LSD: Difference between revisions
m →Notable people who have commented on their LSD experiences: alphabetize |
|||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
* [[Syd Barrett]] |
* [[Syd Barrett]] |
||
* [[William Burroughs]], article in ''Journal of Psychoactive Drugs'' |
* [[William Burroughs]], article in ''Journal of Psychoactive Drugs'' |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Eric Clapton]] |
* [[Eric Clapton]] |
||
* [[Kurt Cobain]] |
* [[Kurt Cobain]] |
||
* Dr. [[Sidney Cohen]], who introduced [[Henry Luce]] to LSD |
* Dr. [[Sidney Cohen]], who introduced [[Henry Luce]] to LSD |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Stewart Copeland]] |
* [[Stewart Copeland]] |
||
* [[David Crosby]] |
* [[David Crosby]] |
||
| Line 233: | Line 233: | ||
* [[Frank Olson]] |
* [[Frank Olson]] |
||
* Dr. [[Humphry Osmond]] |
* Dr. [[Humphry Osmond]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[John Reynolds (actor)]] |
* [[John Reynolds (actor)]] |
||
* [[Keith Richards]], interviewed in ''[[Rolling Stone magazine|Rolling Stone]]'', October 17, 2002 |
* [[Keith Richards]], interviewed in ''[[Rolling Stone magazine|Rolling Stone]]'', October 17, 2002 |
||
| Line 238: | Line 239: | ||
* [[Tawl Ross]] |
* [[Tawl Ross]] |
||
* [[Jean-Paul Sartre]] |
* [[Jean-Paul Sartre]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Edie Sedgwick]] |
* [[Edie Sedgwick]] |
||
* [[Grace Slick]] |
* [[Grace Slick]] |
||
Revision as of 09:07, 11 June 2005
D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide, commonly called acid, LSD, or LSD-25, is a powerful semisynthetic drug that can function either as a hallucinogen or a psychedelic entheogen. A typical dose of LSD is only 100 micrograms, a tiny amount roughly equal to one-tenth the weight of a grain of sand. LSD causes a powerful intensification and alteration of senses, feelings, memories, and self-awareness for 6 to 12 hours. In addition, LSD usually produces visual effects such as moving geometric patterns, "trails" behind moving objects, and brilliant colors. LSD usually does not produce hallucinations in the strict sense, but instead illusions and vivid daydream-like fantasies. At higher concentrations it can cause synaesthesia.
The immediate effects are sometimes followed by long-lasting or even permanent changes in a user's psychology, point of view, and personality. LSD is synthesized from lysergic acid and is sensitive to oxygen, ultraviolet light, and chlorine, especially in solution. In pure form it is colorless, odorless, and bitter. LSD is typically delivered orally, usually on a substrate such as absorbent blotter paper, a sugarcube, or gelatin. In all these preparations, LSD is tasteless.
Introduced by Sandoz as a drug with various psychiatric uses, LSD quickly became a therapeutic agent that appeared to show great promise. However, the extra-medical use of the drug in western society in the middle years of the twentieth century led to a political firestorm which resulted in the banning of the substance for recreational as well as medical and spiritual uses.
Origin
"LSD" is an abbreviation of the German chemical name of the compound, Lysergsäure-diäthylamid. It was first synthesized in 1938 by Swiss chemist Dr. Albert Hofmann in Basel at the Sandoz Laboratories as part of a large research program dealing with ergot alkaloid derivatives as cure for head aches. Its psychedelic properties were unknown until Hofmann, acting on a hunch, returned to work on the chemical 5 years later. He attributed the discovery to absorption through the skin of a microscopic amount of the 25th batch (hence the precise name "LSD-25") due to accidental contact on April 16, which led to him testing it on himself for psychoactivity (full story).
Until 1966, LSD and psilocybin were provided by Sandoz Laboratories free of charge to interested scientists. The use of these compounds by psychiatrists to gain a better subjective understanding of the schizophrenic experience was an accepted practice. Many clinical trials were conducted on the potential use of LSD in psychedelic psychotherapy, generally with very positive results. LSD first became popular recreationally among a small group of mental health professionals such as psychiatrists and psychologists during the 1950s, as well as by socially prominent and politically powerful individuals such as Henry and Clare Boothe Luce.
Cold War era intelligence services were keenly interested in the possibilities of using LSD for interrogation and mind control (see MK-ULTRA), and also for large-scale social engineering (see counterculture). The CIA conducted extensive research on LSD, which alledgedly was mostly destroyed.
Several mental health professionals, notably Harvard psychology professors Drs. Timothy Leary and Richard Alpert (later known as Ram Dass), became convinced of LSD's potential as a tool for spiritual growth, but accused of possession of a less than scientific spirit they were dismissed from the traditional psychological community, and as such cut off from scientific aquisition of the drug. Dr. Leary was then (alledgedly unbeknownst to himself) approached by agents of the CIA, who supplied him with such quantity of purified LSD-25, that he and Dr. Alpert/Ram Dass with infective spiritual-psychological fervor was more than indirect cause for the drug being made available to a much wider portion of the public - and as countercultural spiritual gurus making LSD a household brand among the hippies of the 1960s. The drug was banned in the United States in 1967, for scientific therapeutic research as well as individual research and recreation. Many other countries quickly followed suit.
Since 1967, underground recreational and therapeutic LSD use has continued in many countries, supported by a black market and popular demand for the drug. Legal, academic research experiments on the effects and mechanisms of LSD are also conducted on occasion, but rarely involve human subjects.
Dosage
LSD is by weight one of the most potent drugs yet discovered. Both subjective reports and pharmacological methods such as receptor binding assays determine LSD to be, per mole, around 100 times more potent than psilocybin and psilocin and around 4000 times more potent than mescaline. Dosages of LSD are measured in micrograms (µg), or millionths of a gram. By comparison, dosages of almost all other drugs, both recreational and medical, are measured in milligrams, or thousandths of a gram.
The dosage level that will produce a threshold hallucinogenic effect in humans is generally considered to be 25 micrograms, with the drug's effects becoming markedly more evident at higher dosages. In the late 1990s, LSD obtained during drug law enforcement operations in the United States has usually ranged between 20 and 80 micrograms per dose. During the 1960s, dosages were commonly 300 micrograms or more.
Effects
Physical
Physical reactions to LSD are highly variable and may include: uterine contractions, body temperature increase, elevated blood sugar levels, dry-mouth, goose bumps, heart-rate increase, jaw clenching, nausea, perspiration, pupil-dilation, salivation, mucus production, sleeplessness and tremors. Cramps and muscle tension are also fairly commonly reported, but rather than being direct effects of LSD in the bloodstream, these symptoms are believed to be the result of awkward positions assumed by users experiencing fluctuations in their awareness of the passage of time and their own physical discomfort.
LSD has been studied in the past as a painkiller for serious and chronic pain caused by cancer or other major trauma. Even at low (sub-psychedelic) dosages, it was found to be at least as effective as traditional opiates while being much longer lasting (pain reduction lasting as long as a week—after peak effects had subsided).
Pharmacological
LSD affects a huge number of receptors, including all dopamine receptor subtypes, all adrenoreceptor subtypes as well as many others. LSD binds to most serotonin receptor subtypes except for 5-HT3 and 5-HT4. The hallucinogenic effects of LSD are attributed to its partial agonist effects at 5-HT2A receptors. Exactly how this produces hallucinations are unknown, but it is thought that it works by increasing excitation in cortical layers which facilitate the spread of information throughout the cortex. Through this, LSD causes parts of the brain which would not normally be activated by a given stimulus to become engaged.
Psychological
LSD's psychological effects (colloquially called a "trip") vary greatly from person to person, from one trip to another, and even as time passes during a single trip. Widely different effects emerge based on set and setting — the 'set' being the general mindset of the user, and the 'setting' being the physical and social environment in which the drug's effects are experienced.
An LSD trip can have long lasting or even permanent neutral, negative, and positive psychoemotional effects. LSD experiences can range from indescribably ecstatic to extraordinarily difficult; many difficult experiences (or "bad trips") result from a panicked user feeling that he or she has been permanently severed from reality and his or her ego. If the user is in a hostile or otherwise unsettling environment, or is not mentally prepared for the powerful distortions in perception and thought that the drug causes, effects are more likely to be unpleasant.
