2004 Pacific typhoon season: Difference between revisions
| Line 194: | Line 194: | ||
===Typhoon Rananim (Karen)=== |
===Typhoon Rananim (Karen)=== |
||
{{hurricane main|Typhoon Rananim}} |
|||
{{Infobox Hurricane Small |
{{Infobox Hurricane Small |
||
|Basin=WPac |
|Basin=WPac |
||
| Line 205: | Line 204: | ||
|Pressure=950 |
|Pressure=950 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Rananim formed on [[August 7]] and reached its maximum intensity of 90 kts/105 mph on [[August 12]] before making landfall in the Zhejiang Province of [[China]] later that day. In advance of the storm, 415,000 people were evacuated. Rananim caused as much as 686 mm/27" of rain in parts of Zhejiang, killing 115 people, injuring 1800 and causing US$4 billion in direct economic losses. It was the worst [[typhoon]] to hit [[China]] since [[1997 Pacific typhoon season#Super Typhoon Winnie .28Ibiang.29|Winnie]] in 1997. Rananim is the [[Chuuk]]ese word for 'hello'. |
Rananim formed on [[August 7]] and reached its maximum intensity of 90 kts/105 mph on [[August 12]] before making landfall in the Zhejiang Province of [[China]] later that day. In advance of the storm, 415,000 people were evacuated. Rananim caused as much as 686 mm/27" of rain in parts of Zhejiang, killing 115 people, injuring 1800 and causing US$4 billion in direct economic losses. It was the worst [[typhoon]] to hit [[China]] since [[1997 Pacific typhoon season#Super Typhoon Winnie .28Ibiang.29|Winnie]] in 1997. Rananim is the [[Chuuk]]ese word for 'hello'. The name Rananim was retired after this year. |
||
<div style="clear: both"></div> |
<div style="clear: both"></div> |
||
Revision as of 01:11, 22 August 2008
| 2004 Pacific typhoon season | |
|---|---|
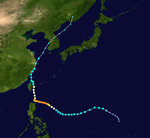
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | April 5, 2004 |
| Last system dissipated | December 21, 2004 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Chaba |
| • Maximum winds | 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 910 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total storms | 29 |
| Typhoons | 19 |
| Super typhoons | 6 |
| Total fatalities | 2,073 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
The 2004 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 2004, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November.[1] These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 2004 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west pacific basin are assigned a name by the Tokyo Typhoon Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
Storms
In storm information below, wind-speed advisories differ from the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) to the JMA as the JTWC uses the United States criteria of 1-minute mean to designate maximum sustained winds, while the JMA uses the 10-minute mean wind criteria to designate tropical cyclone maximum sustained winds. This difference generally results in JTWC maximum winds appearing higher than the maximum winds described by the JMA for the same cyclone.
Typhoon Sudal (Cosme)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | April 5 – April 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min); 940 hPa (mbar) |
On April 4, Tropical Depression 03W began its life between Chuuk and Pohnpei. As it drifted to the northwest, it strengthened into a tropical storm. Sudal turned to the west, and steadily intensified to become a typhoon on April 6. On the April 9, with maximum sustained winds of 115 kt/130 mph, Typhoon Sudal hit the island of Yap. After ravaging the island, Sudal reached a peak of 125 kt/150 mph winds. The typhoon turned to the northeast and became extratropical on the April 15. Yap experienced catastrophic damage, with 90% of buildings destroyed, 1,500 left homeless, and one fatality. Sudal is a Korean word meaning otter.
Typhoon Nida (Dindo)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 14 – May 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min); 935 hPa (mbar) |
The monsoon trough spawned Tropical Depression 04W east of the Philippines on May 13. The depression quickly strengthened, reaching tropical storm intensity on May 14 and typhoon status just six hours later. On May 15 and May 16 while moving northwest towards the Philippine coast, Nida rapidly intensified to a 135 kt/160 mph super typhoon, and crossed the eastern Philippines shortly thereafter. Nida weakened slightly over the islands, and began to move to the north and northeast in response to a break in the subtropical ridge. It became extratropical on May 21 east of Japan, after causing 31 deaths and about $1.3 million in damage. Nida is a Thai female name.
In the Philippines, evacuation centers were opened to accommodate 2,986 people. The typhoon approach canceled ferry operations stranding 15,057 passengers.[2] In Taiwan, forecasters at the Central Weather Bureau issued a typhoon warning as forecast models predicted a high probability of the typhoon hitting Taiwan.[3]
Severe Tropical Storm Omais (Eteng)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 18 – May 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
A tropical disturbance southwest of Chuuk organized into a tropical depression on May 16, one of 3 active tropical cyclones in the Western Pacific at the time. The depression developed quickly, reaching tropical storm status later that day and reaching a peak of 60 kt/70 mph winds three days later on May 19. A weakening ridge brought Omais northward, where it became extratropical on May 22. Operationally, Omais was classified as a typhoon, but in post-analysis, it was dropped to a tropical storm. Omais is a Palauan word meaning 'wandering around'.
Typhoon Conson (Frank)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 6 – June 11 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min); 960 hPa (mbar) |
In the South China Sea, a stationary area of disturbed weather developed into Tropical Depression 07W on June 4. It tracked eastward then northeastward, becoming a tropical storm on June 5 and a typhoon on June 7. Conson passed between Luzon and Taiwan, and peaked with 100 kt/115 mph winds on June 9. Conson weakened as it continued northeastward, and became extratropical on June 11 near Japan without causing any reported damage. Conson is an area in Vietnam containing many historical monuments.
