and that they can act as an [[aphrodisiac]].{{fact}} |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 74: | Line 75: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} |
||
{{Pheromones and pherines}} |
{{Pheromones and pherines}} |
||
Revision as of 03:02, 16 November 2023
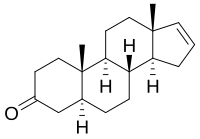
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5α-Androst-16-en-3-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,5aS,9aS,9bS,11aR)-9a,11a-Dimethyl-3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-7H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.367 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H28O | |
| Molar mass | 272.432 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Androstenone (5α-androst-16-en-3-one) is a 16-androstene class steroidal pheromone. It is found in boar's saliva, celery cytoplasm,[citation needed] and truffle fungus.[citation needed] Androstenone was the first mammalian pheromone to be identified. It is found in high concentrations in the saliva of male pigs, and, when inhaled by a female pig that is in heat, results in the female assuming the mating stance. Androstenone is the active ingredient in 'Boarmate', a commercial product made by DuPont sold to pig farmers to test sows for timing of artificial insemination.[1][2][3][4][5]
Biosynthesis
Androstenone is synthesized from androstadienone by 5α-reductase, and can be converted into 3α-androstenol or 3β-androstenol by 3-ketosteroid reductase.[6]
Properties
Depending upon the subject, it is reported to be an unpleasant, sweaty, urinous smell, a woody smell, or even a pleasant floral smell.[3][7][8]
There are two different genotypes that allow an individual to smell androstenone. The first genotype, which consists of two fully functional copies of the gene, is the RT/RT allele, and the second is the RT/WM allele.[citation needed] The OR7D4 receptor[4] has two non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms,[9] which cause the gene to have two amino acid substitutions, which in turn cause the receptor to act differently. Those in possession of the two proper genes, (RT/RT) for OR7D4 tend to describe the odor for the steroid as the odor of stale urine. Those with only one gene (RT/WM) typically described the odor as weak or were not able to detect it. They can also find the smell 'pleasant', 'sweet' or 'similar to vanilla'.[10]
In small amounts, the odor is hardly detectable by most people. This may be due to a polymorphism in the receptor gene that codes for the androstenone receptor.[11] However, the ability to detect the odor varies greatly. It has been shown that the odor can be detected by people down to levels of 0.2 parts per billion to 0.2 parts in 100 million.[12] Several groups report, however, that some individuals who initially cannot smell androstenone can learn to smell it by repeated exposures to it.[13]
Detectability as a pheromone
In humans, androstenone also has been suggested to be a pheromone; however, there is little scientific data to support this claim.[14][better source needed] The vomeronasal organ is an auxiliary olfactory sense organ responsible for the detection of pheromones as more than just an odor. Most adult humans possess something resembling this organ, but there is no active function. Humans lack the sensory cells that exist in other mammals needed to detect pheromones beyond a smell.[clarification needed][dubious – discuss] Humans also lack the genetic ability to produce these sensory cells actively.[citation needed]
There is also a specific anosmia to the odor in some humans; they are unable to smell specific odors, but have, otherwise, a normal sense of smell. However, this should, by no means, be regarded as indicative for being labeled as a pheromone, as it is true of over 80 olfactory compounds.[15]
To animals, the smell of androstenone can act as a social sign of dominance and can be a way of attracting a mate.[citation needed][dubious – discuss]
Commercial use
Some commercially available products are advertised using claims that they contain human sexual pheromones, including androstenone, and that they can act as an aphrodisiac.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ Pierce, John D.; Cohen, Adam B.; Ulrich, Patricia M. (March 2004). "Responsivity to Two Odorants, Androstenone and Amyl Acetate, and the Affective Impact of Odors on Interpersonal Relationships". Journal of Comparative Psychology. 118 (1): 14–19. doi:10.1037/0735-7036.118.1.14. PMID 15008668.