Conversely, a pleasant, comfortable environment and a relaxed, balanced and open mindset will often result in a unique and extremely unusual experience.
The sensory shifts caused by the drug can lead users to sit or lie in awkward positions for extended periods of time, resulting in muscle cramps and soreness that may mistakenly be attributed to the direct physical action of the drug.
Sensory/perception
Generally beginning within thirty to ninety minutes after ingestion and continuing for the following six to twelve hours, the user may experience anything from subtle changes in perception to overwhelming cognitive shifts and vivid illusions
Sensory shifts include "high-level" sensory distortions such as warping of surfaces, appearance of moving geometrical patterns and textures on objects, blurred vision, image trailing, shape suggestibility, and color variations. Users often describe seeing new colors that they have not previously experienced, or colors may appear to have greater intensity. Perspective distortions may occur where items in the foreground appear to become part of the background, or the foreground and background may become temporarily indistinguishable. Changes in aural and visual perception are common, ranging from mild to overwhelming.
Higher doses often bring about shifts at a lower cognitive level - causing intense and fundamental distortions of sensory perception such as synaesthesia, the experience of additional spatial or temporal dimensions, and temporary dissociation.
Spiritual
LSD is considered an entheogen because it often catalyzes intense spiritual experiences where users feel they have come into contact with a greater spiritual or cosmic order. It is common for users to believe that they have achieved insights into the way the mind works and some experience permanent or long-lasting changes in their life perspectives. Some users consider LSD a religious sacrament, or a powerful tool for access to the divine. Many books have been written comparing the LSD trip to the state of enlightenment of eastern philosophy.
Such supposed mystical experiences under the influence of LSD have been observed and documented by researchers such as Timothy Leary and Stanislav Grof.
Acute duration
LSD's primary effects normally last from 6 to 12 hours. One characteristic feature of LSD is that with higher doses, the duration of the experience increases, but not the intensity. It is typical for users of LSD to be unable to sleep restfully until at least 12 hours have passed, and they do not feel completely "back to normal" until after getting one or two full nights of restful sleep, although they will exhibit no outward signs of impairment after the drug has worn off.
LSD has an extremely short half life in the body. Most of the drug's already minuscule dose is eliminated before the trip is even over, suggesting that LSD triggers some sort of neurochemical cascade rather than acting directly to produce its effects.
Anecdotal reports indicate that administration of Thorazine or similar typical antipsychotic tranquilizers will not end an LSD trip, but rather will just immobilize the patient.
Physical dangers
Although LSD is generally considered nontoxic, other dangers may arise from bad judgments made during the experience. As with many drugs, while under the influence of LSD the ability to make sensible judgments and understand common dangers can be impaired, making the user susceptible to personal injury.
If an individual attempts to drive a car or operate machinery under the influence of the drug, that individual's absorption in inner experiences may lead to accidents and injury.
There is also some indication that LSD may trigger a dissociative fugue state in individuals who are taking certain classes of antidepressants such as lithium salts and tricyclics. In such a state, the user has an impulse to wander, and may not be aware of his or her actions, which can lead to physical injury. MAOIs and SSRIs are believed to interact more benignly, tending to diminish LSD's subjective effects greatly.
Flashbacks
There is also a commonly reported possibility of "flashbacks", a psychological phenomenon in which an individual experiences an episode of some of the subjective effects of LSD (this may be a positive or negative experience) long after the drug has been consumed and worn off -- sometimes weeks or months afterward. Flashbacks is an example of a Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder, a DSM-IV diagnosis. Several journal articles have described the disorder (see, for example, Adverse consequences of lysergic acid diethylamide, H.D. Abraham and A. Aldridge, Addiction 1993, 88:1327-1334). Several studies have tried to determine how likely a "normal user" (that is a user not suffering from known psychiatric conditions) of LSD is to experience flashbacks. The larger studies include (Flashback phenomena in basic trainees who enter the US Air Force, Blumenfield, Military Medicine, 136, 39-41, 1971) and (LSD Flashbacks and Ego Functioning, Naditch, M & Fenwick, Journal of Abnormal Psychology, Vol. 86, No 4, 352-359, 1977), arriving at figures of 20% and 28%, respectively.