Severe Tropical Storm Chanthu (Gener)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 10 – June 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min); 975 hPa (mbar) |
A westward moving disturbance was immediately upgraded to Tropical Storm Chanthu on June 9, just east of the Philippines. It crossed the islands, and strengthened in the South China Sea to a typhoon on June 12. After peaking with 75 kt/85 mph winds, Chanthu hit central Vietnam on June 12, and dissipated the next day. Seven people were killed in the heavy flooding. Chanthu is a type of flower found in Cambodia.
Typhoon Dianmu (Helen)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 13 – June 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min); 915 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression 09W, which developed from the monsoon trough on June 13, headed north in the open Western Pacific. On the June 15 and June 16, Dianmu rapidly intensified from a 70 kt/80 mph typhoon to a 155 kt/180 mph super typhoon, one of nine typhoons since 1990 to reach that intensity. It lost some organization on June 18, but re-strengthened on June 19 to a super typhoon while south of Okinawa. Some dry air weakened Dianmu as it continued its northward movement, and hit southern Japan as a 55 kt/65 mph tropical storm on June 21. Dianmu became extratropical that night after causing 3 deaths. Dianmu is the name of the goddess of thunder and lightning in Chinese folklore.
Typhoon Mindulle (Igme)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 23 – July 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min); 940 hPa (mbar) |
The monsoon trough spawned a tropical depression on June 23 near Guam. It tracked westward, becoming a tropical storm that night but slowly strengthening as it continued westward due to vertical wind shear. When the shear abated, Mindulle quickly intensified, reaching typhoon strength on June 27 and peaking at 125 kt/145 mph winds on June 28. Land interaction with Luzon to its south weakened Mindulle, and the typhoon weakened as it turned northward. On July 1 Mindulle hit eastern Taiwan, and after accelerating to the northeast became extratropical near South Korea on July 4. Mindulle caused 56 deaths, with $317.2 million in damage in its path (2004 USD). Mindulle is the Korean word for the dandelion.
Typhoon Tingting
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 26 – July 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min); 955 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression 11W, which developed from the monsoon trough on June 25, steadily strengthened as it tracked to the northwest, and reached tropical storm status on June 26. Tingting passed Saipan on June 27, and reached typhoon status early on June 28. After maximum sustained winds peaked at 80 kts/90 mph, the typhoon turned to the northeast, where it became extratropical on July 3 after causing 3 deaths on Saipan. Tingting is a pet name for young girls in Chinese.
Tropical Storm Kompasu (Julian)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 14 – July 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
An area of thunderstorms and convection organized into Tropical Depression 12W on July 13. Under high vertical shear and with a very small circulation, it was not expected to strengthen further. However, as it tracked erratically westward, it intensified, peaking with 40 kt/50 mph winds on July 14. Kompasu turned northward, hit the eastern part of Hong Kong directly as a minimal tropical storm, and dissipated on July 16. Kompasu is the Japanese word for compass, and the name of the constellation Circinus.
Typhoon Namtheun
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 25 – August 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min); 935 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Namtheun, which formed on July 25, rapidly intensified on July 26 to a 115 kt/135 mph typhoon. Dry air approached the system from the south, and it weakened as it tracked northwest towards Japan. On July 31, Namtheun hit southwest Japan as a 55 kt/65 mph tropical storm, and became extratropical in the Sea of Japan on August 1. The storm caused no deaths or damage, with only 6 injuries. Namtheun is the name of a river in Laos.
Tropical Storm Malou
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 4 – August 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 996 hPa (mbar) |
An area of convection under moderate to high vertical wind shear developed into a tropical depression southeast of Japan on August 4. It became a minimal tropical storm before hitting central Japan on the night of August 4. Malou turned to the northeast and became extratropical in the Sea of Japan on August 5. Malou is the Chinese name for the mineral agate.
Typhoon Meranti
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 4 – August 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min); 960 hPa (mbar) |
Meranti formed near Wake Island on August 2 and reached its peak intensity of 90 kts/105 mph on August 5 before dissipating on August 8. Meranti was the only one of the six August typhoons which did not affect any populated areas. Meranti is a type of tree found in Malaysia.
Typhoon Rananim (Karen)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 8 – August 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min); 950 hPa (mbar) |
Rananim formed on August 7 and reached its maximum intensity of 90 kts/105 mph on August 12 before making landfall in the Zhejiang Province of China later that day. In advance of the storm, 415,000 people were evacuated. Rananim caused as much as 686 mm/27" of rain in parts of Zhejiang, killing 115 people, injuring 1800 and causing US$4 billion in direct economic losses. It was the worst typhoon to hit China since Winnie in 1997. Rananim is the Chuukese word for 'hello'. The name Rananim was retired after this year.
Tropical Storm Malakas
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 11 – August 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
A reverse-oriented monsoon trough extended from the Philippine Sea northeastward for hundreds of miles spawned a disturbed area around 22N/150E late on August 8. A weak tropical depression formed out of this area late on August 9. Deep convection was in a cycling mode, and satellite imagery initially indicated that the system was subtropical in nature. The depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Malakas as it took on a more tropical appearance about 670 miles west-northwest of Wake Island, and it moved northeastward along the northern periphery of the subtropical ridge. By August 12, satellite imagery indicated that Malakas was becoming extratropical. JMA declared the system extratropical on the August 14, placing the weak 25 kt/30 mph low approximately 575 miles north-northwest of Midway Island. Malakas is a Filipino word meaning 'strong' or 'powerful'.[4]
Typhoon Megi (Lawin)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 16 – August 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min); 970 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Megi was the fourth of eight significant tropical cyclones to form during August. Megi was initially spotted 260 miles west of Guam on August 11, slowly developing into Tropical Depression 18W on the August 14, strengthening into a tropical storm on the August 16, and ultimately into a typhoon on the August 18 to the southwest of Japan. Megi moved northwest through the Ryūkyū islands before recurving northeastward towards South Korea and Japan. Megi sped across northern Honshū before completing its transition into a nontropical low off the east coast of Hokkaidō. The resultant ocean cyclone moved rapidly eastward, reaching a point near 42N/174E late on the August 22.