- ^ Dorries, Kathleen M.; Adkins-Regan, Elizabeth; Halpern, Bruce P. (1997). "Sensitivity and Behavioral Responses to the Pheromone Androstenone Are Not Mediated by the Vomeronasal Organ in Domestic Pigs". Brain, Behavior and Evolution. 49 (1): 53–62. doi:10.1159/000112981. PMID 8980852.
- ^ a b Wysocki, C. J.; Dorries, K. M.; Beauchamp, G. K. (1 October 1989). "Ability to perceive androstenone can be acquired by ostensibly anosmic people". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 86 (20): 7976–7978. Bibcode:1989PNAS...86.7976W. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.20.7976. PMC 298195. PMID 2813372.
- ^ a b Wysocki, C. J.; Beauchamp, G. K. (1 August 1984). "Ability to smell androstenone is genetically determined". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 81 (15): 4899–4902. Bibcode:1984PNAS...81.4899W. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.15.4899. PMC 391599. PMID 6589634.
- ^ Bonneau, M.; Walstra, P.; Claudi-Magnussen, C.; Kempster, A.J.; Tornberg, E.; Fischer, K.; Diestre, A.; Siret, F.; Chevillon, P.; Claus, R.; Dijksterhuis, G.; Punter, P.; Matthews, K.R.; Agerhem, H.; Béague, M.P.; Oliver, M.A.; Gispert, M.; Weiler, U.; von Seth, G.; Leask, H.; Font i Furnols, M.; Homer, D.B.; Cook, G.L. (March 2000). "An international study on the importance of androstenone and skatole for boar taint: IV. Simulation studies on consumer dissatisfaction with entire male pork and the effect of sorting carcasses on the slaughter line, main conclusions and recommendations". Meat Science. 54 (3): 285–295. doi:10.1016/s0309-1740(99)00105-9. PMID 22060698.
- ^ Weusten, J. J. A. M. (1989). Biochemical pathways in human testicular steroidogenesis (Thesis). hdl:2066/113615.
- ^ "Sniffers' genes dictate if sweat smells sweet". New Scientist. 19 September 2007.
- ^ Steenhuysen, Julie (16 September 2007). "Stinky? It's not his sweat, it's your nose". Reuters.
- ^ Keller, Andreas; Zhuang, Hanyi; Chi, Qiuyi; Vosshall, Leslie B.; Matsunami, Hiroaki (September 2007). "Genetic variation in a human odorant receptor alters odour perception". Nature. 449 (7161): 468–472. Bibcode:2007Natur.449..468K. doi:10.1038/nature06162. PMID 17873857. S2CID 4417235.
- ^ Swaminathan, Nikhil (18 September 2007). "The Scent of a Man". Scientific American.
- ^ Lundstrom, J. N.; Seven, S.; Olsson, M. J.; Schaal, B.; Hummel, T. (1 October 2006). "Olfactory Event-Related Potentials Reflect Individual Differences in Odor Valence Perception". Chemical Senses. 31 (8): 705–711. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjl012. PMID 16844768.
- ^ Birchall, Annabelle (25 August 1990). "A whiff of happiness: Can smelling a molecule contained in human sweat ease anxiety and stress? Some scientists think so, and argue that 'osmotherapy' may also help people to slim or stop smoking". New Scientist.
- ^ Graham, Sarah (23 October 2002). "Nostrils Share Information for Recognizing Scents". Scientific American.
- ^ Kirk-Smith, M.D.; Booth, D.A. (1980). "Effect of androstenone on choice of location in others' presence". In van der Starre, H (ed.). Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Olfaction and Taste (ISOT VII) and of the 4th Congress of the European Chemoreception Research Organization (ECRO IV): joint meeting held at 'de Leeuwenhorst' Congress Centre, Noordwijkerhout, the Netherlands, 22nd-25th July, 1980. IRL Press. pp. 397–400. ISBN 978-0-904147-20-9. OCLC 63367504.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Araneda, Ricardo C.; Firestein, Stuart (1 January 2004). "The scents of androstenone in humans". The Journal of Physiology. 554 (1): 1. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.057075. PMC 1664751. PMID 14678483.
