Economic geology: Difference between revisions
m Dating maintenance tags: {{Cn}} |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Purpose of studies == |
== Purpose of studies == |
||
The purpose of the study of economic geology is to gain understanding of the [[ore genesis|genesis]] and [[Prospectivity mapping|localization]] of ore deposits plus the minerals associated with ore deposits.<ref>J. M. Gilbert and C. F. Park, Jr., 2007, ''The Geology of Ore Deposits'', 985 pages, Waveband Press, Long Grove, IL</ref> Though metals, minerals and other geologic commodities are non-renewable in human time frames, the impression of a fixed or limited stock paradigm of scarcity has always led to human innovation resulting in a replacement commodity substituted for those commodities which become too expensive. Additionally the fixed stock of most mineral commodities is huge (e.g., copper within the earth's crust given current rates of consumption would last for more than 100 million years.<ref>J.E. Tilton, 2010, "Is Mineral Depletion a threat to sustainable mining?", Society of Economic Geologists Newsletter, No. 82</ref> Nonetheless, economic geologists continue to successfully expand and define known mineral resources.{{Cn}} |
The purpose of the study of economic geology is to gain understanding of the [[ore genesis|genesis]] and [[Prospectivity mapping|localization]] of ore deposits plus the minerals associated with ore deposits.<ref>J. M. Gilbert and C. F. Park, Jr., 2007, ''The Geology of Ore Deposits'', 985 pages, Waveband Press, Long Grove, IL</ref> Though metals, minerals and other geologic commodities are non-renewable in human time frames, the impression of a fixed or limited stock paradigm of scarcity has always led to human innovation resulting in a replacement commodity substituted for those commodities which become too expensive. Additionally the fixed stock of most mineral commodities is huge (e.g., copper within the earth's crust given current rates of consumption would last for more than 100 million years.<ref>J.E. Tilton, 2010, "Is Mineral Depletion a threat to sustainable mining?", Society of Economic Geologists Newsletter, No. 82</ref> Nonetheless, economic geologists continue to successfully expand and define known mineral resources.{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
== Mineral resources == |
== Mineral resources == |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Mineral resources are concentrations of minerals significant for current and future societal needs. Ore is classified as mineralization economically and technically feasible for extraction. Not all mineralization meets these criteria for various reasons. The specific categories of mineralization in an economic sense are: |
Mineral resources are concentrations of minerals significant for current and future societal needs. Ore is classified as mineralization economically and technically feasible for extraction. Not all mineralization meets these criteria for various reasons. The specific categories of mineralization in an economic sense are: |
||
* ''Mineral occurrences'' or prospects of geological interest but not necessarily economic interest{{Cn}} |
* ''Mineral occurrences'' or prospects of geological interest but not necessarily economic interest{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
* ''Mineral resources'' include those potentially economically and technically feasible and those that are not{{Cn}} |
* ''Mineral resources'' include those potentially economically and technically feasible and those that are not{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
* ''Ore reserves'', which must be economically and technically feasible to extract{{Cn}} |
* ''Ore reserves'', which must be economically and technically feasible to extract{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
== Ore geology == |
== Ore geology == |
||
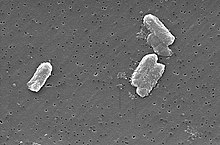
[[Image:Citrobacter freundii.jpg|thumb|''[[Citrobacter]]'' species can have concentrations of uranium in their bodies 300 times higher than in the surrounding environment.]] |
[[Image:Citrobacter freundii.jpg|thumb|''[[Citrobacter]]'' species can have concentrations of uranium in their bodies 300 times higher than in the surrounding environment.]] |
||
{{main|ore genesis}} |
{{main|ore genesis}} |
||
Geologists are involved in the study of [[ore]] deposits, which includes the study of [[ore genesis]] and the processes within the Earth's crust that form and concentrate ore minerals into economically viable quantities.{{Cn}} |
Geologists are involved in the study of [[ore]] deposits, which includes the study of [[ore genesis]] and the processes within the Earth's crust that form and concentrate ore minerals into economically viable quantities.{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
Study of metallic ore deposits involves the use of [[structural geology]], [[geochemistry]], the study of [[metamorphism]] and its processes, as well as understanding [[metasomatism]] and other processes related to ore genesis.{{Cn}} |
Study of metallic ore deposits involves the use of [[structural geology]], [[geochemistry]], the study of [[metamorphism]] and its processes, as well as understanding [[metasomatism]] and other processes related to ore genesis.{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
Ore deposits are delineated by [[mineral exploration]], which uses [[Geochemistry|geochemical]] prospecting, [[Boring (earth)|drilling]] and resource estimation via [[geostatistics]] to quantify economic ore bodies. The ultimate aim of this process is [[mining]].{{Cn}} |