Despite peaking at only minimal typhoon intensity, Megi had a significant impact on both Japan and South Korea. In Japan, the highest storm total rainfall noted was 610 mm at Tomisato between August 17 and August 21, with 398 mm falling in a 24 hour period. The highest wind gust was 109 mph/48.7 m/s at Izuhara, Nagasaki early on the August 19. The lowest measured pressure was 974.1 mb at Isuhara. In South Korea, the heaviest 24 hour rain total was 332.5 mm at Wando between late on the August 17 and August 18. News reports indicated that five people were reported dead or missing after Typhoon Megi in South Korea. The number left homeless rose to more than 2400. Typhoon Megi left at least ten dead in Japan. Megi's landfall on northern Japan resulted in large blackouts as 130,000 homes were left in the dark. A group of about 165 primary school students were stranded by a Megi-induced landslide in western Japan, though were successfully rescued by helicopter. Megi is the Korean word for the catfish.[4]
Typhoon Chaba
| Violent typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 19 – August 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min); 910 hPa (mbar) |
Chaba formed on August 18 in the open Western Pacific. It moved westward, strengthening into a tropical storm on the August 19 and a typhoon on August 20. Chaba turned to the northwest, and rapidly intensified to a 155 kt/180 mph super typhoon on the August 22 with an estimated minimum central pressure of 879 mbar, among the lowest on record. After fluctuating between 100 kt/115 mph and super typhoon status for several days, Chaba weakened as it turned to the north, and hit the southwestern Japanese island of Honshū. It accelerated to the northeast, and became extratropical on August 31. The storm killed seven people and brought extensive flooding to Honshū. Chaba is a type of tropical flower.
Typhoon Aere (Marce)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 20 – August 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min); 955 hPa (mbar) |
Aere is the Marshallese word for 'storm'. A tropical disturbance developed into a tropical depression on the 19th about 400 miles west of Guam, and moved northwest at 10 kts/12 mph along the southwestern periphery of a mid-level steering ridge. The system reached tropical storm status on the 20th, gaining the name Aere. Aere subsequently crossed into the Philippine's area of responsibility and was assigned the name Marce. Aere was upgraded to typhoon intensity on the 21st, and its strength leveled off during the 21st and 22nd. On the 23rd, Typhoon Aere was downgraded to a tropical storm briefly due to vertical wind shear while located 200 miles south of Naha, Okinawa. Aere quickly regained typhoon strength and maintained intensity for the rest of the 23rd and developed a 50-mile wide eye. Aere reached its peak intensity of 85 kts/100 mph late on the 24th, when the pressure lowered to 955 mb. As the storm crossed the northern tip of Taiwan it began to weaken. Aere turned southwestward later that day, a trajectory that carried the storm past Xiamen early on the 26th and close to Shantou later that day before weakening into a tropical storm. The remnants of Typhoon Aere remained a tropical depression until the 31st.
Early on the 25th, six villages located in Gaoqiao Town, Yinzhou District, Ningbo City, were struck by a tornado triggered by Typhoon Aere. The tornado did cause some economic losses, but no casualties were reported. Preliminary statistics indicated that the typhoon had caused 2.485 billion yuan of direct economic losses and was responsible for two deaths in Fujian province. Aere also affected 3,479,900 residents in 421 towns of 48 counties of 6 cities in Fujian, where three cities were flooded, 10,100 houses were toppled, 236 embankments and thousands of water conservancy facilities were damaged. Thirty-four people were killed in Taiwan as a result of the storm, and fifteen died as a mudslide buried a remote mountain village in the north of the island. Agricultural losses were estimated at 7.7 million New Taiwan dollars ($US 313,000). Forty-three deaths in the Philippines were caused by heavy rains induced by the typhoon. Eight provinces in northern and central Luzon were most severely affected with 70% of the provinces under water at one point.[4]
Typhoon Songda (Nina)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 28 – September 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min); 925 hPa (mbar) |
The name Songda is from a branch of the Red River in Vietnam. Songda was the second super typhoon to affect the Marianas and Japan in a week, soon after Super Typhoon Chaba passed through the same area. Tropical Depression 22W underwent rapid strengthening and was soon upgraded to tropical storm intensity on August 28th, and was on the verge of typhoon intensity by local midnight. Sustained winds of tropical storm force and gusts to typhoon force were seen in Eniwetak as the cyclone passed by to the north. Continuing on its west-northwesterly heading, Songda reached typhoon intensity late on the 29th approximately 760 miles east of Saipan. By the 1st, Songda became the fifth super typhoon of 2004. Typhoon-force wind gusts were observed on Pagan and Agrihan as the eyewall of Songda approached. Songda weakened slight below super typhoon force quickly after achieving the intensity and turned northwest. The center of Songda passed 17 miles north-northeast of Agrihan on the 1st. The cyclone then turned westward and headed for Okinawa. On the 3rd, Typhoon Songda gained the name Nina after entering PAGASA's area of warning responsibility. Typhoon Songda's strength began to wane as it neared Okinawa. Typhoon Songda passed a short distance north of the island by late on the 5th with the lowest SLP of 924 mb recorded on the island. Weakening continued as the storm tracked to the northwest. Songda turned north-northwestward on the 6th and headed towards Japan. Songda came ashore near the city of Nagasaki with winds (10-min avg) of 80 kts/90 mph on the 7th. The tropical cyclone accelerated northeastwards at 34 kts/39 mph as it moved across southwestern Japan. Weakening continued, with winds below typhoon strength at by early on the 8th. Its forward speed increased to 50 kts/58 mph, and Songda became a nontropical low later that day. The extratropical gale continued eastward as it slowly weakened, and by late on the 10th it had crossed the Dateline into the Bering Sea.
