Project design flood: Difference between revisions
Mostly units |
Delink non-obscure units. Conversions. Report bugs to Lightmouse |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The '''project design flood''' is a hypothetical "maximum probable" flood of the [[Mississippi River]] used by the [[United States Army Corps of Engineers]] to aid in the design and execution of flood protection in the [[Mississippi Valley]].<ref name='USACE 2008' /><ref name='MRT 2011'>{{citation | contribution = MR&T PROJECT | title = MISSISSIPPI RIVER & TRIBUTARIES PROJECT | publisher = U. S. Army Corps of Engineers | date = February | year = 2011| id = | contribution-url = http://www.mvd.usace.army.mil/Offices/pa/brochures/MR&T%20WEB.pdf | format = PDF | accessdate = 2011-05-18}}</ref> |
The '''project design flood''' is a hypothetical "maximum probable" flood of the [[Mississippi River]] used by the [[United States Army Corps of Engineers]] to aid in the design and execution of flood protection in the [[Mississippi Valley]].<ref name='USACE 2008' /><ref name='MRT 2011'>{{citation | contribution = MR&T PROJECT | title = MISSISSIPPI RIVER & TRIBUTARIES PROJECT | publisher = U. S. Army Corps of Engineers | date = February | year = 2011| id = | contribution-url = http://www.mvd.usace.army.mil/Offices/pa/brochures/MR&T%20WEB.pdf | format = PDF | accessdate = 2011-05-18}}</ref> |
||
The current project design flood was developed in 1956 by the [[Mississippi River Commission]] with input from the [[Weather Bureau]]. It is based on a scenario of three rain events in the lower Mississippi Valley occurring 3 days apart: the January 1937 (increased by 10%), January 1950, and then the February 1938 rain event with its center adjusted 90 |
The current project design flood was developed in 1956 by the [[Mississippi River Commission]] with input from the [[Weather Bureau]]. It is based on a scenario of three rain events in the lower Mississippi Valley occurring 3 days apart: the January 1937 (increased by 10%), January 1950, and then the February 1938 rain event with its center adjusted {{convert|90|mi|km}} to the north and rainfall pattern rotated to achieve a hypothetical worst-case flood of the tributaries of the Mississippi River. Assumptions were made based on the completion of tributary reservoirs and dams by 1960. When the Commission reviewed the plan after the [[1973 Mississippi River floods]], the Project Design Flood in use was determined to be "based on sound technology that was still reliable by current standards. The project design flood peak discharges remained unchanged."<ref name='USACE 2008' /> |
||
Once the project design flood was developed, flow rates at critical points are used to determine how high [[levee]]s need to be, how deep the [[dredging]] needs to be, and the flowrates at which flood control structures need to be used. |
Once the project design flood was developed, flow rates at critical points are used to determine how high [[levee]]s need to be, how deep the [[dredging]] needs to be, and the flowrates at which flood control structures need to be used. |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
In response to the [[Great Mississippi Flood of 1927]], the [[Flood Control Act of 1928]] authorized the Mississippi River and Tributaries Project (MR&T), which is implemented by the [[Mississippi River Commission]] (MRC). The MRC estimated a maximum probably flood discharge of {{convert|2250000|cuft/s|commas=on|lk=on}} at [[Cairo, Illinois]] that was greater than the 1927 flood but less than the 1927 flood combined with the maximum recorded discharge of the [[Ohio River]] in 1913. In a separate analysis, the [[U.S. Weather Bureau]] determined that a "maximum possible" flood would result in a discharge of {{convert|2400000|cuft/s|commas=on}} based on the maximum recorded flows of the upper Mississippi, Ohio, [[Cumberland River|Cumberland]], and [[Tennessee River]]s. In a combined analysis, the higher flow rate estimate was used. |
In response to the [[Great Mississippi Flood of 1927]], the [[Flood Control Act of 1928]] authorized the Mississippi River and Tributaries Project (MR&T), which is implemented by the [[Mississippi River Commission]] (MRC). The MRC estimated a maximum probably flood discharge of {{convert|2250000|cuft/s|commas=on|lk=on}} at [[Cairo, Illinois]] that was greater than the 1927 flood but less than the 1927 flood combined with the maximum recorded discharge of the [[Ohio River]] in 1913. In a separate analysis, the [[U.S. Weather Bureau]] determined that a "maximum possible" flood would result in a discharge of {{convert|2400000|cuft/s|commas=on}} based on the maximum recorded flows of the upper Mississippi, Ohio, [[Cumberland River|Cumberland]], and [[Tennessee River]]s. In a combined analysis, the higher flow rate estimate was used. |
||
Adding the flows of the [[Arkansas River|Arkansas]] and [[White River (Arkansas)|White River]]s, the maximum flow farther downriver at [[Arkansas City, Arkansas]] was estimated to be {{convert|2850000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on|lk=on}} with a flood stage of 74 |
Adding the flows of the [[Arkansas River|Arkansas]] and [[White River (Arkansas)|White River]]s, the maximum flow farther downriver at [[Arkansas City, Arkansas]] was estimated to be {{convert|2850000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on|lk=on}} with a flood stage of {{convert|74|ft|m}}. Adding the flows of the [[Yazoo River|Yazoo]] and [[Red River (Mississippi River)|Red River]]s, the Weather Bureau estimated a flow of {{convert|3000000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on}} just North of [[Baton Rouge, Louisiana|Baton Rouge]] at [[Red River Landing, Louisiana]]. |