Debate continues over the nature and causes of flashbacks. Some say flashbacks are a manifestation of post-traumatic stress disorder, not directly related to LSD's mechanism, and varying according to the susceptibility of the individual to the disorder. Many emotionally intense experiences can lead to flashbacks when a person is reminded acutely of the original experience.
Several urban legends claim that flashbacks are the result of trace amounts of LSD or related chemicals being dislodged and released into the body after having been crystallized and stored in fat or spinal fluid cells. However, scientific research has disproven this conjecture; LSD (which is water soluble) is metabolized in the liver, as with many other drugs, and its metabolites are excreted normally in the urine.
Psychoses
There are numerous reported cases of LSD inducing or triggering a psychosis in people that were apparently healthy prior to taking LSD. In most cases, the psychosis is of short duration, but in other cases it may be chronic, possibly even permanent. While it is clear that LSD has some relation to psychosis, it is difficult to determine if LSD in itself induces psychosis or if it merely triggers latent conditions that would have manifested themselves sooner or later. Several studies have tried to estimate the prevalence of LSD-induced prolonged psychosis arriving at numbers of around 4 in 1000 individuals.
Addiction potential
LSD is not considered addictive, in that its users do not exhibit the medical community's commonly accepted definitions of addiction and physical dependence. Rapid tolerance build-up prevents regular use, and there is cross-tolerance shown between LSD, mescaline and psilocybin. This tolerance diminishes after a few days' abstention from use.
Many experts consider drugs such as LSD to be a sort of anti-drug (encourages users to stop using drugs), as it forces the user to face issues and problems in that individual's psyche. In contrast, the harder drugs (alcohol, heroin, and cocaine) are used to escape from reality. Studies in the 1950s in using LSD to treat alcoholism professed a 50% success rate. Alcoholics Anonymous, on the other hand, has a success rate of 5% or less.
History
LSD was first synthesized in 1938, recognized as a potent consciousness-altering agent in 1943, and distributed as a drug in the mid-forties. It is closely related to two plants traditionally used as entheogens, the ergot fungus, thought by some to have been used as the trigger for the mystical experiences reported by participants at the Eleusinian mysteries in Ancient Greece, and Morning glory seeds, used by Native Americans in Central America for divination and other spiritual purposes.
Its medical uses ranged from facilitating psychotherapy to treating autistic children, alcoholics, and depressed people. It was also used for spiritual purposes in both formal and informal settings, and it eventually became widely used as a recreational substance. Due to its powerful and unpredictable effects, especially outside of controlled environments, it was blamed for mishaps, accidents, and irreversible mental damage which was claimed to have occurred as a result of its use. It also was seen as the driving force behind a social revolution that threatened mainstream values. As a result, powerful political forces joined to counter its effects, and it was banned in the United States in 1967 and in the rest of the world shortly thereafter.
See History of LSD, and Entheogen
Chemistry
| LSD | |
|---|---|
| Chemical name | D-Lysergic acid diethylamide or: (6aR,9R)-N,N-diethyl-7-methyl- 4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo [4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide |
| Chemical formula | C20H25N3O |
| Molecular mass | 323.43 g/mol |
| Melting point | 80 - 85 °C |
| CAS number | 50-37-3 |
| SMILES | O=[C@@](N(CC)CC)[C@H] 1CN(C)[C@](C2=C1)([H]) CC3=CNC4=C3C2=CC=C4 |
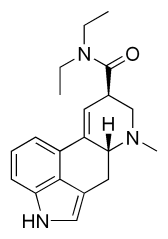 | |
LSD is an example of an ergoline derivative. It is commonly produced from lysergic acid, which is made from the tartrate salt of ergotamine, a substance derived from the ergot fungus on rye, or from ergine (lysergic acid amide), a chemical found in morning glory seeds. Although theoretically possible, manufacture of LSD from morning glory seeds is not economically feasible and these seeds have never been found to be a successful starting material for LSD production.