Storm total rainfall amounts in Japan ranged as high as 905 mm at Morotsuka between the 4th and 9th, with 358 mm falling between the early morning of the 6th and 7th. The highest wind gust of 135 mph/60.2 m/s was measured at Hiroshima. The lowest pressure measured in Japan was 944.3 mb at Saga. In the Republic of Korea, Ulleungdo measured 112.0 mm between the 6th and 7th. News reports indicated that Typhoon Songda killed 20 people and injured 700 others in Japan. In addition, 15 crew members of a vessel were reported missing. Songda arrived shortly after three earthquakes had struck the country a few days prior.[4]
Severe Tropical Storm Sarika
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 4 – September 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
The name Sarika is originally from a songbird found in Cambodia. JMA classified a tropical depression early on September 4th. By the 5th, a typhoon warning was issued for the island of Agrihan. Moving west-northwest along the southern periphery of the subtropical ridge, Tropical Depression 23W was upgraded to Tropical Storm Sarika that day. An upper-level LOW located to the southeast was providing an efficient eastern outflow channel in addition to the decent equatorial outflow. Rapid intensification ensued for a while with the MSW rising to 60 kts/70 mph late on the 5th, which was the peak intensity for Sarika. By the 6th, Tropical Storm Sarika passed 220 miles north of Saipan. Shortly afterward, the system's centre made its closest approach to Agrihan, tracking 10 miles south of that island. Near-typhoon conditions occurred on both Agrihan and Pagan while tropical storm-force winds were experienced on Alamagan. At its peak Sarika possessed a very compact wind field with gales extending no further than 90 miles from the centre while the radius of strongest winds never exceeded 15 miles. By the 6th, Sarika had turned westward 100 miles west of Agrihan. Early on the 7th, Sarika began to weaken as it entered a hostile shearing environment associated with Typhoon Songda's outflow. Sarika subsequently turned to the north-northwest at 9 mph/8 kts about 820 miles south of Tokyo, Japan while becoming fully-exposed. It slowed as it turned northward late on the 7th. The system remained a tropical storm until the 8th when Sarika weakened back into a depression.[5]
Tropical Storm Haima (Ofel)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 11 – September 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 996 hPa (mbar) |
Haima is the Chinese word for the sea horse. Early on September 11th, an area of thunderstorms was observed 150 nm southwest of Taipei, Taiwan. Later that day, the newly-formed tropical depression saw its thunderstorms track across Taiwan, leaving the circulation center behind east of the mountainous isle as it took on a subtropical appearance. By the 12th, it had strengthened into a tropical storm named Haima by Japan and Ofel by the Philippines...the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considered the system a tropical depression or subtropical storm, but never a tropical storm. The center track just east of Taiwan on the 12th, towards the southeast coast of China. Haima made landfall south of Shanghai on the 13th before turning to the northwest. Haima soon become a completely sheared system due to interaction with the upper level winds over a frontal zone located to its west, and was declared dissipated on the 14th.
In China, the lowest reported pressure was 998 mb in Yongqiang Town on the 13th and the highest 24 hour rainfall recorded was 250.8 mm at Pingtan in Fuzhou City between the 09th and 10th, which set a new September daily rainfall record for the station. In Taiwan, daily rainfall ranged as high as 393 mm in Taipei county, and 611.5 mm in Taipei City. The highest wind gust reported was 80 mph/35.9 m/s at Lanyu on the 11th. The storm damaged 78 square kilometres of farmland in Zhejiang Province, China, where direct economic losses were estimated to have been over 53 million yuan. Torrential rains (Sep 7-10), including those in the monsoonal flow around the pre-Haima depression had caused 54.6 million yuan of direct economic losses in Pingtan County and Changle City. In Japan, rainfall and winds were relatively light. In South Korea, the highest 24 hour rainfall report noted was 104.5 mm at Wando between the 11th and 12th.[5]
Typhoon Meari (Quinta)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 20 – September 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min); 940 hPa (mbar) |
Meari is Korean for 'echo'. Late on September 18th, an area of convection was spotted 510 miles east of Guam. On the 20th, Tropical Depression 25W organized out of this mass and was located just 35 miles southeast of Guam. Tropical Depression 25W turned more westward and began to accelerate as it moved along the southern periphery of a warm-core ridge. On the 21st, the system was upgraded to Tropical Storm Meari. It intensified steadily while moving more northwestward. The system was upgraded to typhoon intensity by late on the 22nd. Typhoon Meari possessed a very asymmetric circulation, elongated a bit to the north and northeast. Meari became a strong 100-kt/115 mph typhoon by late on the 23rd, and was assigned the name Quinta by PAGASA. After reaching 120 kts/140 mph on the 24th, its strength plateaued for the rest of the day. As it passed 70 miles south of Okinawa early on the 26th, Meari was slowly weakening. The cyclone ceased movement on the 27th about 170 miles west of Okinawa as it became lodged between two anticyclones. A slow northward drift began later that day and vertical wind shear associated with the subtropical jet stream began to take its toll on Meari. By the 29th, Meari was beginning its approach to the Japanese island of Kyūshū. Typhoon Meari made landfall over the southern tip of Kyūshū around midday local time with maximum sustained winds of 70 kts/80 mph. Meari weakened back into a tropical storm late on the 29th. The forward motion began to accelerate as Meari increasingly interacted with the westerlies. The system was followed until the 30th, when it became a nontropical low, which continued tracking eastwards through the north Pacific.
