London Buses route 360: Difference between revisions
add newer photo |
WP:CAPTION |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|image = Go-Ahead London SEe50 (LJ66CJX) Vauxhall Bridge 16.01.2024.jpg |
|image = Go-Ahead London SEe50 (LJ66CJX) Vauxhall Bridge 16.01.2024.jpg |
||
|image_width = 300 |
|image_width = 300 |
||
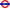
|caption = [[London Central]] [[Alexander Dennis Enviro200EV]] on [[Vauxhall Bridge]] |
|caption = [[London Central]] [[Alexander Dennis Enviro200EV]] on [[Vauxhall Bridge]] |
||
|bgcolor = red |
|bgcolor = red |
||
|titlecolor = white |
|titlecolor = white |
||
Revision as of 17:53, 19 April 2024
| 360 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Operator | London Central[1] |
| Garage | Camberwell |
| Vehicle | Alexander Dennis Enviro200EV |
| Route | |
| Start | Royal Albert Hall |
| Via | Kensington Sloane Square Pimlico Vauxhall Lambeth |
| End | Elephant and Castle |
London Buses route 360 is a Transport for London contracted bus route in London, England. Running between Royal Albert Hall and Elephant and Castle, it is operated by London Central.
History
The route was the first in London to use hybrid electric buses, with six vehicles built by Wrightbus, branded Electrocity, entering service in February 2006.[2] The trial was announced in March 2005; route 360 was chosen as it is one of few single-deck routes to operate in central London.[3] Six diesel buses were operated alongside the hybrids for comparison.[4] The hybrids were temporarily withdrawn shortly after their introduction following problems with engine overheating.[5]
In November 2009, it was announced that London Central had successfully tendered to retain the route, which would be converted to full hybrid operation using a mixture of new and existing vehicles from 23 January 2010, the first route to use only hybrid vehicles.[6] In August 2014, new passenger information screens were introduced on one bus on the route.[7][8][9]
The hybrid buses were replaced by electric Alexander Dennis Enviro200EV single-deckers in November 2017.[10]
Current route
Route 360 operates via these primary locations:[11]
- Royal Albert Hall
- South Kensington station
- Sloane Square station

- Lister Hospital
- Pimlico station

- Vauxhall Bridge
- Vauxhall bus station
 for Vauxhall station
for Vauxhall station 

- Albert Embankment
- Imperial War Museum
- Elephant & Castle station


References
- ^ "Who runs your bus". Transport for London. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ ""Cleaner, greener" buses for route 360". London SE1. Bankside Press. 7 February 2006. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ "First Electrocity order for Wrightbus". Bus & Coach Magazine. 18 March 2005. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011.
- ^ Bond, Sam (8 February 2006). "Red buses go green in London". Edie. Faversham House. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Milmo, Dan (26 October 2006). "London plans hybrid bus fleet to cut carbon emissions". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Aldridge, John (November 2009). "Route 360 to go 100% hybrid in latest contract shake-up". Buses (656). Ian Allan Publishing: 16–17.
- ^ Hopping, Clare (7 August 2014). "TfL to trial WiFi on Number 12 and RV1 London buses". Recombu. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ Worth, Dan (6 August 2014). "TfL will trial bus WiFi and digital seat data displays". V3. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ "WiFi trial on RV1 bus route". London SE1. 6 August 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ "London's 360 electrified". Coach and Bus Week. 28 November 2017. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Route 360 Map Transport for London
External links
 Media related to London Buses route 360 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to London Buses route 360 at Wikimedia Commons