Ore deposits are delineated by [[mineral exploration]], which uses [[Geochemistry|geochemical]] prospecting, [[Boring (earth)|drilling]] and resource estimation via [[geostatistics]] to quantify economic ore bodies. The ultimate aim of this process is [[mining]].{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
== Coal and petroleum geology == |
== Coal and petroleum geology == |
||
[[Image:Mudlogging.JPG|thumb|[[Mud log]] in process, a common way to study the lithology when drilling oil wells.]] |
[[Image:Mudlogging.JPG|thumb|[[Mud log]] in process, a common way to study the lithology when drilling oil wells.]] |
||
:''See main articles [[Coal]] and [[Petroleum geology]] |
:''See main articles [[Coal]] and [[Petroleum geology]] |
||
The study of [[sedimentology]] is of prime importance to the delineation of economic reserves of [[petroleum]] and [[coal]] energy resources.{{Cn}} |
The study of [[sedimentology]] is of prime importance to the delineation of economic reserves of [[petroleum]] and [[coal]] energy resources.{{Cn|date=January 2021}} |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 02:16, 8 January 2021

Economic geology is concerned with earth materials that can be used for economic and/or industrial purposes. These materials include precious and base metals, nonmetallic minerals and construction-grade stone. Economic geology is a subdiscipline of the geosciences; according to Lindgren (1933) it is “the application of geology”. Today, it may be called the scientific study of the Earth's sources of mineral raw materials and the practical application of the acquired knowledge.[1] The term commonly refers to metallic mineral deposits and mineral resources. The techniques employed by other earth science disciplines (such as geochemistry, mineralogy, geophysics, petrology and structural geology) might all be used to understand, describe, and exploit an ore deposit.
Economic geology is studied and practiced by geologists. Economic geology may be of interest to other professions such as engineers, environmental scientists, and conservationists because of the far-reaching impact that extractive industries have on society, the economy, and the environment.
Purpose of studies
The purpose of the study of economic geology is to gain understanding of the genesis and localization of ore deposits plus the minerals associated with ore deposits.[2] Though metals, minerals and other geologic commodities are non-renewable in human time frames, the impression of a fixed or limited stock paradigm of scarcity has always led to human innovation resulting in a replacement commodity substituted for those commodities which become too expensive. Additionally the fixed stock of most mineral commodities is huge (e.g., copper within the earth's crust given current rates of consumption would last for more than 100 million years.[3] Nonetheless, economic geologists continue to successfully expand and define known mineral resources.[citation needed]
Mineral resources
Mineral resources are concentrations of minerals significant for current and future societal needs. Ore is classified as mineralization economically and technically feasible for extraction. Not all mineralization meets these criteria for various reasons. The specific categories of mineralization in an economic sense are:
- Mineral occurrences or prospects of geological interest but not necessarily economic interest[citation needed]
- Mineral resources include those potentially economically and technically feasible and those that are not[citation needed]
- Ore reserves, which must be economically and technically feasible to extract[citation needed]
Ore geology
Geologists are involved in the study of ore deposits, which includes the study of ore genesis and the processes within the Earth's crust that form and concentrate ore minerals into economically viable quantities.[citation needed]
Study of metallic ore deposits involves the use of structural geology, geochemistry, the study of metamorphism and its processes, as well as understanding metasomatism and other processes related to ore genesis.[citation needed]
Ore deposits are delineated by mineral exploration, which uses geochemical prospecting, drilling and resource estimation via geostatistics to quantify economic ore bodies. The ultimate aim of this process is mining.[citation needed]
Coal and petroleum geology

- See main articles Coal and Petroleum geology
The study of sedimentology is of prime importance to the delineation of economic reserves of petroleum and coal energy resources.[citation needed]
See also
- Important publications in economic geology
- Mineral economics
- Mineral resource classification
- Ore
- Ore genesis
- Coal
References
- ^ Pohl, W.L., 2011. Economic Geology, Principles and Practice: Metals, Minerals, Coal and Hydrocarbons – an Introduction to Formation and Sustainable Exploitation of Mineral Deposits. 663 Pages, Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford.
- ^ J. M. Gilbert and C. F. Park, Jr., 2007, The Geology of Ore Deposits, 985 pages, Waveband Press, Long Grove, IL
- ^ J.E. Tilton, 2010, "Is Mineral Depletion a threat to sustainable mining?", Society of Economic Geologists Newsletter, No. 82
- Lindgren, W., 1933. Mineral Deposits. 930 pp. McGraw-Hill, New York.
- U.S. Geological Survey Circular 831, Principles of a Resource/Reserve Classification for Minerals (PDF format)
- Dill, H.G., 2010. The “chessboard” classification scheme of mineral deposits: Mineralogy and geology from aluminum to zirconium. Earth-Science Reviews Volume 100, pp. 1–420, 2010