The highest wind gust reported was 118 mph/52.7 m/s in Kagoshima early on the 29th. The lowest pressure measured during the passage of Meari was 975.5 mb, also at Kagoshima on the 29th. Three tornadoes were spawned in Japan, with two touching down in Okinawa Prefecture and one in Aichi Prefecture. The heaviest rains in Japan were saved for Osawe, where 904 mm fell between late on the 24th and the 30th, with 741 mm falling between late on the 28th and 29th. Reports indicate that at least 18 people died with several more reported missing as a result of Typhoon Meari. The worst affected areas were the prefectures of Mie and Ehime in Japan where torrential rains caused widespread flooding and mudslides destroyed several homes. Train and ferry services were suspended, stranding thousands of people.[5]
Typhoon Ma-on (Rolly)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 4 – October 10 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min); 920 hPa (mbar) |
Ma-on is the name of a mountain in Hong Kong. Ma-on formed from a cluster of thunderstorms in the vicinity of Guam on September 29th. The small system eventually trekked west-northwesterly. After days of sputtering across the western Pacific, Tropical Depression 26W formed on October 4th, and quickly became named Tropical Storm Ma-on. The system became stationary approximately 650 nm southeast of Okinawa, Japan. PAGASA named the cyclone Rolly when it passed the 135th meridian. On the 5th, a northward drift ensued while well southeast of Okinawa. Upon reaching typhoon intensity late on the 06th, Ma-on turned northwest and ultimately became the sixth super typhoon of the year on the 8th while 250 miles southeast of Okinawa. The typhoon become the worst storm to hit eastern Japan in over ten years, only a week after Typhoon Meari had made landfall in that nation. Ma-on started to accelerate northeastward and its eye began to shrink in diameter and became more ragged. A slow weakening trend materialized as it entered the early stages of extratropical transition. Recurving northeast at a high rate of translation, Ma-on made landfall on the Izu Peninsula, Honshū, Japan, late on the 9th with maximum sustained winds of 90 kts/105 mph. Ma-on weakened rapidly and was downgraded to a tropical storm by the 10th, and quickly completed its transformation into a nontropical low. The remnant system moved more east-northeastward away from eastern Japan before slowing its motion 1100 miles southeast of Hokkaidō.
Ma-on was one of the most powerful storms to strike eastern Japan over the last ten years. The highest wind gust reported was 151 mph/67.6 m/s in Irouzaki late on the 9th. The lowest pressure was also recorded at Irouzaki; 964 mb late on the 9th. The typhoon left at least six people dead, and three persons were reported missing. Plane, train and ferry services nationwide were disrupted, stranding thousands of travellers. Heavy downpours also disrupted practice sessions for Formula One's Japanese Grand Prix in Suzuka. The highest storm total amount was noted at Omaezaki, where a 413 mm deluge was seen between late on the 6th and 9th, with 360 mm falling in a 24 hour period. Rescuers on boats plucked dozens of residents from waterlogged homes in Shizuoka Prefecture.[6]
Typhoon Tokage (Siony)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 13 – October 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min); 940 hPa (mbar) |
Tokage is the Japanese word for lizard. On October 12th, an area of convection existed 480 miles east-southeast of Guam. The system developed into Tropical Depression 27W at late that day, moving in a west-northwesterly at 15 kts about 200 miles east of Guam. On the October 13, the system developed into a tropical storm, and was named Tokage, subsequently moving very close to the islands of Rota and Guam. Typhoon intensity was achieved early on October 14 when centered 970 miles southeast of Okinawa. Later that day, Tokage briefly turned to the west-southwest. The storm's path curved back to a northwesterly heading by the October 15. The storm curled towards the north as a major shortwave over weakened the subtropical ridge and by October 17 Tokage reached its peak intensity of 125 kts/145 mph. Weakening began later that day as the storm turned back to a more northwesterly heading towards Okinawa and Japan. On October 18, Typhoon Tokage was 290 miles south of Kadena Air Base, Okinawa. Recurvature back to the north-northeast towards Japan ensued while the typhoon slowly weakened. Tokage made its closest approach to Okinawa late on October 19 when it was passed just to the south-southeast. The storm turned to the northeast as continued to accelerate as its extratropical transition began. Tokage made landfall over Tosa-Shimizu, near the southern tip of Shikoku, Japan still at typhoon strength. By October 21, the cyclone weakened into a tropical storm 130 nm west of Tokyo, and later that day, the system completed the transition to a nontropical low. The extratropical remains of Tokage moved rapidly northeastward, crossing the International Dateline around midday on October 23.
