Hepatitis B: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<!-- Cause --> |
<!-- Cause --> |
||
The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or [[body fluids]].<ref name=WHOfactsheet/> [[Perinatal infection|Infection around the time of birth]] is the most common way the disease is acquired in areas of the world where is common.<ref name=WHOfactsheet/> In areas |
The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or [[body fluids]].<ref name=WHOfactsheet/> [[Perinatal infection|Infection around the time of birth]] is the most common way the disease is acquired in areas of the world where is common.<ref name=WHOfactsheet/> In areas where the disease is uncommon [[intravenous drug use]] and sex are the most common routes of infection.<ref name=WHOfactsheet/> Other risk factors include working in a healthcare setting, [[blood transfusions]], [[dialysis]], sharing razors or toothbrushes with an infected person, travel in countries where it is common, and living in an institution.<ref name=WHOfactsheet/><ref>{{cite book|last=Sleisenger|first=MH|title=Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management|year=2006|publisher=Saunders|location=Philadelphia|edition=8th|author2=Feldman M |author3=Friedman LS }}</ref><ref name="CDC HBV Transmission">{{cite web|title=Hepatitis B FAQs for the Public — Transmission|url=http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/B/bFAQ.htm#transmission|publisher=U.S. [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]] (CDC) |accessdate=2011-11-29}}</ref> Tattooing and [[acupuncture]] led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility.<ref>{{cite book|first1=Howard c. Thomas|title=Viral Hepatitis|date=2013|publisher=Wiley|location=Hoboken|isbn=9781118637302|page=83|edition=4th ed.|url=http://books.google.ca/books?id=7aQeAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA83}}</ref> The {{nowrap|hepatitis B}} viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.<ref name="CDC HBV Transmission"/><ref name="PubMed Health">{{cite web|title=Hepatitis B|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001324|publisher=National Institute of Health|accessdate=2010-11-23}}</ref> The {{nowrap|hepatitis B}} virus is a [[hepadnavirus]]—''hepa'' from ''hepatotropic'' (attracted to the liver) and ''dna'' because it is a [[DNA virus]].<ref name=Baron/> The viruses [[Viral replication|replicate]] through an [[RNA]] intermediate form by [[reverse transcription]], which in practice [[pararetrovirus|relates them]] to [[retrovirus]]es.<ref name="pmid15192795"/> It is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.<ref>{{cite web | title = Understanding Hepatitis -- the Basics | publisher = WebMD | url =http://www.webmd.com/hepatitis/understanding-hepatitis-basics?page=2}}</ref> |
||
<!-- Prevention and Treatment --> |
<!-- Prevention and Treatment --> |
||
Revision as of 19:11, 18 September 2014
| Hepatitis B | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Infectious diseases |
Hepatitis B is an infectious illness of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that affects hominoidea, including humans. It was originally known as "serum hepatitis".[1] Many people have no symptoms during the initial infected.[2] Some develop an acute illness with vomiting, yellow skin, dark urine and abdominal pain.[2] Often these symptoms last a few weeks[2] and rarely result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin.[2] Less than 10% of those infected develop chronic hepatitis B.[2] In those with chronic disease cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop.[3]
The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids.[2] Infection around the time of birth is the most common way the disease is acquired in areas of the world where is common.[2] In areas where the disease is uncommon intravenous drug use and sex are the most common routes of infection.[2] Other risk factors include working in a healthcare setting, blood transfusions, dialysis, sharing razors or toothbrushes with an infected person, travel in countries where it is common, and living in an institution.[2][4][5] Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility.[6] The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.[5][7] The hepatitis B virus is a hepadnavirus—hepa from hepatotropic (attracted to the liver) and dna because it is a DNA virus.[8] The viruses replicate through an RNA intermediate form by reverse transcription, which in practice relates them to retroviruses.[9] It is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.[10]
The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982.[11][2] During the initial infected care is based on the symptoms present.[2] In those who developed chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however are expensive.[2]
About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives,[2] including 350 million who are chronic carriers.[12] Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B a year.[2] The disease has caused outbreaks in parts of Asia and Africa, and it is now only common in China.[13] Between 5 and 10% of adults in sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia have chronic disease.[2] Research is in progress to create edible HBV vaccines in foods such as potatoes, carrots, and bananas.
