Canigou: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
It is visible from [[Marseille]] on the 8th February and 31st October |
It is visible from [[Marseille]] on the 8th February and 31st October |
||
== Geography == |
== Geography == |
||
[[File:Canigou April 1st 2024.jpg|thumb|center|Caningo from Bompas, Perpignan, 1st April 2024]] |
[[File:Canigou April 1st 2024.jpg|thumb|center|Caningo from Bompas, Perpignan, 1st April 2024]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
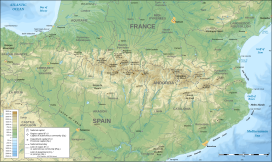
The Canigó is located in [[Pyrénées-Orientales]], south of [[Prades, Pyrénées-Orientales|Prades]] and north of [[Prats-de-Mollo-la-Preste]]. Its summit lies on the border between two communes: [[Vernet-les-Bains]] and [[Taurinya]] (although the territories of two other communes - [[Casteil]] and [[Valmanya]] - approach quite closely to the summit).<ref>Pierre Bousigue, Canigou - de l'ombre à la lumière, 2019, p118</ref> Its location makes it visible from the plains of [[Roussillon]] and from [[Conflent]] in [[France]], and as well from [[Empordà]] in [[Spain]].<ref>''Guide du Roussillon et de l'Andorre : touristique, historique, social, économique'', Perpignan, Sud Roussillon, 1968, 286 p.</ref> |
The Canigó is located in [[Pyrénées-Orientales]], south of [[Prades, Pyrénées-Orientales|Prades]] and north of [[Prats-de-Mollo-la-Preste]]. Its summit lies on the border between two communes: [[Vernet-les-Bains]] and [[Taurinya]] (although the territories of two other communes - [[Casteil]] and [[Valmanya]] - approach quite closely to the summit).<ref>Pierre Bousigue, Canigou - de l'ombre à la lumière, 2019, p118</ref> Its location makes it visible from the plains of [[Roussillon]] and from [[Conflent]] in [[France]], and as well from [[Empordà]] in [[Spain]].<ref>''Guide du Roussillon et de l'Andorre : touristique, historique, social, économique'', Perpignan, Sud Roussillon, 1968, 286 p.</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Twice a year, in early February and at the end of October, with good weather, the Canigó can be seen at sunset from as far as [[Marseille]], {{cvt|250|km}} away, by [[refraction]] of light.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://canigou.allauch.free.fr/Explications.htm | title=Le Canigou vu depuis Allauch et Marseille }}</ref> This phenomenon was observed in 1808 by baron [[Franz Xaver von Zach]] from the [[Notre-Dame de la Garde]] basilica in Marseille.<ref>{{66 PHPC}}</ref> All year long, it can also be seen, with good weather, from [[Agde]], [[Port-Camargue]] and the [[Montagne Noire]]. |
Twice a year, in early February and at the end of October, with good weather, the Canigó can be seen at sunset from as far as [[Marseille]], {{cvt|250|km}} away, by [[refraction]] of light.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://canigou.allauch.free.fr/Explications.htm | title=Le Canigou vu depuis Allauch et Marseille }}</ref> This phenomenon was observed in 1808 by baron [[Franz Xaver von Zach]] from the [[Notre-Dame de la Garde]] basilica in Marseille.<ref>{{66 PHPC}}</ref> All year long, it can also be seen, with good weather, from [[Agde]], [[Port-Camargue]] and the [[Montagne Noire]]. |
||
Revision as of 09:27, 28 May 2024
| Canigó | |
|---|---|
 Canigó, December 2004 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2,784 m (9,134 ft) |
| Prominence | 550 m (1,800 ft) |
| Listing | Mountains of France |
| Coordinates | 42°31′08″N 02°27′24″E / 42.51889°N 2.45667°E |
| Geography | |
| Parent range | Pyrenees |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | According to tradition, in 1285 by Peter III of Aragon |
| Easiest route | hike |
The Canigó (Template:Lang-ca Template:IPA-ca, Template:IPA-ca; Template:Lang-fr Template:IPA-fr; Template:Lang-la) is a mountain located in the Pyrenees of southern France.
