Vatican City: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [pending revision] |
AndrewBellis (talk | contribs) Reverting because of vandalism |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
* [http://www.vatican.va/vatican_city_state/ Vatican City official website] |
* [http://www.vatican.va/vatican_city_state/ Vatican City official website] |
||
* [http://www.vaticanphilately.org Vatican Philatelic Society] Premier online source of information about Vatican City postage stamps |
* [http://www.vaticanphilately.org Vatican Philatelic Society] Premier online source of information about Vatican City postage stamps |
||
* [http://eudocs.lib.byu.edu/index.php/History_of_Vatican_City:_Primary_Documents History of Vatican City: Primary Documents] |
|||
* [http://www.hot-maps.de/europe/italy/vatican/homeen.html Map of Vatican City] |
* [http://www.hot-maps.de/europe/italy/vatican/homeen.html Map of Vatican City] |
||
* [http://www.stpetersbasilica.org stpetersbasilica.org] Largest online source for St. Peter's in the Vatican |
* [http://www.stpetersbasilica.org stpetersbasilica.org] Largest online source for St. Peter's in the Vatican |
||
Revision as of 23:46, 5 June 2006
Template:Vatican Infobox Vatican City 41°54′10″N 12°27′9″E / 41.90278°N 12.45250°E — formally State of the Vatican City, or Vatican City State (Italian: Stato della Città del Vaticano, Latin: Status Civitatis Vaticanae) — is a tiny sovereign state whose territory consists of a landlocked enclave within the city of Rome, Italy. The entire state is about 44 Hectares (108.7 acres) and thus is a European microstate. It is the smallest independent nation in the world. Since it is governed by the Bishop of Rome (the Pope), its government can be described as ecclesiastical and the highest state functionaries are in fact clergymen. It is the sovereign territory of the Holy See (Latin:Sancta Sedes) and the location of the Apostolic Palace—the Pope's official residence—and the Roman Curia. Thus, although the principal ecclesiastical seat of the Holy See (Basilica of St. John Lateran) is located in Rome itself, the Vatican City can be said to be the governmental capital of the Roman Catholic Church of both East and West.
The territory
The placename is ancient and predates Christianity, coming from the Latin Mons Vaticanus, Vatican Hill. It is part of the Mons Vaticanus, and of the adjacent former Vatican Fields upon which St. Peter's Basilica, the residence of the popes called the Apostolic Palace, with its Sistine Chapel, and museums were built, along with various other buildings. The area was never fully incorporated into the urban conglomeration of Rome until the last century, being separated from the city by the river Tiber. It was thus an outcrop of the city and was protected by being included in a loop of the city wall. When the 1929 Lateran treaties that gave the state its present form was being prepared, the fact that a good part of the proposed territory was all but enclosed by this loop led to the present territorial definition being adopted. For some tracts of the frontier there was no wall, but the line of certain buildings supplied part of the boundary, and for a small part of the frontier a modern wall was constructed. The territory included St. Peter's Square, which it was not possible to isolate from the rest of Rome and therefore a largely imaginary border with Italy runs along the outer limit of the square where it touches on Piazza Pio XII and Via Paolo VI.
Although technically not included within the territory of the Vatican City State, according to the Lateran treaties, certain properties of the Holy See have an extraterritorial status similar to that of foreign embassies. These include the papal summer residence of Castelgandolfo in the nearby hills, the Lateran Basilica, the basilicas of St. Mary Major and of St Paul Outside the Walls, and a number of other buildings in Rome. Castelgandolfo and the named basilicas are patrolled internally by police agents of the Vatican City State and not by Italian police. St. Peter's Square is ordinarily policed jointly by both.