The highest measured wind gust was 142 mph/63.7 m/s at Unzendake, Nagasaki on October 20. The lowest pressure from a land station was 949.4 mb at Okinoerabu, Kagoshima late on October 19. The highest rainfall amount noted in Japan was 550 mm at Fukuharaasahi between late on October 17 and October 21, with 470 mm falling within a 24 hour period. News reports indicated Tokage was the worst storm to strike Japan since Typhoon Mireille thirteen years before. A total of 69 deaths were attributed to high winds, flooding and mudslides caused by Tokage. A total of 18,000 people were forced to evacuate their homes.[6]
Typhoon Nock-ten (Tonyo)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 16 – October 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min); 945 hPa (mbar) |
The name Nock-ten is taken from a type of bird found in Laos. Typhoon Nock-ten originated from a disturbance that formed amongst the Marshall Islands early on October 13 while 45 miles west of Kwajalein Atoll. Tropical Depression 28W developed on October 14 about 275 miles east-northeast of Pohnpei and moving westward along the southern periphery of the subtropical ridge. The system assumed a more west-northwesterly track, becoming a tropical storm by late on October 16, and was named Nock-ten. Early on October 18, the storm turned southwest and slowed its forward motion. The system strengthened into a typhoon by noon local time and curved back towards the west. Nock-ten soon accelerated and moved more northwesterly, partially due to the remains of Typhoon Tokage. Typhoon Nock-ten passed 160 miles south of Guam on October 20. Nock-ten reached its peak intensity of 110 kts/125 mph on October 23 as it tracked 480 miles south of Okinawa. Turning to a northerly track, Typhoon Nock-ten passed closest to Taipei during the afternoon of October 25, lying just off the northeastern tip of Taiwan by evening. The storm weakened and by local midnight the track became north-northeast. Nock-ten's motion to the east-northeast accelerated to 26 kts/29 mph, and the typhoon had become a nontropical low by the evening of October 26.
Typhoon Nock-ten lashed northern Taiwan with powerful winds and driving rain. The highest 24 hour rainfall on the island was 322 mm in Taipei City between early October 25 and October 27. The highest wind gust measured was 122 mph/54.4 m/s in Lanyu on October 24. Three fatalities occurred as a result of flash flooding. In Japan, the highest rainfall amount was spotted at Tanegashima which recorded 133.5 mm between midday October 26 and October 27.[6]
Typhoon Muifa (Unding)
| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 14 – November 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min); 950 hPa (mbar) |
The name Muifa is taken from the ume blossom. The disturbance that was to become Typhoon Muifa was noted early on November 14th when located 215 nm north of Palau. It became Tropical Depression 29W later that day and strengthened into a tropical storm by early the 15th when centered 550 miles east-southeast of Manila, Philippines. PAGASA assigned the name Unding on the 14th as it passed the 135th meridian. On the 16th, the tropical cyclone started drifting north-northeast. Muifa turned back onto a west-northwest heading and intensified. It reached typhoon intensity on the 17th just prior to beginning a two-day clockwise loop. Late on the 18th, Muifa's intensity peaked at 115 kts/130 mph still to the east of the Philippines. Muifa/Unding made landfall very late on the 19th near Naga City with maximum winds of 70 kts/80 mph. The system ambled across the Philippine Archipelago, dropping down to tropical storm intensity on the afternoon of the 20th. On the 21st, Muifa regained typhoon intensity in the South China Sea. Now moving west-southwest, early on the 22nd Muifa re-strengthened into a 90-kt/105 mph typhoon 440 miles east of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Muifa held onto typhoon status until late on the 23rd when its weakened to a tropical storm once more. On the 25th, Tropical Storm Muifa accelerated westward at a 21 kt/23 mph clip. By early on the 26th, a weakening Tropical Depression Muifa was located 250 nm south of Bangkok, Thailand. Later that day Muifa turned northward into an environment of increased wind shear and dissipated 120 nm south-southwest of Bangkok.
The highest 24 hour rainfall amount from the Philippines was 246.4 mm at Catanduanes between midday the 15th and 16th. The lowest pressure at Naga City was 986.1 mb early on the 16th. The death toll reported from the Philippines was 68 dead, 160 injured, and 69 unaccounted for. A total of 26,238 houses were destroyed and 76,062 damaged; total damage reached 1.0089 billion pesos. Typhoon Muifa had a destructive impact on Vietnam. The highest 24-hour rainfall amount reported was 251.5 mm at Prachuap Khirikhan between the afternoon of the 25th and 26th. Floods and landslides triggered by the typhoon killed about 40 people, and 40 more people were reported missing. There were also many villages in the mountains which needed urgent relief but which could not be quickly reached. Hoi An, which is the town of world heritage, was hit by the flood, and more than 80 old houses were in danger of collapse.[7]
Tropical Storm Merbok (Violeta)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Duration | November 22 – November 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
Merbok is the Malaysian word for the spotted-necked dove. This is the first tropical cyclone recognized by the Japan Meteorological Agency, but not Joint Typhoon Warning Center, since Changmi in 2002. Tropical Storm Merbok emanated from a disturbance located in the Philippine Sea and was first recognized as Tropical Depression Violeta by PAGASA on November 22nd. Later that day, it developed into a tropical storm. Tropical Storm Merbok tracked slowly towards the northwest and made landfall south of Baer on the east coast of Luzon. The storm's intensity held steady at 35 kts/40 mph (its peak strength) as it ambled its way across the mountains of Luzon, finally emerging off the northwest coast late on the 23rd. By this time, Merbok had lost most or all of its deep convection, the remnants continuing slowly north-westwards before dissipating southwest of Taiwan.
