Hegang: Difference between revisions
Cleaned up English. |
|||
| Line 163: | Line 163: | ||
== History == |
== History == |
||
===Early History=== |
===Early History=== |
||
In 1906, the area of Hegang City was under the administration of [[Tangyuan County]] |
In 1906, the area of Hegang City was under the administration of [[Tangyuan County]] under the [[Qing Dynasty]]. Since then, the government has been encouraging people to farm in the region. The Hegang mines were founded in 1916 by a Chinese entrepreneur with Russian capital. Hegang has witnessed rapid economic growth thanks to its rich coal resources. In 1926 a rail was built between Hegang and [[Jiamusi]], some 30 miles to the south on the [[Songhua River]]. The mines were further developed during the Japanese occupation of Manchuria. The area was named Xingshan after the Xinghua Coal Mine until 1949, when Hegang was renamed and set up as a prefecture-level city in Heilongjiang.<ref>[http://scenery.cultural-china.com/en/147Scenery7881.html Hegang - China culture]</ref> |
||
===People's Republic=== |
===People's Republic=== |
||
After 1949 the city experienced further rapid growth. The mines were extended and modernized, and their annual output increased dramatically. Most of the coal is high-quality coking coal that is also used to make coal gas; apart from a small quantity consumed in Jiamusi, the bulk of it is shipped by rail to [[Anyang]] in [[Henan Province]] and to other industrial cities in the southern Northeast region. By the late 1950s the coal industry employed more than 80 percent of the working population. Although the mines continued to be developed and output increased, Hegang's industrial activity was beginning to diversify, especially after a large thermal-power-generating installation was constructed by the early 1970s.<ref>{{Cite book|title=鹤岗市志 History of Hegang |author=《鹤岗市地方志》编纂委员会办公室 |year=1990 |publisher=黑龙江人民出版社 Heilongjiang People's Press |isbn=9787207017376}}</ref> |
After 1949 the city experienced further rapid growth. The mines were extended and modernized, and their annual output increased dramatically. Most of the coal is high-quality coking coal that is also used to make coal gas; apart from a small quantity consumed in Jiamusi, the bulk of it is shipped by rail to [[Anyang]] in [[Henan Province]] and to other industrial cities in the southern Northeast region. By the late 1950s the coal industry employed more than 80 percent of the working population. Although the mines continued to be developed and output increased, Hegang's industrial activity was beginning to diversify, especially after a large thermal-power-generating installation was constructed by the early 1970s.<ref>{{Cite book|title=鹤岗市志 History of Hegang |author=《鹤岗市地方志》编纂委员会办公室 |year=1990 |publisher=黑龙江人民出版社 Heilongjiang People's Press |isbn=9787207017376}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 06:57, 27 December 2011
Hegang
鹤岗 | |
|---|---|
| 鹤岗市 | |
| Hegang Century Square Hegang Century Square | |
 Hegang (red) in Heilongjiang province (orange) and China | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Heilongjiang |
| County-level divisions | 8 |
| Settled | 1906 AD |
| Area | |
| 14,784 km2 (5,708 sq mi) | |
| • Urban | 270 km2 (104 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 104 km2 (40 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 280 m (920 ft) |
| Population (2010 Census) | |
| 1,058,665 | |
| • Density | 72/km2 (190/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 489,232 |
| • Urban density | 1,800/km2 (4,700/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 489,232 |
| • Metro density | 4,700/km2 (12,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard Time) |
| Postal code | 154100 - 154200 |
| Area code | +86/086 |
| License plate prefixes | 黑H |
| ISO 3166-2 | CN-11 |
| GDP (2007) | CNY 19.6 billion |
| - per capita | CNY 17818 |
| Website | http://www.hegang.gov.cn |
Hegang (simplified Chinese: 鹤岗; traditional Chinese: 鶴崗; pinyin: Hègǎng, also known as Haoli, is a prefecture-level city in Heilongjiang province of the People's Republic of China. It is a prefecture-level municipality situated in the southeastern section of the Lesser Khingan Range, facing Jiamusi across the Songhua River to the south and Russia across the Heilongjiang River to the north. Hegang is one of the principal coal-producing cities in China. Hegang city covers an area of 14,784 km² and according to the 2010 Census, has a population of 1,058,665 inhabitants[1]. Its built up area is home to 489,232 inhabitants spread out over 4 urban districts excluding Dongshan, which is still largely rural.
Subdivisions
The prefecture-level city of Hegang is divided into 6 districts and 2 counties. The information presented here uses the metric system and data from the 2010 Census.
