List of optical illusions: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Use Kanizsa triangle as an example of illusory contour |
+ |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|[[File:Duck-Rabbit illusion.jpg|100px]] |
|[[File:Duck-Rabbit illusion.jpg|100px]] |
||
| |
| |
||
|This type of illusions is designed to exploit graphical similarities. |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Ames room]] illusion |
|[[Ames room]] illusion |
||
Revision as of 20:15, 11 April 2011
List of optical illusions
| Name | Example 1 | Example 2 | Description/Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afterimage illusion | 
|
||
| Afterimage on empty shape (also known as color dove illusion) | 
|
An afterimage or ghost image is an optical illusion that refers to an image continuing to appear in one's vision after the exposure to the original image has ceased. | |
| Ambiguous image | 
|
This type of illusions is designed to exploit graphical similarities. | |
| Ames room illusion | 
|
||
| Ames trapezoid window illusion | An Ames room is a distorted room that is used to create an optical illusion. | ||
| ASCII stereogram | |||
| Autokinesis visual illusion | |||
| Autokinetic effect | |||
| Autostereogram | 
|

|
An autostereogram is a single-image stereogram (SIS), designed to create the visual illusion of a three-dimensional (3D) scene from a two-dimensional image in the human brain. |
| Barberpole illusion | 
|
The barber pole illusion is a visual illusion that reveals biases in the processing of visual motion in the human brain. | |
| Benham's top | 
|
||
| Beta movement | |||
| Bezold Effect | 
|
||
| Blivet | |||
| Café wall illusion | 
|
||
| Catoptric cistula | 
|
||
| Chubb illusion | 
|
||
| Color constancy | 
|
||
| Color Phi phenomenon | |||
| Contingent perceptual aftereffect | |||
| Convergence micropsia | |||
| Cornsweet illusion | 
|
||
| Delboeuf illusion | |||
| Disappearing Model | 
|
||
| Ebbinghaus illusion | 
|
||
| Ehrenstein illusion | 
|

|
The Ehrenstein illusion is an optical illusion studied by the German psychologist Walter Ehrenstein in which the sides of a square placed inside a pattern of concentric circles take an apparent curved shape. |
| Fechner color | |||
| Figure-ground (perception) | 
|
||
| Filling-in | 
|
||
| Flash lag illusion | |||
| Forced perspective | |||
| Fraser spiral illusion | 
|
||
| Gravity hill | |||
| Grid illusion | 
|
||
| Hering illusion | 
|
||
| Hollow-Face illusion | 
|
The Hollow-Face illusion is an optical illusion in which the perception of a concave mask of a face appears as a normal convex face. | |
| Hybrid image | A Hybrid Image is an optical illusion developed at MIT in which an image can be interpreted in one of two different ways depending on viewing distance. | ||
| Illusory contours | 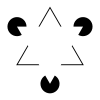
|
Illusory contours or subjective contours are a form of visual illusion where contours are perceived without a luminance or color change across the contour. | |
| Illusory motion | |||
| Impossible object | 
|
||
| Irradiation illusion | |||
| Isometric illusion | 
|
An isometric illusion (also called an ambiguous figure or inside/outside illusion) is a type of optical illusion, specifically one due to multistable perception. | |
| Jastrow illusion | 
|
The Jastrow illusion is an optical illusion discovered by the American psychologist Joseph Jastrow in 1889. | |
| Kanizsa triangle | 
|
The Kanizsa triangle is an optical illusion first described by the Italian psychologist Gaetano Kanizsa in 1955. It is a triangle formed of illusory contours. | |
| Leaning tower illusion | The Leaning Tower Illusion is an optical illusion that presents two identical images of the Leaning Tower of Pisa side by side. | ||
| Lilac chaser | 
|
Lilac chaser is a visual illusion, also known as the Pac-Man illusion. | |
| Liquid crystal shutter glasses | |||
| Mach bands | 
|
Mach bands is an optical illusion named after the physicist Ernst Mach. | |
| Magic Eye | |||
| McCollough effect | 
|
||
| Missing square puzzle | 
|

|
The missing square puzzle is an optical illusion used in mathematics classes to help students reason about geometrical figures. |
| Moon illusion | 
|
The Moon illusion is an optical illusion in which the Moon appears larger near the horizon than it does while higher up in the sky. | |
| Motion aftereffect | |||
| Motion illusion | 
|
||
| Müller-Lyer illusion | 
|
The Müller-Lyer illusion is an optical illusion consisting of a stylized arrow. | |
| Multistability | |||
| Musion Eyeliner | |||
| Necker cube illusion | The Necker Cube is an optical illusion first published in 1832 by Swiss crystallographer Louis Albert Necker. | ||
| Necker Cube | 
|
||
| Numerosity adaptation effect | 
|
||
| Orbison illusion | 
|
The Orbison illusion is an optical illusion that was first described by the psychologist Roy Orbison in 1939. | |
| Penrose stairs | 
|
||
| Penrose triangle | 
|
||
| Pepper's ghost | File:ToT PeppersGhost.jpg | ||
| Perceived visual angle | |||
| Peripheral drift illusion | 
|
||
| Phantogram | 
|
Phantograms, also known as Phantaglyphs, Op-Ups, free-standing anaglyphs, levitated images, and book anaglyphs, are a form of optical illusion. | |
| Phi phenomenon | |||
| Poggendorff illusion | 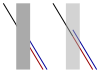
|
||
| Poiuyt | |||
| Ponzo illusion | 
|
||
| Rubin vase | File:Rubin2.jpg | ||
| Same color | 
|

|
|
| Sander illusion | |||
| Silencing | 
|
Silencing is an illusion in which a set of objects that change in luminance, hue, size, or shape appears to stop changing when it moves. | |
| Size-weight illusion | The size-weight illusion is also known as the Charpentier illusion (or Charpentier-Koseleff illusion). | ||
| Stroboscopic effect | |||
| Swept-plane display | |||
| Ternus illusion | |||
| Thaumatrope | 
|
A thaumatrope is a toy that was popular in Victorian times. | |
| The Spinning Dancer | 
|
||
| Trompe-l'œil | |||
| Troxler's fading | |||
| Vertical–horizontal illusion | |||
| Wagon-wheel effect | 
|
||
| White's illusion | 
|
||
| Wundt illusion | 
|
||
| Zoetrope | 
|
||
| Zöllner illusion | 
|
The Zöllner illusion is a classic optical illusion named after its discoverer, German astrophysicist Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner. |
See also
- Adaptation (eye)
- Alice in Wonderland syndrome
- Auditory illusion
- Barber's pole
- Camouflage
- Contingent perceptual aftereffect
- Contour rivalry
- Depth perception
- Emmert's law
- Entoptic phenomenon
- Forced perspective - application used in film and architecture to create the illusion of larger, more distant objects.
- Gestalt psychology
- Gravity hill
- Infinity pool
- Kinetic depth effect
- Mirage
- Multistable perception
- Op Art
- Trompe l'oeil
- Visual reorientation illusions
Notes
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Optical illusion.
- Optical Illusions Types & Related Images
- Optical Illusions & Visual Phenomena by Michael Bach
- Optical Illusions Database by Mighty Optical Illusions
- Optical illusions and perception paradoxes by Archimedes Lab
- http://ilusaodeotica.com hundreds of optical illusions
- Project LITE Atlas of Visual Phenomena
- Akiyoshi's illusion pages Professor Akiyoshi KITAOKA's anomalous motion illusions
- Spiral Or Not? by Enrique Zeleny, Wolfram Demonstrations Project
- Magical Optical Illusions by Rangki
- Hunch Optical Illusions by Hunch