Signs and symptoms
Acute infection with hepatitis B virus is associated with acute viral hepatitis – an illness that begins with general ill-health, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, body aches, mild fever, and dark urine, and then progresses to development of jaundice. It has been noted that itchy skin has been an indication as a possible symptom of all hepatitis virus types. The illness lasts for a few weeks and then gradually improves in most affected people. A few people may have more severe liver disease (fulminant hepatic failure), and may die as a result. The infection may be entirely asymptomatic and may go unrecognized.[14]
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus either may be asymptomatic or may be associated with a chronic inflammation of the liver (chronic hepatitis), leading to cirrhosis over a period of several years. This type of infection dramatically increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). Across Europe hepatitis B and C cause approximately 50% of hepatocellular carcinomas.[15][16] Chronic carriers are encouraged to avoid consuming alcohol as it increases their risk for cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis B virus has been linked to the development of membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN).[17]
Symptoms outside of the liver are present in 1–10% of HBV-infected people and include serum-sickness–like syndrome, acute necrotizing vasculitis (polyarteritis nodosa), membranous glomerulonephritis, and papular acrodermatitis of childhood (Gianotti–Crosti syndrome).[18][19] The serum-sickness–like syndrome occurs in the setting of acute hepatitis B, often preceding the onset of jaundice.[20] The clinical features are fever, skin rash, and polyarteritis. The symptoms often subside shortly after the onset of jaundice, but can persist throughout the duration of acute hepatitis B.[21] About 30–50% of people with acute necrotizing vasculitis (polyarteritis nodosa) are HBV carriers.[22] HBV-associated nephropathy has been described in adults but is more common in children.[23][24] Membranous glomerulonephritis is the most common form.[21] Other immune-mediated hematological disorders, such as essential mixed cryoglobulinemia and aplastic anemia.[21]
Virology
Structure

Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a member of the hepadnavirus family.[8] The virus particle (virion) consists of an outer lipid envelope and an icosahedral nucleocapsid core composed of protein. These virions are 30-42 nm in diameter. The nucleocapsid encloses the viral DNA and a DNA polymerase that has reverse transcriptase activity.[9] The outer envelope contains embedded proteins that are involved in viral binding of, and entry into, susceptible cells. The virus is one of the smallest enveloped animal viruses, and the 42 nM virions, which are capable of infecting hepatocytes, are referred to as "Dane particles".[25] In addition to the Dane particles, filamentous and spherical bodies lacking a core can be found in the serum of infected individuals. These particles are not infectious and are composed of the lipid and protein that forms part of the surface of the virion, which is called the surface antigens (HBsAg), and is produced in excess during the life cycle of the virus.[26]
Genome
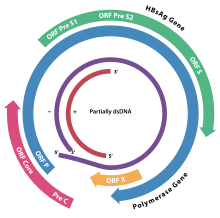
The genome of HBV is made of circular DNA, but it is unusual because the DNA is not fully double-stranded. One end of the full length strand is linked to the viral DNA polymerase. The genome is 3020–3320 nucleotides long (for the full-length strand) and 1700–2800 nucleotides long (for the short length-strand).[27] The negative-sense (non-coding) is complementary to the viral mRNA. The viral DNA is found in the nucleus soon after infection of the cell. The partially double-stranded DNA is rendered fully double-stranded by completion of the (+) sense strand and removal of a protein molecule from the (-) sense strand and a short sequence of RNA from the (+) sense strand. Non-coding bases are removed from the ends of the (-) sense strand and the ends are rejoined. There are four known genes encoded by the genome, called C, X, P, and S. The core protein is coded for by gene C (HBcAg), and its start codon is preceded by an upstream in-frame AUG start codon from which the pre-core protein is produced. HBeAg is produced by proteolytic processing of the pre-core protein. The DNA polymerase is encoded by gene P. Gene S is the gene that codes for the surface antigen (HBsAg). The HBsAg gene is one long open reading frame but contains three in frame "start" (ATG) codons that divide the gene into three sections, pre-S1, pre-S2, and S. Because of the multiple start codons, polypeptides of three different sizes called large, middle, and small (pre-S1 + pre-S2 + S, pre-S2 + S, or S) are produced.[28] The function of the protein coded for by gene X is not fully understood but it is associated with the development of liver cancer. It stimulates genes that promote cell growth and inactivates growth regulating molecules.[29]
Replication

The life cycle of hepatitis B virus is complex. Hepatitis B is one of a few known pararetroviruses: non-retroviruses that still use reverse transcription in their replication process. The virus gains entry into the cell by binding to NTCP [30] on the surface and being endocytosed. Because the virus multiplies via RNA made by a host enzyme, the viral genomic DNA has to be transferred to the cell nucleus by host proteins called chaperones. The partially double stranded viral DNA is then made fully double stranded and transformed into covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) that serves as a template for transcription of four viral mRNAs. The largest mRNA, (which is longer than the viral genome), is used to make the new copies of the genome and to make the capsid core protein and the viral DNA polymerase. These four viral transcripts undergo additional processing and go on to form progeny virions that are released from the cell or returned to the nucleus and re-cycled to produce even more copies.[28][31] The long mRNA is then transported back to the cytoplasm where the virion P protein (the DNA polymerase) synthesizes DNA via its reverse transcriptase activity.
