Dockerin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
{{Refimprove|date=June 2008}} |
{{Refimprove|date=June 2008}} |
||
'''Dockerin''' is a [[protein domain]] found in the [[Cellulosome]] cellular structure. It is part of [[endoglucanase]] enzymes. The dockerin's binding partner is the [[cohesin domain|cohesin]] domain. This interaction is essential to the construction of the Cellulosome complex |
'''Dockerin''' is a [[protein domain]] found in the [[Cellulosome]] cellular structure. It is part of [[endoglucanase]] enzymes. The dockerin's binding partner is the [[cohesin domain|cohesin]] domain, which is located on the [[Scaffoldin]] protein. This interaction is essential to the construction of the Cellulosome complex. The Dockerin domain has two in-tandem repeats of a non-[[EF hand]] calcium binding motif. Each motif is characterized by a [[loop-helix structure]].<ref>{{SCOP|63447}}</ref> The three dimensional structure of dockerin has been determined in solution,<ref name="pmid11273698">{{PDB|1DAQ}}; {{cite journal | author = Lytle BL, Volkman BF, Westler WM, Heckman MP, Wu JH | title = Solution structure of a type I dockerin domain, a novel prokaryotic, extracellular calcium-binding domain | journal = J. Mol. Biol. | volume = 307 | issue = 3 | pages = 745–53 | year = 2001 | month = March | pmid = 11273698 | doi = 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4522 | url = }}</ref> as well as in complex with Cohesin.<ref name="pmid14623971">{{PDB|1OHZ}}; {{cite journal | author = Carvalho AL, Dias FM, Prates JA, Nagy T, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ, Ferreira LM, Romão MJ, Fontes CM | title = Cellulosome assembly revealed by the crystal structure of the cohesin–dockerin complex | journal = Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | volume = 100 | issue = 24 | pages = 13809–14 | year = 2003 | month = November | pmid = 14623971 | pmc = 283503 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.1936124100 | url = }}</ref> |
||
There are three types of Dockerin domains: I, II and III which bind to Cohesin Type I, Cohesin Type II and Cohesin Type III respectively. A type I dockerin domain is 65-70 [[residue (chemistry)|residue]]s long.<ref>[[InterPro]]: {{InterPro|IPR016134}}</ref> The binding specificity of Type I interaction was well studied by structural and [[mutagenesis]] studies. Type II interaction is less well characterized.<ref name="pmid15697243">{{cite journal | author = Adams JJ, Webb BA, Spencer HL, Smith SP | title = Structural characterization of type II dockerin module from the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum: calcium-induced effects on conformation and target recognition | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 44 | issue = 6 | pages = 2173–82 | year = 2005 | month = February | pmid = 15697243 | doi = 10.1021/bi048039u | url = }}</ref> |
There are three types of Dockerin domains: I, II and III which bind to Cohesin Type I, Cohesin Type II and Cohesin Type III respectively. A type I dockerin domain is 65-70 [[residue (chemistry)|residue]]s long.<ref>[[InterPro]]: {{InterPro|IPR016134}}</ref> The binding specificity of Type I interaction was well studied by structural and [[mutagenesis]] studies. Type II interaction is less well characterized.<ref name="pmid15697243">{{cite journal | author = Adams JJ, Webb BA, Spencer HL, Smith SP | title = Structural characterization of type II dockerin module from the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum: calcium-induced effects on conformation and target recognition | journal = Biochemistry | volume = 44 | issue = 6 | pages = 2173–82 | year = 2005 | month = February | pmid = 15697243 | doi = 10.1021/bi048039u | url = }}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 16:10, 19 March 2012
| Dockerin domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
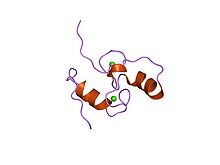 Structure of the Dockerin type I domain from C. thermocellum cellulosome. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Dockerin_1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00404 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR018242 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00416 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1daq / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2008) |
Dockerin is a protein domain found in the Cellulosome cellular structure. It is part of endoglucanase enzymes. The dockerin's binding partner is the cohesin domain, which is located on the Scaffoldin protein. This interaction is essential to the construction of the Cellulosome complex. The Dockerin domain has two in-tandem repeats of a non-EF hand calcium binding motif. Each motif is characterized by a loop-helix structure.[1] The three dimensional structure of dockerin has been determined in solution,[2] as well as in complex with Cohesin.[3]
There are three types of Dockerin domains: I, II and III which bind to Cohesin Type I, Cohesin Type II and Cohesin Type III respectively. A type I dockerin domain is 65-70 residues long.[4] The binding specificity of Type I interaction was well studied by structural and mutagenesis studies. Type II interaction is less well characterized.[5]
See also
References
- ^ SCOP 63447
- ^ PDB: 1DAQ; Lytle BL, Volkman BF, Westler WM, Heckman MP, Wu JH (2001). "Solution structure of a type I dockerin domain, a novel prokaryotic, extracellular calcium-binding domain". J. Mol. Biol. 307 (3): 745–53. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4522. PMID 11273698.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ PDB: 1OHZ; Carvalho AL, Dias FM, Prates JA, Nagy T, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ, Ferreira LM, Romão MJ, Fontes CM (2003). "Cellulosome assembly revealed by the crystal structure of the cohesin–dockerin complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (24): 13809–14. doi:10.1073/pnas.1936124100. PMC 283503. PMID 14623971.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ InterPro: InterPro: IPR016134
- ^ Adams JJ, Webb BA, Spencer HL, Smith SP (2005). "Structural characterization of type II dockerin module from the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum: calcium-induced effects on conformation and target recognition". Biochemistry. 44 (6): 2173–82. doi:10.1021/bi048039u. PMID 15697243.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
Protein Structure:
- Lytle BL, Volkman BF, Westler WM, Heckman MP, Wu JH (2001). "Solution structure of a type I dockerin domain, a novel prokaryotic, extracellular calcium-binding domain". J Mol Biol. 307 (3): 745–753. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4522. PMID 11273698.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Bayer EA, Shimon LJ, Shoham Y, Lamed R (1998). "Cellulosomes-structure and ultrastructure". J Struct Biol. 124 (2–3): 221–234. doi:10.1006/jsbi.1998.4065. PMID 10049808.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Specificity Characterization:
- Haimovitz R, Barak Y, Morag E, Voronov-Goldman M, Shoham Y, Lamed R, Bayer EA (2008). "Cohesin-dockerin microarray: Diverse specificities between two complementary families of interacting protein modules". Proteomics. 8 (5): 968–979. doi:10.1002/pmic.200700486. PMID 18219699.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Adams JJ, Webb BA, Spencer HL, Smith SP (2005). "Structural characterization of type II dockerin module from the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum: calcium-induced effects on conformation and target recognition". Biochemistry. 44 (6): 2173–2182. doi:10.1021/bi048039u. PMID 15697243.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Jindou S, Soda A, Karita S, Kajino T, Béguin P, Wu JH, Inagaki M, Kimura T, Sakka K, Ohmiya K (2004). "Cohesin-dockerin interactions within and between Clostridium josui and Clostridium thermocellum: binding selectivity between cognate dockerin and cohesin domains and species specificity". J Biol Chem. 279 (11): 9867–9874. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308673200. PMID 14688277.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