The Canigó is located less than 50 kilometres (31 mi) from the sea and has an elevation of 2,784.66 metres (9,136.0 ft). Due to its sharp flanks and its dramatic location near the coast, until the 18th century the Canigou was believed to be the highest mountain in the Pyrenees.[1]
Being between south and Northern Catalonia, the mountain has a historical symbolical significance for Catalan people.[2]
It is visible from Marseille on the 8th February and 31st October
Geography


The Canigó is located in Pyrénées-Orientales, south of Prades and north of Prats-de-Mollo-la-Preste. Its summit lies on the border between two communes: Vernet-les-Bains and Taurinya (although the territories of two other communes - Casteil and Valmanya - approach quite closely to the summit).[3] Its location makes it visible from the plains of Roussillon and from Conflent in France, and as well from Empordà in Spain.[4]
Twice a year, in early February and at the end of October, with good weather, the Canigó can be seen at sunset from as far as Marseille, 250 km (160 mi) away, by refraction of light.[5] This phenomenon was observed in 1808 by baron Franz Xaver von Zach from the Notre-Dame de la Garde basilica in Marseille.[6] All year long, it can also be seen, with good weather, from Agde, Port-Camargue and the Montagne Noire.
Trekking and sightseeing
Jeep tracks on the north side of the massif lead to the Chalet des Cortalets (at 2150 m) which is a popular outpost with walkers.
There are two ancient monasteries at the foot of the mountain, Martin-du-Canigou and Saint-Michel-de-Cuxa.
Canigó Flame
The mountain has symbolical significance for Catalan people. On its summit stands a cross that is often decorated with the Catalan flag.[7] Every year on 23 June, the night before St. John's day (nit de Sant Joan), there is a ceremony called Flama del Canigó. French Catalans carry a flaming torch from Perpignan to the cross and the Catalonian flag on top of the mountain, and people light bonfires throughout the area.[8]
Literature
The Canigó inspired the epic poem "Canigó"[9] by Catalan poet Jacint Verdaguer i Santaló. In these verses Verdaguer compares the snowy mountain to a Magnolia flower (pages 27–28):

Lo Canigó és una magnòlia immensa |
The Canigó is an immense magnolia |
While he was staying in Vernet-les-Bains in 1911, Kipling wrote about Canigou. In a letter to the Club Alpin, he praised it as a "magician among mountains".
Kipling also wrote a light-hearted short story entitled Why Snow Falls at Vernet. It makes fun of the English habit of always talking about the weather.[10]
See also
Notes
- ^ Histoire du Roussillon - Le relief des Pyrénées-Orientales
- ^ Ribas, Joseph (1996). El Canigó història i mite. Vic: Eumo Editorial. pp. 11–12. ISBN 9788476027578.
- ^ Pierre Bousigue, Canigou - de l'ombre à la lumière, 2019, p118
- ^ Guide du Roussillon et de l'Andorre : touristique, historique, social, économique, Perpignan, Sud Roussillon, 1968, 286 p.
- ^ "Le Canigou vu depuis Allauch et Marseille".
- ^ Cárdenas, Fabricio (2014). 66 petites histoires du Pays Catalan [66 Little Stories of Catalan Country] (in French). Perpignan: Ultima Necat. ISBN 978-2-36771-006-8. OCLC 893847466.
- ^ Pyrénées Team - Croix du Canigó
- ^ Raguenaud, Virginie (2012). The Colors of Catalonia: In the Footsteps of Twentieth-Century Artists. Gemma. pp. 58–59. ISBN 9781934848425.
- ^ Ribas, Joseph (1993). Canigou, montagne sacrée des Pyrénées (1 ed.). Portet-sur-Garonne: Loubatières. pp. 128–129. ISBN 978-2-86266606-8.
- ^ "Why Snow Falls at Vernet ( Kipling, 1911)". 20 February 2003.
References
External links
- Canigo.cat Archived 2013-05-26 at the Wayback Machine All information about the Canigou massif: nature, culture and itineraries (in Catalan)