Serotypes and genotypes
The virus is divided into four major serotypes (adr, adw, ayr, ayw) based on antigenic epitopes presented on its envelope proteins, and into eight genotypes (A-H) according to overall nucleotide sequence variation of the genome. The genotypes have a distinct geographical distribution and are used in tracing the evolution and transmission of the virus. Differences between genotypes affect the disease severity, course and likelihood of complications, and response to treatment and possibly vaccination.[32][33]
Genotypes differ by at least 8% of their sequence and were first reported in 1988 when six were initially described (A-F).[34] Two further types have since been described (G and H).[35] Most genotypes are now divided into subgenotypes with distinct properties.[36]
Mechanisms
Hepatitis B virus primarily interferes with the functions of the liver by replicating in liver cells, known as hepatocytes. A functional receptor is NTCP.[30] There is evidence that the receptor in the closely related duck hepatitis B virus is carboxypeptidase D.[37][38] The virions bind to the host cell via the preS domain of the viral surface antigen and are subsequently internalized by endocytosis. HBV-preS-specific receptors are expressed primarily on hepatocytes; however, viral DNA and proteins have also been detected in extrahepatic sites, suggesting that cellular receptors for HBV may also exist on extrahepatic cells.[39]
During HBV infection, the host immune response causes both hepatocellular damage and viral clearance. Although the innate immune response does not play a significant role in these processes, the adaptive immune response, in particular virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes(CTLs), contributes to most of the liver injury associated with HBV infection. CTLs eliminate HBV infection by killing infected cells and producing antiviral cytokines, which are then used to purge HBV from viable hepatocytes.[40] Although liver damage is initiated and mediated by the CTLs, antigen-nonspecific inflammatory cells can worsen CTL-induced immunopathology, and platelets activated at the site of infection may facilitate the accumulation of CTLs in the liver.[41]
Transmission
Transmission of hepatitis B virus results from exposure to infectious blood or body fluids containing blood. Possible forms of transmission include sexual contact,[42] blood transfusions and transfusion with other human blood products,[43] re-use of contaminated needles and syringes,[44] and vertical transmission from mother to child (MTCT) during childbirth. Without intervention, a mother who is positive for HBsAg confers a 20% risk of passing the infection to her offspring at the time of birth. This risk is as high as 90% if the mother is also positive for HBeAg. HBV can be transmitted between family members within households, possibly by contact of nonintact skin or mucous membrane with secretions or saliva containing HBV.[45] However, at least 30% of reported hepatitis B among adults cannot be associated with an identifiable risk factor.[46] And Shi et al. showed that breastfeeding after proper immunoprophylaxis did not contribute to MTCT of HBV.[47]
Diagnosis
The tests, called assays, for detection of hepatitis B virus infection involve serum or blood tests that detect either viral antigens (proteins produced by the virus) or antibodies produced by the host. Interpretation of these assays is complex.[48]
The hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is most frequently used to screen for the presence of this infection. It is the first detectable viral antigen to appear during infection. However, early in an infection, this antigen may not be present and it may be undetectable later in the infection as it is being cleared by the host. The infectious virion contains an inner "core particle" enclosing viral genome. The icosahedral core particle is made of 180 or 240 copies of core protein, alternatively known as hepatitis B core antigen, or HBcAg. During this 'window' in which the host remains infected but is successfully clearing the virus, IgM antibodies specific to the hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc IgM) may be the only serological evidence of disease. Therefore most hepatitis B diagnostic panels contain HBsAg and total anti-HBc (both IgM and IgG).[49]
Shortly after the appearance of the HBsAg, another antigen called hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) will appear. Traditionally, the presence of HBeAg in a host's serum is associated with much higher rates of viral replication and enhanced infectivity; however, variants of the hepatitis B virus do not produce the 'e' antigen, so this rule does not always hold true.[50] During the natural course of an infection, the HBeAg may be cleared, and antibodies to the 'e' antigen (anti-HBe) will arise immediately afterwards. This conversion is usually associated with a dramatic decline in viral replication.

If the host is able to clear the infection, eventually the HBsAg will become undetectable and will be followed by IgG antibodies to the hepatitis B surface antigen and core antigen (anti-HBs and anti HBc IgG).[8] The time between the removal of the HBsAg and the appearance of anti-HBs is called the window period. A person negative for HBsAg but positive for anti-HBs either has cleared an infection or has been vaccinated previously.
Individuals who remain HBsAg positive for at least six months are considered to be hepatitis B carriers.[51] Carriers of the virus may have chronic hepatitis B, which would be reflected by elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels and inflammation of the liver, if they are in the immune clearance phase of chronic infection. Carriers who have seroconverted to HBeAg negative status, in particular those who acquired the infection as adults, have very little viral multiplication and hence may be at little risk of long-term complications or of transmitting infection to others.[52]
PCR tests have been developed to detect and measure the amount of HBV DNA, called the viral load, in clinical specimens. These tests are used to assess a person's infection status and to monitor treatment.[53] Individuals with high viral loads, characteristically have ground glass hepatocytes on biopsy.