||
==1941 project design flood== |
==1941 project design flood== |
||
The [[Ohio River flood of 1937]] caused the flood stage at Cairo to reach 59.5 |
The [[Ohio River flood of 1937]] caused the flood stage at Cairo to reach {{convert|59.5|ft|m}} despite a flow of only {{convert|2100000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on}}.<ref name='USACE 2008' /> In response, the [[United States Congress]] ordered the MR&T to review of the flood control plan. Maximum flows were changed to {{convert|2600000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on}} at Cairo, {{convert|3065000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on}} at Arkansas City with the White River backwater area levee overtopped, and Red River Landing unchanged at {{convert|3000000|cuft/s|abbr=on|commas=on}}. |
||
==Current project design flood== |
==Current project design flood== |
||
Revision as of 19:19, 23 September 2011

The project design flood is a hypothetical "maximum probable" flood of the Mississippi River used by the United States Army Corps of Engineers to aid in the design and execution of flood protection in the Mississippi Valley.[1][2]
The current project design flood was developed in 1956 by the Mississippi River Commission with input from the Weather Bureau. It is based on a scenario of three rain events in the lower Mississippi Valley occurring 3 days apart: the January 1937 (increased by 10%), January 1950, and then the February 1938 rain event with its center adjusted 90 miles (140 km) to the north and rainfall pattern rotated to achieve a hypothetical worst-case flood of the tributaries of the Mississippi River. Assumptions were made based on the completion of tributary reservoirs and dams by 1960. When the Commission reviewed the plan after the 1973 Mississippi River floods, the Project Design Flood in use was determined to be "based on sound technology that was still reliable by current standards. The project design flood peak discharges remained unchanged."[1]
Once the project design flood was developed, flow rates at critical points are used to determine how high levees need to be, how deep the dredging needs to be, and the flowrates at which flood control structures need to be used.
1928 project design flood
In response to the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927, the Flood Control Act of 1928 authorized the Mississippi River and Tributaries Project (MR&T), which is implemented by the Mississippi River Commission (MRC). The MRC estimated a maximum probably flood discharge of 2,250,000 cubic feet per second (64,000 m3/s)* at Cairo, Illinois that was greater than the 1927 flood but less than the 1927 flood combined with the maximum recorded discharge of the Ohio River in 1913. In a separate analysis, the U.S. Weather Bureau determined that a "maximum possible" flood would result in a discharge of 2,400,000 cubic feet per second (68,000 m3/s)* based on the maximum recorded flows of the upper Mississippi, Ohio, Cumberland, and Tennessee Rivers. In a combined analysis, the higher flow rate estimate was used.
Adding the flows of the Arkansas and White Rivers, the maximum flow farther downriver at Arkansas City, Arkansas was estimated to be 2,850,000 cu ft/s (81,000 m3/s)* with a flood stage of 74 feet (23 m). Adding the flows of the Yazoo and Red Rivers, the Weather Bureau estimated a flow of 3,000,000 cu ft/s (85,000 m3/s)* just North of Baton Rouge at Red River Landing, Louisiana.
1941 project design flood
The Ohio River flood of 1937 caused the flood stage at Cairo to reach 59.5 feet (18.1 m) despite a flow of only 2,100,000 cu ft/s (59,000 m3/s)*.[1] In response, the United States Congress ordered the MR&T to review of the flood control plan. Maximum flows were changed to 2,600,000 cu ft/s (74,000 m3/s)* at Cairo, 3,065,000 cu ft/s (86,800 m3/s)* at Arkansas City with the White River backwater area levee overtopped, and Red River Landing unchanged at 3,000,000 cu ft/s (85,000 m3/s)*.
Current project design flood
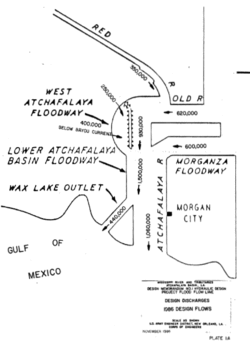

The current project design flood was developed at the request of the Senate Public Works Committee in 1954.[3] The Mississippi River Commission and the Weather Bureau worked together to investigate hypothetical flood conditions. The study of a set of 35 combinations of actual storms resulted in the selection of combination called "Hypo-Flood 58A," a combination of previous storms in 1937, 1938, and 1950. The peak discharges were found to be 2,360,000 cu ft/s (67,000 m3/s)* at Cairo, 2,890,000 cu ft/s (82,000 m3/s)* at Arkansas City, and 3,030,000 cu ft/s (86,000 m3/s)* at Red River Landing.
After the 1973 Mississippi River floods, the MRC reviewed the project design flood and found that it was still reliable based on current standards.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "The Mississippi River & Tributaries Project: Designing the Project Flood" (PDF), United States Army Corps of Engineers, April, retrieved 2011-05-16
{{citation}}:|format=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - ^ "MR&T PROJECT" (PDF), MISSISSIPPI RIVER & TRIBUTARIES PROJECT, U. S. Army Corps of Engineers, February, retrieved 2011-05-18
{{citation}}:|format=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - ^ Wohl. Inland flood hazards: human, riparian, and aquatic communities. p. 387. ISBN 0521624193.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