Only a small amount of ergotamine tartrate is required to produce LSD in large batches. For example, 25 kilograms of ergotamine tartrate can produce 5 or 6 kilograms of pure LSD crystal that, under ideal circumstances, could be processed into 100 million dosage units (at 50 micrograms per dose), more than enough to meet what is believed to be the entire annual U.S. demand for the drug. LSD manufacturers need only create a small quantity of the substance and, thus, enjoy the advantages of ease of concealment and transport not available to traffickers of other illegal drugs, primarily marijuana and cocaine.
Manufacturing LSD is time consuming and dangerous. Relatively sophisticated and expensive laboratory equipment is required, and it takes from 2 to 3 days to produce 30 to 100 grams of pure compound. Some of the reactions necessary may cause significant explosions if not performed properly by a trained organic chemist. It is believed that LSD usually is not produced in large quantities, but rather in a series of small batches. Production of LSD in small batches also minimizes the loss of precursor chemicals in case a synthetic step doesn't work as expected.
Forms of LSD
LSD is produced in crystalline form and then mixed with excipients or diluted as a liquid for production in ingestible forms. Often, LSD is sold in tablet form (usually small tablets known as microdots), on sugar cubes, in thin squares of gelatin (commonly referred to as window panes), and most commonly, as blotter paper (sheets of paper soaked in or impregnated with LSD, covered with colorful designs or artwork, and perforated into small squares of individual dosage units). LSD is sold under more than 80 street names including acid, blotter, doses and trips, as well as names that reflect the designs on the sheets of blotter paper. On occasion, authorities have encountered the drug in other forms-- including powder or crystal, liquid, and capsule-- and laced on other substances. More than 200 types of LSD tablets have been encountered since 1969 and more than 350 paper designs have been acquired since 1975. Designs range from simple five-point stars in black and white to exotic artwork in full four-color print.
Legal status
The United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances (adopted in 1971) requires its parties to prohibit LSD. Hence, it is illegal in all parties to the convention, which includes the United States and most of Europe. However, enforcement of extant laws varies from country to country.
LSD is easy to conceal and smuggle. A tiny vial can contain thousands of doses. Not much money is made from retail-level sales of LSD, so the drug is typically not associated with the violent organized criminal organizations involved in cocaine and opiate smuggling.
Unlike alcohol prohibition, LSD prohibition does not make an exception for religious use, presumably because nontraditional entheogen-centered religions are extremely uncommon and not generally accepted by modern societies. By contrast, the United States government permits some tribes of Southwestern American Indians to cultivate and use hallucinogenic peyote cactus in traditional religious rituals.
LSD was legal in the United States until 1967. The US Federal Government classified it as a Schedule I drug according to the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. As such, the Drug Enforcement Administration holds that LSD meets the following three criteria: it is deemed to have a high potential for abuse; it has no legitimate medical use in treatment; and there is a lack of accepted safety for its use under medical supervision. Lysergic acid and lysergic acid amide, LSD precursors, are both classified in Schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act. Ergotamine tartrate, a precursor to lysergic acid, is regulated under the Chemical Diversion and Trafficking Act.
LSD in the United States
Prior to 1967, LSD was available legally in the United States as a prescription psychiatric drug. LSD 'apostle' Al Hubbard actively promoted the drug between the 1950s and the 1970s and introduced thousands of people to it.
LSD has been manufactured illegally since the 1960s. A limited number of chemists, probably less than a dozen, are believed to have manufactured nearly all of the illicit LSD available in the United States. The best known of these is undoubtedly Augustus Owsley Stanley III, usually known simply as Owsley. The former chemistry student set up a private LSD lab in the mid-Sixties in San Francisco and supplied the LSD consumed at the famous Acid Test parties held by Ken Kesey and his Merry Pranksters, and other major events such as the Gathering of the Tribes in San Francisco in January 1967. He also had close social connections to leading San Francisco bands the Grateful Dead, Jefferson Airplane and Big Brother and The Holding Company, regularly supplied them with his LSD and also worked as their live sound engineer and made many tapes of these groups in concert. Owsley's LSD activities—immortalized by Steely Dan in their song "Kid Charlemagne"—ended with his arrest at the end of 1967, but some other manufacturers probably operated continuously for 30 years or more.