Prevention
Vaccines for the prevention of hepatitis B have been routinely recommended for infants since 1991 in the United States.[54] Most vaccines are given in three doses over a course of months. A protective response to the vaccine is defined as an anti-HBs antibody concentration of at least 10 mIU/ml in the recipient's serum. The vaccine is more effective in children and 95 percent of those vaccinated have protective levels of antibody. This drops to around 90% at 40 years of age and to around 75 percent in those over 60 years. The protection afforded by vaccination is long lasting even after antibody levels fall below 10 mIU/ml. Vaccination at birth is recommended for all infants of HBV infected mothers. A combination of hepatitis B immune globulin and an accelerated course of HBV vaccine prevents perinatal HBV transmission in around 90% of cases.[55]
All those with a risk of exposure to body fluids such as blood should be vaccinated, if not already.[54] Testing to verify effective immunization is recommended and further doses of vaccine are given to those who are not sufficiently immunized.[54]
In assisted reproductive technology, sperm washing is not necessary for males with hepatitis B to prevent transmission, unless the female partner has not been effectively vaccinated.[56] In females with hepatitis B, the risk of transmission from mother to child with IVF is no different from the risk in spontaneous conception.[56]
Those at high risk of infection should be tested as there is effective treatment for those who have the disease.[57] Groups that screening is recommended for include those who have not been vaccinated and one of the following: people from areas of the world where hepatitis B occurs in more than 2%, those with HIV, intravenous drug users, men who have sex with men, and those who live with someone with hepatitis B.[57]
Treatment
Acute hepatitis B infection does not usually require treatment and most adults clear the infection spontaneously.[58][59] Early antiviral treatment may be required in fewer than 1% of people, whose infection takes a very aggressive course (fulminant hepatitis) or who are immunocompromised. On the other hand, treatment of chronic infection may be necessary to reduce the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Chronically infected individuals with persistently elevated serum alanine aminotransferase, a marker of liver damage, and HBV DNA levels are candidates for therapy.[60] Treatment lasts from six months to a year, depending on medication and genotype.[61]
Although none of the available drugs can clear the infection, they can stop the virus from replicating, thus minimizing liver damage. As of 2008, there are seven medications licensed for treatment of hepatitis B infection in the United States. These include antiviral drugs lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera), tenofovir (Viread), telbivudine (Tyzeka) and entecavir (Baraclude), and the two immune system modulators interferon alpha-2a and PEGylated interferon alpha-2a (Pegasys). The use of interferon, which requires injections daily or thrice weekly, has been supplanted by long-acting PEGylated interferon, which is injected only once weekly.[62] However, some individuals are much more likely to respond than others, and this might be because of the genotype of the infecting virus or the person's heredity. The treatment reduces viral replication in the liver, thereby reducing the viral load (the amount of virus particles as measured in the blood).[63] Response to treatment differs between the genotypes. Interferon treatment may produce an e antigen seroconversion rate of 37% in genotype A but only a 6% seroconversion in type D. Genotype B has similar seroconversion rates to type A while type C seroconverts only in 15% of cases. Sustained e antigen loss after treatment is ~45% in types A and B but only 25–30% in types C and D.[64]
Prognosis

Hepatitis B virus infection may be either acute (self-limiting) or chronic (long-standing). Persons with self-limiting infection clear the infection spontaneously within weeks to months.
Children are less likely than adults to clear the infection. More than 95% of people who become infected as adults or older children will stage a full recovery and develop protective immunity to the virus. However, this drops to 30% for younger children, and only 5% of newborns that acquire the infection from their mother at birth will clear the infection.[65] This population has a 40% lifetime risk of death from cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.[62] Of those infected between the age of one to six, 70% will clear the infection.[66]
Hepatitis D (HDV) can occur only with a concomitant hepatitis B infection, because HDV uses the HBV surface antigen to form a capsid.[67] Co-infection with hepatitis D increases the risk of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.[68] Polyarteritis nodosa is more common in people with hepatitis B infection.
Reactivation
Hepatitis B virus DNA persists in the body after infection, and in some people the disease recurs.[69] Although rare, reactivation is seen most often following alcohol or drug use,[70] or in people with impaired immunity.[71] HBV goes through cycles of replication and non-replication. Approximately 50% of overt carriers experience acute reactivation. Males with baseline ALT of 200 UL/L are three times more likely to develop a reactivation than people with lower levels. Although reactivation can occur spontaneously,[72] people who undergo chemotherapy have a higher risk.[73] Immunosuppressive drugs favor increased HBV replication while inhibiting cytotoxic T cell function in the liver.[74] The risk of reactivation varies depending on the serological profile; those with detectable HBsAg in their blood are at the greatest risk, but those with only antibodies to the core antigen are also at risk. The presence of antibodies to the surface antigen, which are considered to be a marker of immunity, does not preclude reactivation.[73] Treatment with prophylactic antiviral drugs can prevent the serious morbidity associated with HBV disease reactivation.[73]
Epidemiology

In 2004, an estimated 350 million individuals were infected worldwide. National and regional prevalence ranges from over 10% in Asia to under 0.5% in the United States and northern Europe.