The head of state
The Head of State is the Pope, who as the supreme executive, legislative, and judicial authority is also the Head of Government. This is a non-hereditary elective monarchy with a sovereign who exercises absolute authority, that is to say supreme legislative, executive and judicial power not only over Vatican City State but also constituting the Holy See. The sovereign is elected for a life term in conclave by cardinals under the age of 80. His principal subordinate government officials are the Secretary of State, the President of the Pontifical Commission for Vatican City State, and the Governor of Vatican City.
The current Pope is Benedict XVI, born Joseph Ratzinger in Germany. Angelo Cardinal Sodano of Italy is the Secretary of State. Edmund Cardinal Szoka serves as both the President of the Pontifical Commission and Governor, born an American of Polish descent. Sodano and Szoka served in their respective roles under Pope John Paul II and were then reappointed to those same roles by his successor.
History

It is supposed that this originally uninhabited part of Rome (the ager vaticanus) had long been considered sacred, or at least not available for habitation, even before the arrival of Christianity. In 326, the first church, the Constantinian basilica, was built over the site that later Roman Catholic apologists argue was the tomb of Saint Peter, buried in a common cemetery on the spot; from then on the area started to become more populated, but mostly only by dwelling houses connected with the activity of St Peter's.
Popes in their secular role gradually came to govern neighbouring regions and, through the Papal States, ruled a large portion of the Italian peninsula for more than a thousand years until the mid 19th century, when most of the territory of the Papal States was seized by the newly created Kingdom of Italy. For much of this time the Vatican was not the habitual residence of the Popes, but rather the Lateran Palace, and in recent centuries, the Quirinal Palace, while the residence from 1309-1377 was at Avignon in France.
In 1870, the Pope's holdings were left in an uncertain situation when Rome itself was annexed by the Piedmontese after a nominal resistance of the papal forces. The popes were left between 1870 and 1929 in a situation somewhat like that of the last emperor of China, undisturbed in their palace, but with no official status recognized by the Italian State.[citation needed] Other states maintained international recognition of the Holy See as a sovereign entity, and in practice Italy made no attempt to interfere with the Holy See. During this period it became fashionable to speak of the Pope as a "prisoner".[citation needed] This situation was resolved on February 11, 1929 under the premiership of Mussolini by the three Lateran treaties, which established the independent State of the Vatican City and granted Catholicism special status in Italy. The cathedra (official seat) of the Bishop of Rome, the Pope, is in the Lateran Basilica, Rome's cathedral. In 1984, a new concordat between the Holy See and Italy modified certain provisions of the earlier treaty, including the position of Catholicism as the Italian state religion.
Government
For historical reasons, the government of Vatican City has a unique structure. As noted, the principal figures are the Secretary of State, the President of the Pontifical Commission for the Vatican City State, and the Governor of Vatican City. These, like all other officials, are appointed by the Pope and can be dismissed by him at any time.
During a sede vacante (papal vacancy), the Chamberlain of the Holy Roman Church, former Secretary of State, and former President of the Pontifical Commission form a commission that performs some of the functions of the head of state; while another made up of the Chamberlain and three cardinals (one being chosen by lot every three days from each order of cardinals), performs other functions of the head of state. All decisions of these commissions must be approved by the College of Cardinals.
Administration of Vatican City
The Governor of Vatican City, sometimes known as the President of Vatican City, has duties similar to those of a mayor or city executive, concentrating on material questions concerning the state's territory, including local security, but excluding external relations. The Vatican City maintains two modern security corps, the famous Swiss Guards, a voluntary military force drawn from male Swiss citizens, and the Corpo della Gendarmeria dello Stato della Città del Vaticano. They are not really an army of the Vatican City State so much as a police force and the personal bodyguard of the Pope.
Legislative power is vested in the Pontifical Commission for Vatican City State, led by a president. Members are cardinals appointed by the pope for terms of five years.
The judicial functions are handled by three tribunals — the Apostolic Signatura, the Sacra Rota Romana, and the Apostolic Penitentiary, which are also the judicial arm of the Holy See (see below). The legal system is based on canon, or ecclesiastical, law; if Canon Law is not applicable, special laws of the territory apply, often modelled on Italian provisions.
Communications
Vatican City has its own post office, commissary (supermarket), bank (the automatic teller machines are the only ones in the world to use Latin), railway station, electricity generating plant, and publishing house.
The Vatican also issues its own coins and stamps and controls its own Internet domain (.va).
Vatican Radio, the official radio station, is one of the most influential in Europe. "L'Osservatore Romano" is the semi-official newspaper, published daily in Italian, and weekly in English, Spanish, Portuguese, German, and French (plus a monthly edition in Polish). It is published by Catholic laymen but carries official information.
Geography
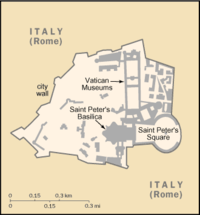
The Vatican City, one of the European microstates, is situated on the Vatican Hill in the north-western part of Rome, several hundred metres west of the Tiber river, on the latter's right bank. Its borders (3.2 km or 2 miles in total, all within Italy) closely follow the city wall constructed to protect the Pope from outside attack. The situation is more complex at the famous St. Peter's Square in front of the St. Peter's Basilica, where the correct border is just outside the ellipse formed by Bernini's colonnade. The Vatican City is the smallest sovereign state in the world at 0.44 square kilometres (108.7 acres).
Its climate is clearly mostly the same as Rome's; a temperate, Mediterranean climate with mild, rainy winters from September to mid-May and hot, dry summers from May to August. There are some local features, principally mists and dews, caused by the anomalous bulk of St Peter's Basilica, the elevation, the fountains and the size of the large paved square.
Economy
This unique, non-commercial economy is also supported financially by contributions (known as Peter's Pence) from Catholics throughout the world, the sale of postage stamps and tourist mementos, fees for admission to museums, and the sale of publications. The incomes and living standards of lay workers are comparable to, or somewhat better than, those of counterparts who work in the city of Rome.
Vatican City has used the euro as its currency since January 1, 1999, owing to a special agreement with the EU (council decision 1999/98/CE). Euro coins and notes were introduced in January 1, 2002. Due to its rarity, Vatican euro coins are highly sought by collectors.
It also has its own bank, Vatican Bank.
- Budget: Revenues (2003) $252 million; expenditures (2003) $264 million.
- Industries: printing and production of few mosaics and staff uniforms; worldwide banking and financial activities.
Demographics

Almost all of Vatican City's 932 citizens live inside the Vatican's walls. The Vatican citizenry consists mainly of clergy, including high dignitaries, priests, nuns, as well as the Swiss Guard. There are also about 3,000 lay workers who comprise the majority of the Vatican work force, but who reside outside the Vatican.
The official language is Latin. Italian and, to a lesser extent, other languages are generally used for most conversations, publications, and broadcasts. German is the official language of the Swiss Guard.
Citizenship
Citizenship of the Vatican City is granted ius officii. That means it is invested to those who have been appointed to work at the Vatican, and it is usually revoked upon the termination of their employment. Also in the period of employment citizenship can also be extended to a Vatican citizen's spouse (unless the marriage is annulled or dissolved, or if a conjugal separation is decreed) and children (until they turn 25 if they are capable of working, or in the case of daughters, if they marry). Terms about citizenship are defined in the Lateran treaties and laws concerning the creation of the Vatican state in 1929, sought to restrict the number of people who could be granted Vatican citizenship. The only passports issued by the Vatican are diplomatic passports.
On 31 December 2002 there were 555 people with Vatican citizenship, of whom all are dual-citizens to other countries (the majority being Italian). The Lateran Treaty states that in the event a Vatican citizen has their other nationality revoked, they will be automatically granted Italian citizenship. This would have been important had the authorities in pre-Solidarity Poland decided to strip Pope John Paul II of his Polish citizenship.
