Danish overseas colonies: Difference between revisions
Tag: blanking |
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by 82.143.69.98 to version by LiamKasbar. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (2973549) (Bot) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
Today, the only remaining vestiges of this empire are two originally Norwegian colonies that are currently within the [[Danish Realm]], the [[Faroe Islands]] and [[Greenland]]; the Faroes were a Danish county until 1948, while Greenland's colonial status ceased in 1953. They are now autonomous countries of the Kingdom of Denmark with [[home rule]], in a relationship referred to as the "[[Unity of the Realm]]". |
Today, the only remaining vestiges of this empire are two originally Norwegian colonies that are currently within the [[Danish Realm]], the [[Faroe Islands]] and [[Greenland]]; the Faroes were a Danish county until 1948, while Greenland's colonial status ceased in 1953. They are now autonomous countries of the Kingdom of Denmark with [[home rule]], in a relationship referred to as the "[[Unity of the Realm]]". |
||
==Overview== |
|||
dkejfhibi;vbsefkjawibvhDa;kdfbvbc AebhfwebABebwe dcQE wrgw aer |
|||
===Africa=== |
|||
{{main article|Danish Gold Coast}} |
|||
[[File:Christiansborg Castle2.jpg|250px|thumb|A contemporary depiction of Fort Christiansborg]] |
|||
Denmark maintained several tradings stations and four forts on the [[Gold Coast (British colony)|Gold Coast]] in west Africa, especially around modern day [[Ghana]]. Three trading stations were built:<ref name="Dictionary">{{cite book |editor1-first=James Stuart |editor1-last=Olson |editor2-first=Robert |editor2-last=Shadle |year=1991 |title=Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uyqepNdgUWkC&pg=PA167&lpg=PA167|accessdate=September 4, 2012}}</ref> [[Fort Frederiksborg]], Kpompo; [[Osu Castle]] by [[Accra]] in 1661, that was purchased from Sweden; and Frederiksberg. The forts were [[Fort Prinsensten]] built in 1784, [[Fort Augustaborg]] from 1787, Fort Friedensborg and Fort Kongensten, several of which are ruins today. Of these, only one is still used today, Fort Christiansborg, which is the Ghanaian president's residence in Ghana. |
|||
Plantations were established by Frederiksborg, but they failed. Fort Christiansborg became the base for Danish power in west Africa, and the centre for slave trade to the Danish West Indies. In 1807, Denmark's African business partners were suppressed by the [[Akan people]] subgroup-[[Ashanti people|Ashanti]], which led to the abandonment of all trading stations. Denmark sold its forts to the United Kingdom in 1850. |
|||
===Americas=== |
|||
{{main article|Danish colonization of the Americas}} |
|||
[[File:Høgensborg, Plantation, St. Croix, Danish West Indies.jpg|thumb|The Høgensborg estate on St. Croix, [[Danish West Indies]], 1833]] |
|||
====Greenland==== |
|||
{{main article|History of Greenland|Royal Greenland Trade Department|}} |
|||
With the ratification of the [[Kalmar Union]] in 1397, [[Denmark-Norway]] inherited [[Greenland]] which was previously part of [[Norway]] since its settlement in the [[Viking Age]]. After the [[Norsemen|Norse]] [[Norse colonization of the Americas|settlement in Greenland]] finally disappeared in the 15th century, Europeans did not settle the island again until 1721, when the [[Lutheran]] minister [[Hans Egede]] arrived and established the town now known as [[Nuuk]]. After Norway was ceded to [[Sweden]] in 1814 following the [[Napoleonic Wars]], Denmark retained the old territorial claims as a condition of the [[Treaty of Kiel]]. |
|||
The development and settlement of Greenland accelerated in 1945, instigated by the region's geostrategic importance in [[the Cold War]] era, itself exemplified and manifested by the US-Air base of [[Thule Air Base|Thule]] from 1943. Another reason and driving force was the emergence of fundamental technical abilities, such as aircraft and [[icebreakers]] at Greenland's disposition, giving the otherwise remote island a supply situation somewhat similar to Europe. |
|||
====Danish West Indies==== |
|||
{{main article|Danish West Indies|Danish West India Company}} |
|||
Denmark-Norway acquired the island of [[Saint Thomas, United States Virgin Islands|St. Thomas]] in 1671<ref name="Dictionary" /> and [[Saint John, U.S. Virgin Islands|St. Jan]] (now St. John) in 1718, and bought [[St. Croix]] from [[France]] in 1733. All of the islands' economies were based primarily on [[sugar]]. These islands were known as the [[Danish West Indies]] and were eventually sold to the [[United States]] in 1917 for 25 million dollars.<ref name="Dictionary" /> Several Danish-American succession talks had been made since 1870 due to a rising amount of riots and unrest from the poorer English speaking population. The Zahle Government (1914-1920) held a heavily boycotted election for Danish mainland constituencies, which produced a minority for the sale of the islands. The United States hoped to use them as naval bases. Since 1917, the islands have been known as the [[U.S. Virgin Islands]]. |