Routes of infection include vertical transmission (such as through childbirth), early life horizontal transmission (bites, lesions, and sanitary habits), and adult horizontal transmission (sexual contact, intravenous drug use).[75]
The primary method of transmission reflects the prevalence of chronic HBV infection in a given area. In low prevalence areas such as the continental United States and Western Europe, injection drug abuse and unprotected sex are the primary methods, although other factors may also be important.[76] In moderate prevalence areas, which include Eastern Europe, Russia, and Japan, where 2–7% of the population is chronically infected, the disease is predominantly spread among children. In high-prevalence areas such as China and South East Asia, transmission during childbirth is most common, although in other areas of high endemicity such as Africa, transmission during childhood is a significant factor.[77] The prevalence of chronic HBV infection in areas of high endemicity is at least 8% with 10-15% prevalence in Africa/Far East.[78] As of 2010, China has 120 million infected people, followed by India and Indonesia with 40 million and 12 million, respectively. According to World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 600,000 people die every year related to the infection.[79]
In the United States about 19,000 new cases occurred in 2011 down nearly 90% from 1990.[54]
History
The earliest record of an epidemic caused by hepatitis B virus was made by Lurman in 1885.[80] An outbreak of smallpox occurred in Bremen in 1883 and 1,289 shipyard employees were vaccinated with lymph from other people. After several weeks, and up to eight months later, 191 of the vaccinated workers became ill with jaundice and were diagnosed as suffering from serum hepatitis. Other employees who had been inoculated with different batches of lymph remained healthy. Lurman's paper, now regarded as a classical example of an epidemiological study, proved that contaminated lymph was the source of the outbreak. Later, numerous similar outbreaks were reported following the introduction, in 1909, of hypodermic needles that were used, and, more importantly, reused, for administering Salvarsan for the treatment of syphilis. The virus was not discovered until 1966 when Baruch Blumberg, then working at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), discovered the Australia antigen (later known to be hepatitis B surface antigen, or HBsAg) in the blood of Australian aboriginal people.[81] Although a virus had been suspected since the research published by MacCallum in 1947,[82] D.S. Dane and others discovered the virus particle in 1970 by electron microscopy.[83] By the early 1980s the genome of the virus had been sequenced,[84] and the first vaccines were being tested.[85]
Society and culture
World Hepatitis Day, observed July 28, aims to raise global awareness of hepatitis B and hepatitis C and encourage prevention, diagnosis and treatment. It has been led by the World Hepatitis Alliance since 2007 and in May 2010, it got global endorsement from the World Health Organization.[86]
References
- ^ Barker LF, Shulman NR, Murray R, Hirschman RJ, Ratner F, Diefenbach WC, Geller HM (1996). "Transmission of serum hepatitis. 1970". Journal of the American Medical Association. 276 (10): 841–844. doi:10.1001/jama.276.10.841. PMID 8769597.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Hepatitis B". World Health Organization (WHO). Retrieved 19 September 2009.
- ^ Chang MH (June 2007). "Hepatitis B virus infection". Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 12 (3): 160–167. doi:10.1016/j.siny.2007.01.013. PMID 17336170.
- ^ Sleisenger, MH; Feldman M; Friedman LS (2006). Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders.
- ^ a b "Hepatitis B FAQs for the Public — Transmission". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved 29 November 2011.
- ^ Viral Hepatitis (4th ed. ed.). Hoboken: Wiley. 2013. p. 83. ISBN 9781118637302.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first1=missing|last1=(help) - ^ "Hepatitis B". National Institute of Health. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ a b c Zuckerman AJ (1996). "Hepatitis Viruses". In Baron S; et al. (eds.). Baron's Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). University of Texas Medical Branch. ISBN 0-9631172-1-1.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|editor=(help) - ^ a b Locarnini S (2004). "Molecular Virology of Hepatitis B Virus". Seminars in Liver Disease. 24: 3–10. doi:10.1055/s-2004-828672. PMID 15192795.
- ^ "Understanding Hepatitis -- the Basics". WebMD.
- ^ Pungpapong S, Kim WR, Poterucha JJ (2007). "Natural History of Hepatitis B Virus Infection: an Update for Clinicians". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 82 (8): 967–975. doi:10.4065/82.8.967. PMID 17673066.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Schilsky ML (2013). "Hepatitis B "360"". Transplantation Proceedings. 45 (3): 982–985. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.02.099. PMID 23622604.
- ^ Williams R (2006). "Global challenges in liver disease". Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 44 (3): 521–526. doi:10.1002/hep.21347. PMID 16941687.
- ^ Terrault N, Roche B, Samuel D (July 2005). "Management of the hepatitis B virus in the liver transplantation setting: a European and an American perspective". Liver Transpl. 11 (7): 716–32. doi:10.1002/lt.20492. PMID 15973718.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL (June 2007). "Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis". Gastroenterology. 132 (7): 2557–76. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.061. PMID 17570226.
- ^ El-Serag HB (22 September 2011). "Hepatocellular carcinoma". New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (12): 1118–27. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001683. PMID 21992124.
- ^ Gan SI, Devlin SM, Scott-Douglas NW, Burak KW (October 2005). "Lamivudine for the treatment of membranous glomerulopathy secondary to chronic hepatitis B infection". Canadian journal of gastroenterology = Journal canadien de gastroenterologie. 19 (10): 625–9. PMID 16247526.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dienstag JL (February 1981). "Hepatitis B as an immune complex disease". Seminars in Liver Disease. 1 (1): 45–57. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1063929. PMID 6126007.
