Autodesk Softimage: Difference between revisions
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
* Autodesk Softimage 2010 released September 14, 2009 |
* Autodesk Softimage 2010 released September 14, 2009 |
||
* Autodesk Softimage 7.5 released February 20, 2009 |
* Autodesk Softimage 7.5 released February 20, 2009 |
||
* Mod Tool 4.2, December 2004.<ref>{{cite web|title=Announcement|url=http://www.halflife2.net/forums/showthread.php?63742-Announding-XSI-Mod-Tool-and-New-VMF-Exporter-for-XSI}}</ref> |
* Mod Tool 4.2, December 2004.<ref>{{cite web|title=Mod Tool Announcement at halflife2.net|url=http://www.halflife2.net/forums/showthread.php?63742-Announding-XSI-Mod-Tool-and-New-VMF-Exporter-for-XSI}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 06:41, 12 August 2011
 User interface of Softimage 2012 | |
| Developer(s) | Autodesk, Inc. |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2012 (10.0)
/ 2011-03-16 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows, Linux |
| Type | 3D computer graphics |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | www.softimage.com |
Autodesk Softimage, or simply Softimage (Template:Pron-en), is a 3D computer graphics application owned by Autodesk for producing 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling, and computer animation. Formerly Softimage|XSI, the software is predominantly used in the film, video game, and advertising industries for creating computer generated characters, objects, and environments.
Released in 2000 as the successor to Softimage|3D, Softimage|XSI was developed by Softimage, Co., then a subsidiary of Avid Technology. On Oct. 23, 2008, Autodesk acquired from Avid the Softimage brand and 3D animation assets for approximately $35 million, thereby ending Softimage Co. as a distinct entity.[1] In February 2009, Softimage|XSI was rebranded Autodesk Softimage.
A free version of the software, called Softimage Mod Tool, was developed for the game modding community to create games using the Microsoft XNA toolset for PC and Xbox 360, or to create mods for games using Valve Software's Source engine, Epic Games' Unreal Engine and others.
Overview of the software
Autodesk Softimage is a 3D animation application that contains tools for a wide range of production steps.
Modeling tools allow the generation of polygonal or NURBS models. Subdivision modeling is very intuitive, as it requires no additional operators and works directly on the polygonal geometry. Each modeling operation is tracked by a construction history stack, which enables artists to work non-destructively. Operators in history stacks can be re-ordered, removed or changed at any time, and all adjustments propagate to the final model.
Control rigs are created using bones with automatic IK, constraints and specialized solvers like spine or tail. Optionally, the ICE system can be used to create light-weight rigs in a node-based environment. The rigging process can be sped up through the use of adaptable biped and quadruped rigs, FaceRobot for facial rigs and automatic lip syncing.
Animation features include layers and a mixer, which allows combining animation clips non-linearly. Animation operators are tracked in a construction history stack that is separate from the modeling stack, enabling users to change the underlying geometry of already animated characters and objects. MOTOR is a feature that transfers animation between characters, regardless of their size or proportions. GATOR can transfer attributes such as textures, UVs, weight maps or envelopes between different models. Softimage also contains tools to simulate particles, particle strands, rigid body dynamics, soft body dynamics, cloth, hair and fluids.
The default and tightly integrated rendering engine in Softimage is mental ray. Materials and shaders are built in a node-based fashion. When users activate a so-called render region in a camera view, it will render this section of the scene using the specified rendering engine and update completely interactively. The FX Tree is a built-in node-based compositor that has direct access to image clips used in the scene. It can thus not only be used to finalize and composite rendered frames, but also as an integral part of scene creation.
In addition to the node-based ICE platform described below, Softimage has an extensive API and scripting environment that can be used to extend the software. The available scripting languages include C#, Python, VBScript and JScript. A C++ SDK is also available for plug-in developers.
ICE Interactive Creative Environment
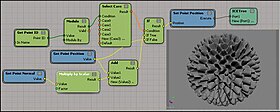
On July 7, 2008 the Softimage, Co. announced Softimage|XSI 7,[2] which introduced the ICE (Interactive Creative Environment) architecture. ICE is a visual programming platform that allows users to extend the capabilities of Softimage quickly and intuitively using a node-based dataflow diagram. This enables artists to create complex 3D effects and tools without scripting. Among the main uses for ICE are procedural modeling, deformation, rigging and particle simulation. It can also be used to control scene attributes without the need to write expressions, for example to add camera wiggle or make a light pulsate. ICE is a parallel processing engine that takes advantage of multi-core CPUs, giving users highly scalable performance.
ICE represents Softimage functionality using a collection of nodes, each with its own specific capabilities. Users can connect nodes together, visually representing the data flow, to create powerful tools and effects. Softimage ships with several hundred nodes; among them are both low level nodes, such as Multiply or Boolean, as well as a number of high level nodes called compounds. Compounds serve as "wrapper nodes" to collapse ICE graphs into a single node. Softimage allows users to add custom compounds to its main menu system for easy reusability.
The screenshot on the right shows an example of a simple geometry deformation ICE graph. In a practical scenario, one would collapse the graph into a compound and expose important parameters, for instance the deformation intensity. After adding the tool to the user interface it can easily be applied to other objects. Compounds can also be shared between installations because their entire functionality is stored in XML files.
The graph-based approach of ICE is less limiting than traditional development using scripting and/or compiled code. Due to its visual nature and interactivity, it is very accessible for users with no programming experience. Many free and commercial ICE tools have been made available by users and 3rd party developers. Softimage contains an ICE-based fluid and physics simulator called Lagoa as well as an ICE-based version of the Syflex cloth simulator.
Industry usage
Softimage is primarily used in the film, video game and advertising industries as a tool to generate digital characters, environments and visual effects. Examples of films made with the help of Softimage are Thor,[3] Predators[4] or District 9.[5]
Releases
- Autodesk Softimage 2012 released April 7, 2011
- Autodesk Softimage 2011 SAP (Subscription Advantage Pack) released October 7, 2010
- Autodesk Softimage 2011 released April 6, 2010
- Autodesk Softimage 2010 released September 14, 2009
- Autodesk Softimage 7.5 released February 20, 2009
- Mod Tool 4.2, December 2004.[6]
See also
References
- ^ "Autodesk Acquires Softimage For $35 Million", Gamasutra, October 2008
- ^ "Softimage, Co. announces Softimage". i3D_Eddy. 2008-07-07. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
{{cite web}}: Text "XSI 7 powered by ICE'" ignored (help) - ^ Vincent Frei (2011-06-27). "THOR: Jonathan Harb – VFX Supervisor & Founder – Whiskytree". The Art of VFX. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
- ^ Bill Desowitz (2010-07-13). "Letting the Predator Hounds Loose". Animation World Network. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
- ^ "Embassy on 'Distric 9'". CG Society. 2009-08-22. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
- ^ "Mod Tool Announcement at halflife2.net".