American LSD usage declined in the 1970s and 1980s — this is often attributed to a large anti-drug program targeted at young people in the U.S. LSD then experienced a mild resurgence in popularity in the 1990s. Although there were many distribution channels during this decade, the U.S. DEA identified continued tours by the psychedelic rock band The Grateful Dead and the then-burgeoning rave scene as primary venues for LSD trafficking and consumption. American LSD usage fell sharply circa 2000. The decline is attributed to the arrest of two chemists whom the DEA claims were manufacturing 95% of the LSD sold in America and much of the European supply. The arrests were a result of the largest LSD manufacturing raid in DEA history.

LSD manufacturers and traffickers can be separated into two groups. The first group was based in northern California and later identified by the DEA as run by chemists (referred to as cooks) William Leonard Pickard and Clyde Apperson. Initial distribution points for this group's LSD were usually in the San Francisco area, or coordinated elsewhere through informal meetings at Grateful Dead concerts. These men worked in close association with trusted traffickers. The government claims that these two men were responsible for the vast majority of LSD sold illegally in the United States and a significant amount of the LSD sold in Europe, and that black market LSD availability dropped by 95% after the two were arrested in 2000. [1]
In November of 2003, Pickard and Apperson were sentenced to two life sentences and two 30 year sentences, respectively, after being convicted in Federal Court of running a large scale LSD manufacturing operation out of several clandestine laboratories, including a former missile silo near Wamego, Kansas.
The second group of cooks consists of small independent producers who, operating on a comparatively limited scale, can be found throughout the country. As a group, independent producers are of less concern to the Drug Enforcement Agency than the northern California group, as their production is intended for local consumption only.
Notable people who have commented on their LSD experiences
Please add to this list.
- Paul Allen
- Dr. Richard Alpert (now Ram Dass), in his book, Be Here Now
- Bill Bailey
- J. G. Ballard
- John Perry Barlow
- Syd Barrett
- William Burroughs, article in Journal of Psychoactive Drugs
- Eric Clapton
- Kurt Cobain
- Dr. Sidney Cohen, who introduced Henry Luce to LSD
- John Coltrane, attributed to the book, Chasin' the Trane: The music and mystique of John Coltrane
- Stewart Copeland
- David Crosby
- Robert Crumb, cartoonist
- Adelle Davis
- Philip K. Dick, in the book VALIS
- Donovan
- Bob Dylan (in one of his videos there is a car that has a license-plate = "LSD 25")
- Dock Ellis, professional baseball player who pitched a no-hitter while high on LSD
- Eminem
- Dr. Douglas Engelbart, in John Markoff's 2005 book, What the Dormouse Said
- Peter Fonda
- Michel Foucault
- Jerry Garcia, numerous interviews.
- Bill Gates, interview in the December 1994 Playboy: [2]
- William Gibson
- Allen Ginsberg
- Philip Glass
- Dr. Sidney Gottlieb
- Cary Grant, in the September, 1959 Look Magazine, relates how LSD treatment has brought him inner peace.
- Alex Grey, in an interview with the Online Noetic Network and in numerous other interviews and personal writings
- Alyson Grey, in many interviews and writings by herself and with her husband Alex Grey
- Dr. Stanislav Grof
- Larry Hagman in his autobiography, Hello Darlin'
- George Harrison, in his book I, Me, Mine and in the television/home video production The Beatles Anthology.
- Anne Heche, in her book Call Me Crazy
- Mitch Hedberg, in his comedy act
- Jimi Hendrix
- Bill Hicks, in his comedy albums Dangerous and Relentless, among others
- Alex Hixon
- Abbie Hoffman
- Dr. Albert Hofmann
- Aldous Huxley
- Phil Jackson, in his 1975 book Maverick
- Dr. Oscar Janiger
- Steve Jobs of Apple Computer describes taking LSD as "one of the two or three most important things he has done in his life" in John Markoff's 2005 book, What the Dormouse Said; also in an interview in Time Magazine
- Dan Joergensen
- Ernst Jünger
- Ken Kesey
- Lemmy Kilmister
- Peter Kuper, cartoonist
- Dr. R. D. Laing
- Dr. Timothy Leary
- John Lennon
- Dr. John C. Lilly in his book Centre of the Cyclone and other works
- Clare Boothe Luce
- Henry Luce Founder of Time/Life [3]
- William H. Macy, in the July 2001 issue of Maxim
- Groucho Marx
- Paul McCartney
- Terence McKenna, interviewed in Psychedelic Island Views
- Jim Morrison
- Kary Mullis, in his essay collection Dancing Naked in the Mind Field.
