Nickel aluminide: Difference between revisions
remove definition - article intermetallic already exists Tag: references removed |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Nickel aluminide''' (Ni<sub>3</sub>Al) is an [[intermetallic |
'''Nickel aluminide''' (Ni<sub>3</sub>Al) is an [[intermetallic alloy]] of [[nickel]] and [[aluminum]] with properties similar to both a ceramic and a metal. |
||
There are three materials called nickel aluminide: |
There are three materials called nickel aluminide: |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* NiAl<sub>3</sub>, [[CAS number]] 12004-71-6 |
* NiAl<sub>3</sub>, [[CAS number]] 12004-71-6 |
||
* Ni<sub>3</sub>Al, tri-nickel aluminide |
* Ni<sub>3</sub>Al, tri-nickel aluminide |
||
<blockquote>An intermetallic compound can be defined as an ordered alloy phase formed between two metallic elements, where an alloy phase is ordered if two or more sublattices are required to describe its atomic structure. The ordered structure exhibits superior elevated-temperature properties because of the long-range ordered [[superlattice]], which reduces [[dislocation]] mobility and [[diffusion]] processes at elevated temperatures.<ref>Vinod K. Sikka, Intermetallic-based high-temperature materials, Metals and Ceramics Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, March 1999</ref></blockquote> |
|||
Nickel aluminide is used as a strengthening constituent in high-temperature nickel-base [[superalloy]]s, however, unalloyed nickel aluminide has a tendency to exhibit brittle fracture and low ductility at ambient temperatures.<ref>[http://www.asminternational.org/content/ASM/StoreFiles/ACFA9D7.pdf "ASM Specialty Handbook: Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys", p. 104]</ref> |
Nickel aluminide is used as a strengthening constituent in high-temperature nickel-base [[superalloy]]s, however, unalloyed nickel aluminide has a tendency to exhibit brittle fracture and low ductility at ambient temperatures.<ref>[http://www.asminternational.org/content/ASM/StoreFiles/ACFA9D7.pdf "ASM Specialty Handbook: Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys", p. 104]</ref> |
||
Revision as of 19:08, 2 May 2019
Nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) is an intermetallic alloy of nickel and aluminum with properties similar to both a ceramic and a metal.
There are three materials called nickel aluminide:
- NiAl, CAS number 12003-78-0 (see also Raney nickel)
- NiAl3, CAS number 12004-71-6
- Ni3Al, tri-nickel aluminide
Nickel aluminide is used as a strengthening constituent in high-temperature nickel-base superalloys, however, unalloyed nickel aluminide has a tendency to exhibit brittle fracture and low ductility at ambient temperatures.[1] Nickel aluminide is unique in that it has very high thermal conductivity combined with high strength at high temperature. These properties, combined with its high strength and low density, make it ideal for special applications like coating blades in gas turbines and jet engines.
In 2005, the most abrasion-resistant material was reportedly created by embedding diamonds in a matrix of nickel aluminide.[2]
IC-221M
An alloy of Ni3Al, known as IC-221M, is made up of nickel aluminide combined with several other metals including chromium, molybdenum, zirconium and boron. Adding boron increases the ductility of the alloy by positively altering the grain boundary chemistry and promoting grain refinement. The Hall-Petch parameters for this material were σo = 163 MPa and ky = 8.2 MPaˑcm1/2.[3] Boron increases the hardness of bulk Ni3Al by a similar mechanism.
This alloy is extremely strong for its weight, five times stronger than common SAE 304 stainless steel. Unlike most alloys, IC-221M increases in strength from room temperature up to 800 °C.
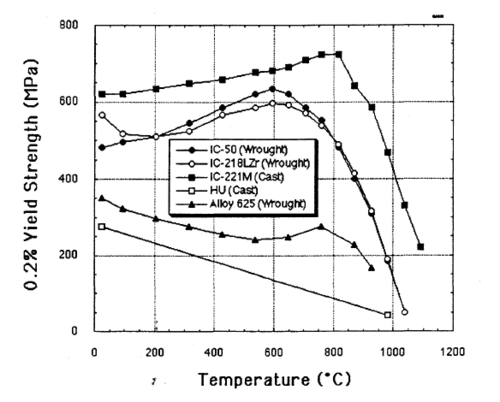
The alloy is very resistant to heat and corrosion, and finds use in heat-treating furnaces and other applications where its longer lifespan and reduced corrosion give it an advantage over stainless steel.[4]
Properties
- Density = 7.16 g/cm3
- Yield Strength = 855 MPa
- Hardness = HRC 12
- Thermal Conductivity Ni3Al = 28.85 (W/m.K)[5]
- Thermal Conductivity NiAl = 76 (W/m.K) [5]
- Melting Point Ni3Al = 1668 K
- Melting Point NiAl = 1955 K
- Thermal expansion coefficient = 12.5 (10−6/K−1)
- Bonding = covalent/metallic
- Electrical resistivity = 32.59 (10−8Ωm)
References
- ^ "ASM Specialty Handbook: Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys", p. 104
- ^ Scientists Develop Nickel Aluminide Composite Material that Can Cut Through Cast Iron and Granite
- ^ Liu, C. T.; White, C. L.; Horton, J. A. (1985). "Effect of boron on grain-boundaries in Ni3Al". Acta Metall. 33 (2): 213–229. doi:10.1016/0001-6160(85)90139-7.
- ^ Crawford, Gerald (April 2003). "Exotic Alloy Finds Niche". Nickel magazine. Retrieved 2006-12-19.
- ^ a b Dey, G. K. (2003). "Physical Metallurgy of Nickel Aluminides" (PDF). Sadhana. 28 (Parts 1 & 2): 247–262. doi:10.1007/bf02717135. Retrieved 2014-03-05.