Among the 555 were:
- the Pope
- 57 cardinals
- 293 members of the clergy who serve as diplomatic envoys abroad
- 56 lesser ranking clergy members who work in the Vatican
- 104 officers, NCOs and men of the Papal Swiss Guard.
- 44 lay persons
Foreign relations
Providing a territorial identity for the Holy See, the State of the Vatican City is a recognized national territory under international law. However, it is the Holy See that is the legal body that conducts diplomatic relations for the Vatican City in addition to the Holy See's usual diplomacy, entering into international agreements and both receives and sends diplomatic representatives. Due to the very limited territory of the Vatican state, foreign embassies to the Holy See are located in the Italian part of Rome; Italy actually hosts its own Embassy of Italy. The Holy See is currently the only European political entity that has a formal diplomatic relation with the Republic of China (Taiwan).
Culture
The Vatican City is itself of great cultural significance. Buildings such as St. Peter's Basilica and the Sistine Chapel are home to some of the most beautiful art in the world, which includes works by artists such as Botticelli, Bernini and Michelangelo. The Vatican Library and the collections of the Vatican Museums are of the highest historical, scientific and cultural importance.
The permanent population of the Vatican City is predominately male, although two orders of nuns live in the Vatican. A minority are senior Catholic clergy; the remainder are members of religious orders. Many workers in the Vatican City live outside its walls, including the Swiss Guard and embassy personnel.
Visitors must adhere to strict dress codes. Clothes that show the legs above the knees are strictly banned.
Tourism and pilgrimages are an important factor in the daily life of the Vatican. The Pope leads weekly Mass and other services, and appears on religious holidays such as Easter. On significant events, such as beatification ceremonies, he leads open-air Mass in Saint Peter's Square.
Crime
As a result of the Vatican having a small resident population, but millions of visitors every year, the state has the highest per capita crime rate of any nation on earth, more than twenty times higher than Italy. In his 2002 report to the pontifical court, Chief Prosecutor Nicola Picardi quoted statistics of 397 civil offences and 608 penal offences. Each year, hundreds of tourists fall victim to pickpockets and purse snatchers. The perpetrators, who are also visitors, are rarely caught, with 90% of crimes remaining unsolved."Vatican crime rate 'soars'".
Normally, for civil offenses the Italian courts will handle the disposition of these cases.
The most recent murder to occur in the Vatican was in 1998, when a member of the Swiss Guard killed two and then himself. [1]
Transport and communications

The Vatican City has no airports. There is one heliport and an 852 metre (932 yd) standard gauge (1435 mm) railway that connects to Italy's network at Rome's Saint Peter's station. The railway is used only to transport freight. Rome's metro line A passes about 10 minutes walk north of the Vatican.
The City is served by an independent, modern telephone system and post office. A bit of conventional wisdom in Rome is that international mail dropped in a mailbox in the Vatican will reach its destination more quickly than one dropped only a few hundred metres away in an Italian mailbox.[citation needed] People sending mail to the Vatican are advised not to write anything other than Vatican City State for the destination on the envelope. The reason for this is that this enables mail to be sent directly to the Vatican - otherwise it would go through the postal systems of other countries, which would cause a delay in shipment to the Vatican. The Vatican has an official website, radio station, and satellite TV channels.
See also
External links
- Template:Wikitravel
- Vatican City official website
- Vatican Philatelic Society Premier online source of information about Vatican City postage stamps
- History of Vatican City: Primary Documents
- Map of Vatican City
- stpetersbasilica.org Largest online source for St. Peter's in the Vatican
- Vaticano web
- Vatican City Itinerary
- The Vatican City on Google Maps.
- Detailed map of Vatican city
- Vatican City Photographs
- Vatican City, Piazza San Pietro VR panorama with map and compass effect by Tolomeus
- Vatican Secret Archive
- Large map of Vatican
- Vatican City and Geometric Art Interactive Panorama View
