2-Ethoxyethanol: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
add to chembox |
add LC50 and LD50 |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| IDLH = 500 ppm<ref name=PGCH/> |
| IDLH = 500 ppm<ref name=PGCH/> |
||
| REL = TWA 0.5 ppm (1.8 mg/m<sup>3</sup>) [skin]<ref name=PGCH/> |
| REL = TWA 0.5 ppm (1.8 mg/m<sup>3</sup>) [skin]<ref name=PGCH/> |
||
| LC50 = 2000 ppm (rat, 7 hr)<br/>1820 ppm (mouse, 7 hr)<ref name=IDLH>{{IDLH|110805|2-Ethoxyethanol}}</ref> |
|||
| LD50 = 2451 mg/kg (mouse, oral)<br/>2125 mg/kg (rat, oral)<ref name=IDLH/> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
||
Revision as of 17:50, 15 June 2015
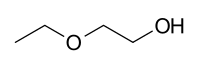
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-ethoxyethanol
| |
| Other names
Cellosolve
ethylene glycol ethyl ether oxitol Ethyl Cellosolve EGEE | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.459 |
| KEGG | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 90.122 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | clear liquid |
| Odor | sweet, ether-like |
| Density | 0.930 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −70 °C (−94 °F; 203 K) |
| Boiling point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K) |
| miscible | |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 44 °C (111 °F; 317 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.7%-15.6%[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2451 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 2125 mg/kg (rat, oral)[2] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
2000 ppm (rat, 7 hr) 1820 ppm (mouse, 7 hr)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 200 ppm (740 mg/m3) [skin][1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.5 ppm (1.8 mg/m3) [skin][1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 ppm[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2-Ethoxyethanol, also known by the trademark Cellosolve or ethyl cellosolve, is a solvent used widely in commercial and industrial applications. It is a clear, colorless, nearly odorless liquid that is miscible with water, ethanol, diethyl ether, acetone, and ethyl acetate.[3]
2-Ethoxyethanol can be manufactured by the reaction of ethylene oxide with ethanol.
As with other glycol ethers, 2-ethoxyethanol has the useful property of being able to dissolve chemically diverse compounds. It will dissolve oils, resins, grease, waxes, nitrocellulose, and lacquers.[3] This is an ideal property as a multi-purpose cleaner, and, therefore, 2-ethoxyethanol is used in products, such as varnish removers and degreasing solutions.
References
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0258". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "2-Ethoxyethanol". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b National Research Council (U.S.). Subcommittee on Spacecraft Maximum Allowable Concentrations (1996). Spacecraft maximum allowable concentrations for selected airborne contaminants. National Academies Press. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-309-05478-2. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
External links
- "Chemical Sampling Information 2-Ethoxyethanol". www.osha.gov. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards