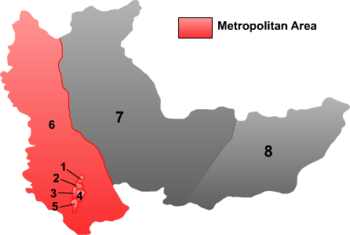
| |||||||
| # | English Name | Simplified | Traditional | Pinyin | Area | Population | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xingshan District | 兴山区 | 興山區 | Xīngshān Qū | 27 | 44,803 | 1,659 |
| 2 | Xiangyang District | 向阳区 | 向陽區 | Xiàngyáng Qū | 9 | 110,916 | 12,324 |
| 3 | Gongnong District | 工农区 | 工農區 | Gōngnóng Qū | 11 | 140,070 | 12,734 |
| 4 | Nanshan District | 南山区 | 南山區 | Nánshān Qū | 30 | 119,047 | 3,968 |
| 5 | Xing'an District | 兴安区 | 興安區 | Xīng'ān Qū | 27 | 74,396 | 2,755 |
| 6 | Dongshan District | 东山区 | 東山區 | Dōngshān Qū | 4,575 | 175,239 | 38 |
| 7 | Luobei County | 萝北县 | 蘿北縣 | Luóběi Xiàn | 6,761 | 220,131 | 33 |
| 8 | Suibin County | 绥滨县 | 綏濱縣 | Suíbīn Xiàn | 3,344 | 174,063 | 52 |
History
Early History
In 1906, the area of Hegang City was under the administration of Tangyuan County under the Qing Dynasty. Since then, the government has been encouraging people to farm in the region. The Hegang mines were founded in 1916 by a Chinese entrepreneur with Russian capital. Hegang has witnessed rapid economic growth thanks to its rich coal resources. In 1926 a rail was built between Hegang and Jiamusi, some 30 miles to the south on the Songhua River. The mines were further developed during the Japanese occupation of Manchuria. The area was named Xingshan after the Xinghua Coal Mine until 1949, when Hegang was renamed and set up as a prefecture-level city in Heilongjiang.[2]
People's Republic
After 1949 the city experienced further rapid growth. The mines were extended and modernized, and their annual output increased dramatically. Most of the coal is high-quality coking coal that is also used to make coal gas; apart from a small quantity consumed in Jiamusi, the bulk of it is shipped by rail to Anyang in Henan Province and to other industrial cities in the southern Northeast region. By the late 1950s the coal industry employed more than 80 percent of the working population. Although the mines continued to be developed and output increased, Hegang's industrial activity was beginning to diversify, especially after a large thermal-power-generating installation was constructed by the early 1970s.[3]
Climate
Hegang has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dwb),[4] with long, bitterly cold, but dry winters, and humid and warm summers. Average high temperatures range from −12.7 °C (9 °F) in January to 26.5 °C (79.7 °F) in July. Close to 2/3 of the annual precipitation falls in the months of June thru August. The average temperature is 3℃.
| Climate data for Hegang (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −12.7 (9.1) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
0.5 (32.9) |
11.1 (52.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.5 (79.7) |
24.7 (76.5) |
18.9 (66.0) |
9.9 (49.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−10.9 (12.4) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −20.8 (−5.4) |
−16.9 (1.6) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
0.4 (32.7) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.7 (56.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
15.7 (60.3) |
8.9 (48.0) |
0.3 (32.5) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−18.3 (−0.9) |
−1 (30.20) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 3.1 (0.12) |
4.2 (0.17) |
9.2 (0.36) |
21.9 (0.86) |
55.9 (2.20) |
113.1 (4.45) |
133.9 (5.27) |
148.6 (5.85) |
75.6 (2.98) |
31.5 (1.24) |
8.8 (0.35) |
6.6 (0.26) |
612.4 (24.11) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 4.7 | 4.1 | 5.6 | 7.3 | 11.9 | 14.1 | 14.5 | 14.7 | 11.7 | 7.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 107.6 |
| Source: Weather China | |||||||||||||
Economy
In 2010, Hegang's GDP grew 16.1% to RMB 25.1 billion, ranking tenth among 13 prefectures and prefecture-level cities in the province.[5] Agriculture and animal husbandry are considered two pillars of the city's primary industry. Heavy industry dominates the city's industrial sector. Other major industries in the city include agricultural products processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, dairy and related products, and the production and supply of electricity.[6]
Transport
The Yichun-Hegang Highway, the Jiamusi-Hegang Highway and the Hegang-Luobei Highway form a comprehensive highway network withinin the city. It takes less than four hours to drive from Hegang to Harbin, the provincial capital of Heilongjiang Province. Luobei Port, which is within a one-hour drive from Hegang, is a major port on the Heilongjiang River. Jiamusi Airport, a one-hour drive from Hegang, operates flights to Beijing, Dalian and other major cities in China.
Town twinning
![]() Birobidzhan, Jewish Autonomous Oblast, Russia
Birobidzhan, Jewish Autonomous Oblast, Russia
References
- ^ Template:Zh icon Compilation by LianXin website. Data from the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China
- ^ Hegang - China culture
- ^ 《鹤岗市地方志》编纂委员会办公室 (1990). 鹤岗市志 History of Hegang. 黑龙江人民出版社 Heilongjiang People's Press. ISBN 9787207017376.
- ^ Climate map of Asia Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L., and McMahon, T. A.
- ^ 2010年鹤岗市国民经济和社会发展统计公报
- ^ Profiles of China Provinces, Cities and Industrial Parks