|||
===Asia=== |
|||
{{main article|Danish India|Danish East India Company}} |
|||
[[Image:European settlements in India 1501-1739.png|thumb|300px|Danish and other European settlements in India.]] |
|||
[[File:A view of Tranquebar - Google Art Project.jpg|250px|thumb|[[Fort Dansborg]] at Tranquebar, built by [[Ove Gjedde]], c. 1658]] |
|||
Denmark maintained a scattering of small colonies and trading posts throughout the Indian sub-continent from the 17th to 19th centuries, after which most were sold or ceded to Britain which had become the dominant power there.<ref name="Dictionary" /> The most important economic aspect was [[spice trade]] and access to the east Asian area, including [[Imperial era of Chinese history|Imperial China]] situated farther to the east. |
|||
The colony at {{lang|da|''Trankebar''}} (modern day: [[Tharangambadi]]) was kept for over 200 years, with a few interruptions, until it was sold to the British in 1845. |
|||
In 1755 Denmark acquired the {{lang|da|''Frederiksnagore''}} (now [[Serampore]]), and later the towns of Achne and Pirapur. They are located about 25 kilometres north of [[Calcutta]]. In 1818 [[Serampore College]] was established in Serampore, which still exists today. These towns were also sold to Britain in 1845. Other colonial ventures include colonization attempts of the [[Nicobar Islands]], called {{lang|da|''Frederiksøerne''}} ("Frederik Islands") or {{lang|da|''Ny Danmark''}} ("New Denmark") by the Danes between 1754 and 1868. |
|||
===Atlantic=== |
|||
====Faroe Islands==== |
|||
{{main article|History of the Faroe Islands}} |
|||
As with Greenland, Denmark-Norway inherited the medieval Norwegian claims to the [[Faroe Islands]] as the successor state to Norway. The Faroes had become part of the Kingdom of Norway in 1035. After Norway was given to Sweden after the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark retained the Faroes as a condition of the Treaty of Kiel. Status as a Danish county ended in 1948, and the Faroes were given a large degree of independence within the Kingdom of Denmark. |
|||
====Iceland==== |
|||
{{main article|History of Iceland}} |
|||
[[File:Gaimard01.jpg|thumb|260px|Reykjavík in 1835]] |
|||
As with Greenland and the Faroe Islands, Norwegian claims to [[Iceland]] were inherited by Denmark-Norway. Also like those possessions, Iceland was retained by Denmark at the Treaty of Kiel. A growing independence movement in Iceland led to Denmark granting it home rule in 1874 and expanding that home rule in 1904. In 1918 Iceland became a fully sovereign kingdom, titled the "[[Kingdom of Iceland]]", in [[personal union]] with Denmark. |
|||
During [[Nazi Germany]]'s [[Occupation of Denmark]] (1940) the Republic of Iceland was declared on June 17, 1944. |
|||
===Danish Estonia and Courland=== |
|||
{{main article|Danish Estonia|Bishopric of Courland}} |
|||
In the 13th-14th centuries, Denmark ruled parts of what is now [[Estonia]]. The colony was initially named the "Duchy of Estonia" ({{lang-da|Hertugdømmet Estland}}) and is retrospectively called [[Danish Estonia]] by historians. |
|||
In 1559 the [[Bishopric of Courland|bishop of Courland]] and [[Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek|Ösel-Wiek]] [[Johannes V von Münchhausen]] sold his lands to the King [[Frederick II of Denmark]] for 30,000 [[thalers]]. The Danish king gave the territory to his younger brother [[Duke Magnus of Holstein]]. After Magnus of Livonia died in 1583, the [[Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth]] invaded his territories in the Bishopric of Courland and [[Frederick II of Denmark]] decided to sell his rights of inheritance. |
|||
In 1645, [[Saaremaa]] was ceded from Denmark to [[Dominions of Sweden|Sweden]] by the [[Second Treaty of Brömsebro (1645)|Treaty of Brömsebro]]. |
|||
==Demise== |
==Demise== |
||
Revision as of 14:11, 16 March 2017
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Danish Colonial Empire Danske kolonier (Danish) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1536–1953 | |||||||||||
| Motto: Ske Herrens vilje "The Lord's will be done" | |||||||||||
| Anthem: Royal and National anthem Kong Christian stod ved højen mast "King Christian stood by the lofty mast" | |||||||||||
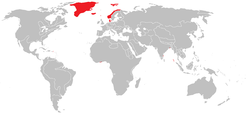 Danish colonial empire at its apex in the mid-eighteenth century. | |||||||||||
| Capital | Copenhagen | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Official language: Danish Regional languages: Norwegian, German | ||||||||||
| Religion | Official religion: Lutheran Minority religions: Roman Catholic, Protestant | ||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy by divine right | ||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 1536 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1953 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 2,655,564.76 km2 (1,025,319.29 sq mi) | |||||||||||
| Currency | Riksdaler | ||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | DK | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Countries today | ||||||||||
The Danish colonial empire (Template:Lang-da) and pre Dano-Norwegian empire (Template:Lang-no) denotes the colonies that Denmark-Norway (Denmark alone after 1814) possessed from 1536 until 1953. At its apex the colonial empire spanned four continents (Europe, South America, Africa and Asia). The period of colonial expansion marked a rise in the status and power of Danes and Norwegians in the union. Being the hegemon of Denmark-Norway or the Statsfædrelandet (lit. State Fathers' Land), Denmark is where the union's monumental palaces are now located and Copenhagen, today the capital of Denmark, was the city which both Norway and Denmark came to establish as their capital. Much of the Norwegian population moved to find work in Copenhagen, attend the University, or join the Royal Fleet. At it hegiht the empire was a area of 2655564,76 km2 [1]
In the 17th century, following territorial losses on the Scandinavian Peninsula, Denmark-Norway began to develop colonies, forts, and trading posts in Africa, the Caribbean, and India. After 1814, when Norway was granted to Sweden following the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark retained what remained of Norway's great medieval colonial holdings. Christian IV first initiated the policy of expanding Denmark-Norway's overseas trade, as part of the mercantilist wave that was sweeping Europe. Denmark-Norway's first colony was established at Tranquebar ([Trankebar] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) on India's southern coast in 1620. Admiral Ove Gjedde led the expedition that established the colony.
Today, the only remaining vestiges of this empire are two originally Norwegian colonies that are currently within the Danish Realm, the Faroe Islands and Greenland; the Faroes were a Danish county until 1948, while Greenland's colonial status ceased in 1953. They are now autonomous countries of the Kingdom of Denmark with home rule, in a relationship referred to as the "Unity of the Realm".
Overview
Africa

Denmark maintained several tradings stations and four forts on the Gold Coast in west Africa, especially around modern day Ghana. Three trading stations were built:[2] Fort Frederiksborg, Kpompo; Osu Castle by Accra in 1661, that was purchased from Sweden; and Frederiksberg. The forts were Fort Prinsensten built in 1784, Fort Augustaborg from 1787, Fort Friedensborg and Fort Kongensten, several of which are ruins today. Of these, only one is still used today, Fort Christiansborg, which is the Ghanaian president's residence in Ghana.
Plantations were established by Frederiksborg, but they failed. Fort Christiansborg became the base for Danish power in west Africa, and the centre for slave trade to the Danish West Indies. In 1807, Denmark's African business partners were suppressed by the Akan people subgroup-Ashanti, which led to the abandonment of all trading stations. Denmark sold its forts to the United Kingdom in 1850.
Americas

Greenland
With the ratification of the Kalmar Union in 1397, Denmark-Norway inherited Greenland which was previously part of Norway since its settlement in the Viking Age. After the Norse settlement in Greenland finally disappeared in the 15th century, Europeans did not settle the island again until 1721, when the Lutheran minister Hans Egede arrived and established the town now known as Nuuk. After Norway was ceded to Sweden in 1814 following the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark retained the old territorial claims as a condition of the Treaty of Kiel.
The development and settlement of Greenland accelerated in 1945, instigated by the region's geostrategic importance in the Cold War era, itself exemplified and manifested by the US-Air base of Thule from 1943. Another reason and driving force was the emergence of fundamental technical abilities, such as aircraft and icebreakers at Greenland's disposition, giving the otherwise remote island a supply situation somewhat similar to Europe.
Danish West Indies
Denmark-Norway acquired the island of St. Thomas in 1671[2] and St. Jan (now St. John) in 1718, and bought St. Croix from France in 1733. All of the islands' economies were based primarily on sugar. These islands were known as the Danish West Indies and were eventually sold to the United States in 1917 for 25 million dollars.[2] Several Danish-American succession talks had been made since 1870 due to a rising amount of riots and unrest from the poorer English speaking population. The Zahle Government (1914-1920) held a heavily boycotted election for Danish mainland constituencies, which produced a minority for the sale of the islands. The United States hoped to use them as naval bases. Since 1917, the islands have been known as the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Asia


Denmark maintained a scattering of small colonies and trading posts throughout the Indian sub-continent from the 17th to 19th centuries, after which most were sold or ceded to Britain which had become the dominant power there.[2] The most important economic aspect was spice trade and access to the east Asian area, including Imperial China situated farther to the east.
The colony at [Trankebar] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (modern day: Tharangambadi) was kept for over 200 years, with a few interruptions, until it was sold to the British in 1845.
In 1755 Denmark acquired the [Frederiksnagore] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (now Serampore), and later the towns of Achne and Pirapur. They are located about 25 kilometres north of Calcutta. In 1818 Serampore College was established in Serampore, which still exists today. These towns were also sold to Britain in 1845. Other colonial ventures include colonization attempts of the Nicobar Islands, called [Frederiksøerne] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ("Frederik Islands") or [Ny Danmark] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ("New Denmark") by the Danes between 1754 and 1868.
Atlantic
Faroe Islands
As with Greenland, Denmark-Norway inherited the medieval Norwegian claims to the Faroe Islands as the successor state to Norway. The Faroes had become part of the Kingdom of Norway in 1035. After Norway was given to Sweden after the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark retained the Faroes as a condition of the Treaty of Kiel. Status as a Danish county ended in 1948, and the Faroes were given a large degree of independence within the Kingdom of Denmark.
Iceland

As with Greenland and the Faroe Islands, Norwegian claims to Iceland were inherited by Denmark-Norway. Also like those possessions, Iceland was retained by Denmark at the Treaty of Kiel. A growing independence movement in Iceland led to Denmark granting it home rule in 1874 and expanding that home rule in 1904. In 1918 Iceland became a fully sovereign kingdom, titled the "Kingdom of Iceland", in personal union with Denmark.
During Nazi Germany's Occupation of Denmark (1940) the Republic of Iceland was declared on June 17, 1944.
Danish Estonia and Courland
In the 13th-14th centuries, Denmark ruled parts of what is now Estonia. The colony was initially named the "Duchy of Estonia" (Template:Lang-da) and is retrospectively called Danish Estonia by historians. In 1559 the bishop of Courland and Ösel-Wiek Johannes V von Münchhausen sold his lands to the King Frederick II of Denmark for 30,000 thalers. The Danish king gave the territory to his younger brother Duke Magnus of Holstein. After Magnus of Livonia died in 1583, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth invaded his territories in the Bishopric of Courland and Frederick II of Denmark decided to sell his rights of inheritance. In 1645, Saaremaa was ceded from Denmark to Sweden by the Treaty of Brömsebro.
Demise
The downfall of the Danish colonial empire was caused by a lack of resources.[2] The empire was quickly eclipsed by those of France, Britain and the Netherlands. Eventually Denmark sold its colonies in India to Britain.[2]
Legacy
Greenland and the Faroe Islands are the last vestiges of the colonial empire. Greenland's colonial status ceased in 1953, and it became an integral part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It gained home rule in 1979 and further autonomy, including self-determination, in 2009. Likewise, the Faroes were incorporated into the Kingdom in the eighteenth century, with the status of a county, and then given home rule in 1948.
See also
References
- ^ Information on Dano-Norwegian empire found on the area of the empire. Possiens of Denmark-Norway (all figures relate to the year 1800)
- Denmark: 42925.46 km²
- Norway: 324220 km²
- Schleswig-Holstein: 15763.18 km²
- Greenland: 2166086 km²
- Iceland: 103000 km²
- Faroe Islands: 1399 km²
- Danish India: 1648.13 km²
- Danish West Indies: 400 km²
- Danish Gold Coast: 126 km²
- ^ a b c d e f Olson, James Stuart; Shadle, Robert, eds. (1991). Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism. Greenwood Publishing Group. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
Further reading
- Pedersen, Mikkel Venborg (2013). Luksus: forbrug og kolonier i Danmark i det 18. århundrede. Kbh.: Museum Tusculanum. ISBN 978-87-635-4076-6.