- ^ Trepo C, Guillevin L (May 2001). "Polyarteritis nodosa and extrahepatic manifestations of HBV infection: the case against autoimmune intervention in pathogenesis". Journal of Autoimmunity. 16 (3): 269–74. doi:10.1006/jaut.2000.0502. PMID 11334492.
- ^ Alpert E, Isselbacher KJ, Schur PH (July 1971). "The pathogenesis of arthritis associated with viral hepatitis. Complement-component studies". The New England Journal of Medicine. 285 (4): 185–9. doi:10.1056/NEJM197107222850401. PMID 4996611.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Liang TJ (May 2009). "Hepatitis B: the virus and disease". Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 49 (5 Suppl): S13–21. doi:10.1002/hep.22881. PMC 2809016. PMID 19399811.
- ^ Gocke DJ, Hsu K, Morgan C, Bombardieri S, Lockshin M, Christian CL (December 1970). "Association between polyarteritis and Australia antigen". Lancet. 2 (7684): 1149–53. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(70)90339-9. PMID 4098431.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lai KN, Li PK, Lui SF, Au TC, Tam JS, Tong KL, Lai FM (May 1991). "Membranous nephropathy related to hepatitis B virus in adults". The New England Journal of Medicine. 324 (21): 1457–63. doi:10.1056/NEJM199105233242103. PMID 2023605.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Takekoshi Y, Tanaka M, Shida N, Satake Y, Saheki Y, Matsumoto S (November 1978). "Strong association between membranous nephropathy and hepatitis-B surface antigenaemia in Japanese children". Lancet. 2 (8099): 1065–8. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(78)91801-9. PMID 82085.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Harrison T (2009). Desk Encyclopedia of General Virology. Boston: Academic Press. p. 455. ISBN 0-12-375146-2.
- ^ Howard CR (1986). "The Biology of Hepadnaviruses". Journal of General Virology. 67 (7): 1215–1235. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1215. PMID 3014045.
- ^ Kay A, Zoulim F (2007). "Hepatitis B virus genetic variability and evolution". Virus research. 127 (2): 164–176. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.021. PMID 17383765.
- ^ a b Beck J, Nassal M (January 2007). "Hepatitis B virus replication". World J. Gastroenterol. 13 (1): 48–64. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48. PMID 17206754.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Li W, Miao X, Qi Z, Zeng W, Liang J, Liang Z (2010). "Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates HSP90alpha expression via activation of c-Myc in human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2". Virol. J. 7: 45. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-7-45. PMC 2841080. PMID 20170530.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G, He W, Jing Z, Gao Z, Huang Y, Qi Y, Peng B, Wang H, Fu L, Song M, Chen P, Gao W, Ren B, Sun Y, Cai T, Feng X, Sui J, Li W (2012). "Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus". ELife. 1: e00049. doi:10.7554/eLife.00049. PMC 3485615. PMID 23150796.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bruss V (January 2007). "Hepatitis B virus morphogenesis". World J. Gastroenterol. 13 (1): 65–73. PMID 17206755.
- ^ Kramvis A, Kew M, François G (March 2005). "Hepatitis B virus genotypes". Vaccine. 23 (19): 2409–23. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.10.045. PMID 15752827.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Magnius LO, Norder H (1995). "Subtypes, genotypes and molecular epidemiology of the hepatitis B virus as reflected by sequence variability of the S-gene". Intervirology. 38 (1–2): 24–34. PMID 8666521.
- ^ Norder H, Couroucé AM, Magnius LO (1994). "Complete genomes, phylogenic relatedness and structural proteins of six strains of the hepatitis B virus, four of which represent two new genotypes". Virology. 198 (2): 489–503. doi:10.1006/viro.1994.1060. PMID 8291231.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Shibayama T, Masuda G, Ajisawa A, Hiruma K, Tsuda F, Nishizawa T, Takahashi M, Okamoto H (May 2005). "Characterization of seven genotypes (A to E, G and H) of hepatitis B virus recovered from Japanese patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1". Journal of Medical Virology. 76 (1): 24–32. doi:10.1002/jmv.20319. PMID 15779062.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Schaefer S (January 2007). "Hepatitis B virus taxonomy and hepatitis B virus genotypes". World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG. 13 (1): 14–21. PMID 17206751.
- ^ Tong S, Li J, Wands JR (1999). "Carboxypeptidase D is an avian hepatitis B virus receptor" (PDF). Journal of Virology. 73 (10): 8696–8702. PMC 112890. PMID 10482623.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Glebe D, Urban S (January 2007). "Viral and cellular determinants involved in hepadnaviral entry". World J. Gastroenterol. 13 (1): 22–38. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.22. PMID 17206752.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Coffin CS, Mulrooney-Cousins PM, van Marle G, Roberts JP, Michalak TI, Terrault NA (April 2011). "Hepatitis B virus (HBV) quasispecies in hepatic and extrahepatic viral reservoirs in liver transplant recipients on prophylactic therapy". Liver Transpl. 17 (8): 955–62. doi:10.1002/lt.22312. PMID 21462295.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Iannacone M, Sitia G, Ruggeri ZM, Guidotti LG (2007). "HBV pathogenesis in animal models: Recent advances on the role of platelets". Journal of Hepatology. 46 (4): 719–726. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2007.01.007. PMC 1892635. PMID 17316876.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Iannacone M, Sitia G, Isogawa M, Marchese P, Castro MG, Lowenstein PR, Chisari FV, Ruggeri ZM, Guidotti LG (November 2005). "Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage". Nat. Med. 11 (11): 1167–9. doi:10.1038/nm1317. PMC 2908083. PMID 16258538.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fairley CK, Read TR (February 2012). "Vaccination against sexually transmitted infections". Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 25 (1): 66–72. doi:10.1097/QCO.0b013e32834e9aeb. PMID 22143117.
- ^ Buddeberg F, Schimmer BB, Spahn DR (September 2008). "Transfusion-transmissible infections and transfusion-related immunomodulation". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Anaesthesiology. 22 (3): 503–17. doi:10.1016/j.bpa.2008.05.003. PMID 18831300.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hughes RA (March 2000). "Drug injectors and the cleaning of needles and syringes". European Addiction Research. 6 (1): 20–30. doi:10.1159/000019005. PMID 10729739.
- ^ "Hepatitis B – the facts: IDEAS –Victorian Government Health Information, Australia". State of Victoria. 28 July 2009. Retrieved 19 September 2009.
- ^ Shapiro CN (May 1993). "Epidemiology of hepatitis B". Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 12 (5): 433–437. doi:10.1097/00006454-199305000-00036. PMID 8392167.
- ^ Shi Z, Yang Y, Wang H, Ma L, Schreiber A, Li X, Sun W, Zhao X, Yang X, Zhang L, Lu W, Teng J, An Y (2011). "Breastfeeding of Newborns by Mothers Carrying Hepatitis B Virus: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review". Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 165 (9): 837–846. doi:10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.72. PMID 21536948.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bonino F, Chiaberge E, Maran E, Piantino P (1987). "Serological markers of HBV infectivity". Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita. 24 (2): 217–23. PMID 3331068.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Karayiannis P, Thomas HC (2009). Desk Encyclopedia of Human and Medical Virology. Boston: Academic Press. p. 110. ISBN 0-12-375147-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Liaw YF, Brunetto MR, Hadziyannis S (2010). "The natural history of chronic HBV infection and geographical differences". Antiviral Therapy. 15: 25–33. doi:10.3851/IMP1621. PMID 21041901.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lok AS, McMahon BJ (February 2007). "Chronic hepatitis B". Hepatology. 45 (2): 507–39. doi:10.1002/hep.21513. PMID 17256718.
- ^ Chu CM, Liaw YF (November 2007). "Predictive factors for reactivation of hepatitis B following hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B". Gastroenterology. 133 (5): 1458–65. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.039. PMID 17935720.
- ^ Zoulim F (November 2006). "New nucleic acid diagnostic tests in viral hepatitis". Semin. Liver Dis. 26 (4): 309–317. doi:10.1055/s-2006-951602. PMID 17051445.
- ^ a b c d Schillie S, Murphy TV, Sawyer M, Ly K, Hughes E, Jiles R, de Perio MA, Reilly M, Byrd K, Ward JW (20 December 2013). "CDC Guidance for Evaluating Health-Care Personnel for Hepatitis B Virus Protection and for Administering Postexposure Management". MMWR. Recommendations and reports : Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Recommendations and reports / Centers for Disease Control. 62 (RR-10): 1–19. PMID 24352112.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Aspinall EJ, Hawkins G, Fraser A, Hutchinson SJ, Goldberg D (December 2011). "Hepatitis B prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care: a review". Occupational medicine (Oxford, England). 61 (8): 531–40. doi:10.1093/occmed/kqr136. PMID 22114089.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Lutgens SP, Nelissen EC, van Loo IH, Koek GH, Derhaag JG, Dunselman GA (22 July 2009). "To do or not to do: IVF and ICSI in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers". Human Reproduction. 24 (11): 2676–8. doi:10.1093/humrep/dep258. PMID 19625309.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b LeFevre, ML (27 May 2014). "Screening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement". Annals of internal medicine. 161 (1): 58–66. doi:10.7326/M14-1018. PMID 24863637.
- ^ Hollinger FB, Lau DT. Hepatitis B: the pathway to recovery through treatment. Gastroenterology Clinics of North America. 2006;35(4):895–931. doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2006.10.002. PMID 17129820.(registration required)
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HBV/HBVfaq.htm#treatment
- ^ Lai CL, Yuen MF. The natural history and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a critical evaluation of standard treatment criteria and end points. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2007;147(1):58–61. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-147-1-200707030-00010. PMID 17606962.
- ^ Alberti A, Caporaso N (January 2011). "HBV therapy: guidelines and open issues". Digestive and Liver Disease : Official Journal of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver. 43 (Suppl 1): S57–63. doi:10.1016/S1590-8658(10)60693-7. PMID 21195373.