Tropical Storm Merbok added to the misery caused by Typhoon Muifa/Unding in the Philippines, killing 31 people and injuring 187 others. In addition, 17 persons were reported missing. A total of 337 houses were destroyed and 1,286 damaged. Total estimated damage reached 253 million pesos with agriculture especially hard hit (210 million pesos.) The heaviest rainfall in the Philippines from this cyclone was 185.2 mm at Casiguran between midday the 22nd and 23rd.[7]
Typhoon Nanmadol (Yoyong)
| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 29 – December 4 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min); 935 hPa (mbar) |
The name Nanmodol is from a famous ruin found on Pohnpei. Super Typhoon Nanmadol developed from a cluster of thunderstorms that was first noted early on November 28 when it was located 155 nm south-southwest of Pohnpei. It developed into Tropical Depression 30W about 690 miles east-southeast of Yap, and into Tropical Storm Nanmadol by midday November 29 as it moved westward south of the subtropical ridge. Nanmadol continued to strengthen, reaching typhoon intensity late that day after passing south of Satawal. The storm's track curved to the west-northwest. Late on November 30, the storm passed just north of Yap, bringing typhoon-force gusts and sustained tropical storm strength winds. The tropical cyclone reached its peak intensity of 130 kts/150 mph midday on December 2, then a super typhoon, 220 miles east of Manila, Philippines. Super Typhoon Nanmadol soon arrived at the Luzon coastline. At this time, the system began to lose strength and was downgraded from super typhoon status.
Turning northwestward Typhoon Nanmadol took roughly six hours to cross the island of Luzon, and by early on December 3 had reemerged back over water. The northwesterly turn took Nanmadol into a weakness in the subtropical ridge before being lured away by a major shortwave trough. Nanmadol weakened markedly during December 3 as it gradually veered more towards the north. The cloud pattern became increasingly asymmetrical as Nanmadol moved east-northeastward across southern Taiwan before becoming extratropical during the afternoon of December 4. Nanmadol became the first known December tropical cyclone in the past 108 years to make landfall on the island. The remnants of Super Typhoon Nanmadol continued to rapidly move to the east-northeast and northeast and ultimately merged with another LOW, forming a powerful extratropical cyclone which brought strong winds and led to unseasonably warm temperatures to Japan.
Because Muifa, Merbok, Winnie, and Nanmadol all occurred within a space of two weeks, the exact number of casualties and total cost of damages is difficult to determine. Nanmadol caused at least 70 fatalities and 157 injuries. Nanmadol destroyed 10,457 houses and damaged 57,435. Agriculture also suffered badly as a result of this typhoon with losses amounting to 2,036 million pesos in the Philippines. The maximum rain in the Philippines was 228.1 mm at Daet between midday on December 2 and December 3. In Taiwan, as much as 907 mm fell in Hualien county between early December 3 and December 4. Puluowan reported the highest storm total accumulation of 1090 mm during the 35-hr period ending on the afternoon of December 4. In China, 106.3 mm fell at Dachen Dao between the morning of December 3 and December 4. In Taiwan, 2 deaths were reported, and agricultural losses there were estimated to have been $670 million New Taiwan dollars.[7]
Tropical Storm Talas (Zosimo)
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 10 – December 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression 31W, which formed on December 10 near Kwajalein, became a tropical storm later that day. Talas moved to the west, peaking at 45 kt/50 mph before weakening due to lack of outflow. A break in the subtropical ridge allowed Talas to turn northward, where it reached 45 kt/50 mph winds before dissipating on December 19. Talas is Filipino for 'acuteness' or 'sharpness'.
Tropical Storm Noru
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 17 – December 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
The final storm of the season, Noru, formed on December 17 to the east-southeast of Saipan. After becoming a tropical storm on December 18 Noru moved to the northwest, where it peaked with 55 kt/65 mph winds. Noru turned to the northeast, and became extratropical on December 21. Noru is the Korean word for the roe deer.
Other storms
These systems were not officially named as tropical storms by the JMA, although the JMA might have monitored them as tropical depressions. They were, however, designated as tropical cyclones by the Philippines (PAGASA), China (CMA), and/or the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC).
Tropical Storm 01W (Ambo)
| Tropical depression (PAGASA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 11 – February 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
The first tropical storm of the 2004 Pacific typhoon season developed on February 11 west of Chuuk. It tracked to the west, organizing slowly due to persistent vertical shear. On February 13 and February 14, the depression executed a clockwise loop. When the storm turned to the southwest, the vertical wind shear overcame it, and the storm dissipated on February 16.
Tropical Storm 02W (Butchoy)
| Tropical storm (PAGASA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | March 16 – March 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 997 hPa (mbar) |
The near-equatorial trough spawned a tropical depression east of the Philippines on March 14. It headed generally northwestward, with a brief turn to the southwest. Just before the storm was about to hit the Philippines, a trough brought it northward, where dry air and vertical shear caused it to dissipate on March 23.
Tropical Storm 05W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 14 – May 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 997 hPa (mbar) |
From May 15 to May 17, Tropical Depression 05W persisted in the South China Sea before dissipating over open waters.
Tropical Storm 21W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 26 – August 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
An area of convection with a possible weak low level circulation center had developed approximately 700 miles east-southeast of Guam on August 24th, and was moving slowly in the direction of the island. It developed into a tropical depression on the 26th. The depression gradually intensified and was upgraded to Tropical Storm 21W by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) early on the 27th when located about 365 miles east of Guam, but not by Japan. By later that day, the center had become fully-exposed with the deep convection being displaced westward over Guam. The storm was downgraded back to depression status by JTWC around local midnight when centered approximately 245 miles east-northeast of Guam, though it was never recognized as a tropical storm by the Japan Meteorological Agency. The weakening system dissipated on the 31st when the weak LOW was located approximately 750 miles west of Saipan. No damage or casualties are known to have resulted from short-lived tropical cyclone.[4]
Tropical Depression Pablo
| Tropical depression (PAGASA) | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 17 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
This system was considered a tropical depression by JMA, PAGASA, the CWB of Taiwan and the Thai Meteorological Department with PAGASA assigning the name Pablo. JTWC released no warnings, but issued a pair of tropical cyclone formation alerts (TCFA) early on the 17th and 18th. Tropical Depression Pablo formed deep in the Philippine Sea east of Mindanao, moved westward across that island, thence turning northwestward and emerging into the South China Sea near the Calamian Group. After crossing the Philippine Archipelago the depression began to slowly weaken but limped across the South China Sea to near the central Vietnamese coastline before dissipating on the 18th where it dropped moderate to heavy rainfall. The maximum winds estimated by any agency were 30 kts/35 mph.[5]
Tropical Depression Winnie
| Tropical depression (PAGASA) | |
| Duration | November 27 – November 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression Winnie was a large system which brought torrential rains to Luzon, resulting in deadly flashfloods and landslides. Winnie formed east of the central Philippines on the 27th of November. JMA and the Central Weather Bureau of Taiwan were the only other agencies classifying Winnie as a tropical depression. The system moved west-northwestward over southeastern Luzon on the 29th. After moving well inland over Luzon, Winnie turned to a more north-northwesterly track up the west side of the island and was last mentioned on the 30th when it was located along the northwestern Luzon coast.