- Jack Nicholson
- Anais Nin, in The Diary Of Anais Nin, Volume 5 (1947-1955)
- Frank Olson
- Dr. Humphry Osmond
- Michelle Phillips
- John Reynolds (actor)
- Keith Richards, interviewed in Rolling Stone, October 17, 2002
- John Robbins, Founder of EarthSave, interviewed in [Mavericks of the Mind]
- Tawl Ross
- Jean-Paul Sartre
- Edie Sedgwick
- Grace Slick
- Dr. Huston Smith, interviewed in Nov/Dec 1997, MotherJones
- Owsley Stanley
- Ringo Starr
- Howard Stern
- Oliver Stone
- Keith Thibodeaux
- Hunter S. Thompson
- Bob Wallace
- Alan Watts
- Dr. Andrew Weil
- Brian Wilson
- Robert Anton Wilson
- William Griffith Wilson, in the Alcoholics Anonymous book, Pass It on
- Steven Wright, in his standup routine.
- Mark Vonnegut, in The Eden Express, Bantam Books, 1975 ISBN 0553027557
- Adam Yauch, of Beastie Boys
According to James Gleick's biography Genius, Richard Feynman experimented with LSD during his professorship at Caltech. Somewhat embarrassed by his actions, Feynman sidestepped the issue when dictating his anecdotes; consequently, the "Altered States" chapter in Surely You're Joking, Mr. Feynman! only describes marijuana and sensory deprivation experiences.
LSD-quotes
"One world before, many worlds after". (anon.)
"Focus on the spaces in between objects and you will find the answers" (L.Miller)
"The seed is as much the point as the flower." (Alan Watts)
"LSD, 100 µg, i.m." (Aldous Huxley's last words, as a written request to his wife from his deathbed)
Related topics
- ALD-52
- Hallucinogenic drug
- Psychedelic
- Entheogen
- Psychedelic psychotherapy
- Drug urban legends
- MKULTRA - CIA experiments with LSD
- Dr. Richard Alpert (later known as Ram Dass)
- Dr. Stanislav Grof Czech researcher
- Dr. Albert Hofmann
- Dr. Timothy Leary
- Dr. John Lilly USA researcher
- Dr. Humphry Osmond
- Owsley Stanley Famous LSD chemist of the 1960's
- Psychedelic rock bands associated with LSD use: Grateful Dead, Phish, the Beatles, the Doors, Jimi Hendrix, Jefferson Airplane, Smashing Pumpkins, Pink Floyd (especially their earlier works and Syd Barrett's solo efforts)
- Related chemical compounds: ergolines, LSA, psilocybin, DMT, serotonin
- Raphael Labro LSD Expressionist
- Bogle-Chandler case, deaths put down to LSD overdoses
External links
Media
- Wired News: Long Trip for Psychedelics, September 27, 2004
- Who's Got the LSD? These Days, Almost Nobody
- Northern Californian LSD makers found guilty
- Pickard And Apperson Sentenced On LSD Charges Official DEA press release on the "Largest LSD Lab Seizure In DEA History"
- LYSERGIC Book Written About Pickard Case
Academic
- A Critical Review of Theories and Research Concerning LSD and Mental Health
- Definitions of Addiction, Physical Dependence, and Tolerance
- LSD - My Problem Child online, by LSD inventor Dr. Albert Hofmann
- The Neurochemistry of Psychedelic Experience, Science & Consciousness Review
- Aldous, F. A. B., Barrass, B. C., Brewster, K., Buxton, D. A., Green, D. M., Finder, R. M., Rich, P., Skeels, M., and Tutt, K. J., "Structure-Activity Relationships in Psychotomimetic Phenylalkylamines," Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 17, 1100-1111 (1974)
- Current LSD Research
- Searchable LSD Bibliography
Urban legends
General