- ^ a b Dienstag JL (2008). "Hepatitis B Virus Infection". New England Journal of Medicine. 359 (14): 1486–1500. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0801644. PMID 18832247.
- ^ Pramoolsinsup C. Management of viral hepatitis B. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2002;17(Suppl):S125–45. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1746.17.s1.3.x. PMID 12000599.(subscription required)
- ^ Cao GW. Clinical relevance and public health significance of hepatitis B virus genomic variations. World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG. 2009;15(46):5761–9. doi:10.3748/wjg.15.5761. PMID 19998495. PMC 2791267.
- ^ Bell SJ, Nguyen T (2009). "The management of hepatitis B" (PDF). Aust Prescr. 23 (4): 99–104.[dead link] [dead link]
- ^ Kerkar N (2005). "Hepatitis B in children: complexities in management". Pediatric transplantation. 9 (5): 685–691. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3046.2005.00393.x. PMID 16176431.
- ^ Taylor JM (2006). "Hepatitis delta virus". Virology. 344 (1): 71–76. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2005.09.033. PMID 16364738.
- ^ Oliveri F, Brunetto MR, Actis GC, Bonino F (November 1991). "Pathobiology of chronic hepatitis virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)". Ital J Gastroenterol. 23 (8): 498–502. PMID 1661197.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vierling JM (November 2007). "The immunology of hepatitis B". Clin Liver Dis. 11 (4): 727–759, vii–759. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2007.08.001. PMID 17981227.
- ^ Villa E, Fattovich G, Mauro A, Pasino M (January 2011). "Natural history of chronic HBV infection: special emphasis on the prognostic implications of the inactive carrier state versus chronic hepatitis". Digestive and Liver Disease : Official Journal of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver. 43 (Suppl 1): S8–14. doi:10.1016/S1590-8658(10)60686-X. PMID 21195374.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Katz LH, Fraser A, Gafter-Gvili A, Leibovici L, Tur-Kaspa R (February 2008). "Lamivudine prevents reactivation of hepatitis B and reduces mortality in immunosuppressed patients: systematic review and meta-analysis". J. Viral Hepat. 15 (2): 89–102. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2007.00902.x. PMID 18184191.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Roche B, Samuel D (January 2011). "The difficulties of managing severe hepatitis B virus reactivation". Liver International : Official Journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 31 (Suppl 1): 104–10. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02396.x. PMID 21205146.
- ^ a b c Mastroianni CM, Lichtner M, Citton R, Del Borgo C, Rago A, Martini H, Cimino G, Vullo V (September 2011). "Current trends in management of hepatitis B virus reactivation in the biologic therapy era". World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG. 17 (34): 3881–7. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3881. PMC 3198017. PMID 22025876.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bonacini, Maurizio, MD. "Hepatitis B Reactivation". University of Southern California Department of Surgery. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)[dead link] [dead link] - ^ Custer B, Sullivan SD, Hazlet TK, Iloeje U, Veenstra DL, Kowdley KV (November–December 2004). "Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus". Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 38 (10 Suppl 3): S158–68. doi:10.1097/00004836-200411003-00008. PMID 15602165.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Redd JT, Baumbach J, Kohn W, Nainan O, Khristova M, Williams I (May 2007). "Patient-to-patient transmission of hepatitis B virus associated with oral surgery". J. Infect. Dis. 195 (9): 1311–4. doi:10.1086/513435. PMID 17397000.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Alter MJ (2003). "Epidemiology and prevention of hepatitis B". Seminars in liver disease. 23 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1055/s-2003-37583. PMID 12616449.
- ^ Komas NP, Vickos U, Hübschen JM, Béré A, Manirakiza A, Muller CP, Le Faou A (1 January 2013). "Cross-sectional study of hepatitis B virus infection in rural communities, Central African Republic". BMC Infectious Diseases. 13: 286. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-286. PMC 3694350. PMID 23800310.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Healthcare stumbling in RI's Hepatitis fight". The Jakarta Post. 13 January 2011.
- ^ Lurman A (1885). "Eine icterus epidemic". Berl Klin Woschenschr (in German). 22: 20–3.
- ^ Alter HJ, Blumberg BS (March 1966). "Further studies on a "new" human isoprecipitin system (Australia antigen)". Blood. 27 (3): 297–309. PMID 5930797.
- ^ MacCallum FO (1947). "Homologous serum hepatitis". Lancet. 2.
- ^ Dane DS, Cameron CH, Briggs M (April 1970). "Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis". Lancet. 1 (7649): 695–8. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(70)90926-8. PMID 4190997.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Galibert F, Mandart E, Fitoussi F, Tiollais P, Charnay P (October 1979). "Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli". Nature. 281 (5733): 646–50. Bibcode:1979Natur.281..646G. doi:10.1038/281646a0. PMID 399327.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Hepatitis B vaccine". Lancet. 2 (8206): 1229–1230. December 1980. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(80)92484-8. PMID 6108398.
- ^ "Viral hepatitis" (PDF).
External links
- "Hepatitis B virus". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 10407.