According to news reports in the Philippines, 1,404 people were killed or left missing[8] during the passage of Tropical Depression Winnie, primarily due to massive flashfloods and landslides in Quezon and Aurora Provinces triggered by the attendant heavy rains. The highest rainfall report from this system was 157.8 mm from Cabanatuan between midday November 29 and November 30.[7]
Storm names
Western North Pacific tropical cyclones are named by the RSMC Tokyo-Typhoon Center of the Japan Meteorological Agency. Names are selected from the following sequential list, there is no annual list. Names were contributed by 13 members of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee, except for Singapore. The 13 nations or territories, along with Micronesia, each submitted 10 names, which are used in alphabetical order by the English name of the country. These are the same names used for the 2003 season, with the exceptions of Peipah, Matmo, Nuri and Molave, which replaced Vamei, Chataan, Rusa and Imbudo. The first storm of 2004 was named Sudal and the final one was named Noru.
| Contributing Nation | Names | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cambodia | Damrey | Kong-rey | Nakri | Krovanh | Sarika |
| China | Longwang | Yutu | Fengshen | Dujuan | Haima |
| DPR Korea | Kirogi | Toraji | Kalmaegi | Maemi | Meari |
| Hong Kong | Kai-Tak | Man-yi | Fung-wong | Choi-wan | Ma-on |
| Japan | Tembin | Usagi | Kammuri | Koppu | Tokage |
| Laos | Bolaven | Pabuk | Phanfone | Ketsana | Nock-ten |
| Macau | Chanchu | Wutip | Vongfong | Parma | Muifa |
| Malaysia | Jelawat | Sepat | Nuri | Melor | Merbok |
| Micronesia | Ewiniar | Fitow | Sinlaku | Nepartak | Nanmadol |
| Philippines | Bilis | Danas | Hagupit | Lupit | Talas |
| RO Korea | Gaemi | Nari | Changmi | Sudal | Noru |
| Thailand | Prapiroon | Vipa | Mekkhala | Nida | Kulap |
| U.S.A. | Maria | Francisco | Higos | Omais | Roke |
| Vietnam | Saomai | Lekima | Bavi | Conson | Sonca |
| Cambodia | Bopha | Krosa | Maysak | Chanthu | Nesat |
| China | Wukong | Haiyan | Haishen | Dianmu | Haitang |
| DPR Korea | Sonamu | Podul | Pongsona | Mindulle | Nalgae |
| Hong Kong | Shanshan | Lingling | Yanyan | Tingting | Banyan |
| Japan | Yagi | Kajiki | Kujira | Kompasu | Washi |
| Laos | Xangsane | Faxai | Chan-hom | Namtheun | Matsa |
| Macau | Bebinca | Peipah | Linfa | Malou | Sanvu |
| Malaysia | Rumbia | Tapah | Nangka | Meranti | Mawar |
| Micronesia | Soulik | Mitag | Soudelor | Rananim | Guchol |
| Philippines | Cimaron | Hagibis | Molave | Malakas | Talim |
| RO Korea | Chebi | Noguri | Koni | Megi | Nabi |
| Thailand | Durian | Rammasun | Morakot | Chaba | Khanun |
| U.S.A. | Utor | Matmo | Etau | Aere | Vicente |
| Vietnam | Trami | Halong | Vamco | Songda | Saola |
Philippines
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) uses its own naming scheme for tropical cyclones within its area of responsibility. Lists are recycled every four years.The names Unding, Violeta and Winnie were retired after this season.
|
|
|
|
See also
- List of Pacific typhoon seasons
- 2004 Pacific hurricane season
- 2004 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2004 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2003-04, 2004-05
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2003-04, 2004-05
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2003-04, 2004-05
References
- ^ http://www.typhoon2000.ph/garyp_mgtcs/may03sum.txt
- ^ May 2004 Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary
- ^ Central Weather Bureau A Real-time MM5/WRF Forecasting system in Taiwan URL Accessed: September 26, 2006
- ^ a b c d e Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary August 2004
- ^ a b c d Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary September 2004
- ^ a b c Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary October 2004
- ^ a b c d Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary November 2004
- ^ http://www.swissre.com/INTERNET/pwsfilpr.nsf/vwFilebyIDKEYLu/SROS-6MQDPM/$FILE/C_2004.pdf
External links
- Typhoon2000 Philippine typhoon website.
- Philippine Area of Responsibility.
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center.
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center 2004 reports
- Meaning of Tokyo Typhoon Centre names
- Gary Padgett Tropical Cyclone reports (Jan. to June)
- Gary Padgett Tropical Cyclone reports (July to Dec.)
- Tracks of the 2004 storms