Bursaray: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
A total of 48 cars of the B80 type ({{convert|27.7|m|ft|adj=on|sp=us}} long) were delivered by [[Siemens]]<ref name="RayHaber">{{cite news|url=http://www.rayhaber.com/2012/bursaray-rotterdam-vagonu-bursa-tren/|title=BursaRay Rotterdam Araçları ve Burulaş (ÖZEL HABER)|newspaper=RayHaber|language=tr|trans-title=BursaRay Rotterdam Vehicles to Burulaş (SPECIAL NEWS)|date=24 November 2012|access-date=2014-06-03|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140225055641/http://www.rayhaber.com/2012/bursaray-rotterdam-vagonu-bursa-tren/|archive-date=25 February 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> (in collaboration with the local company [[TÜVASAŞ]]). Siemens TS supplied the signalling automation systems and the power supply system. |
A total of 48 cars of the B80 type ({{convert|27.7|m|ft|adj=on|sp=us}} long) were delivered by [[Siemens]]<ref name="RayHaber">{{cite news|url=http://www.rayhaber.com/2012/bursaray-rotterdam-vagonu-bursa-tren/|title=BursaRay Rotterdam Araçları ve Burulaş (ÖZEL HABER)|newspaper=RayHaber|language=tr|trans-title=BursaRay Rotterdam Vehicles to Burulaş (SPECIAL NEWS)|date=24 November 2012|access-date=2014-06-03|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140225055641/http://www.rayhaber.com/2012/bursaray-rotterdam-vagonu-bursa-tren/|archive-date=25 February 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> (in collaboration with the local company [[TÜVASAŞ]]). Siemens TS supplied the signalling automation systems and the power supply system. |
||
Later the fleet was enlarged with 30 [[Bombardier |
Later the fleet was enlarged with 30 [[Bombardier Flexity Swift]]<ref name="RayHaber"/> light rail cars (similar to those on the [[U5 (Frankfurt U-Bahn)|U5 line]] on the [[Frankfurt U-Bahn]]) from Bombardier. After that, Burulas purchased 44 used 'Sneltram' [[Duewag]] SG2 (Duewag T-cars) from Rotterdam;<ref name="RayHaber"/> 25 of which were placed in service while the other 19 were used to provide spare parts as needed. |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 22:20, 2 April 2021
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2014) |
| BursaRay | |
|---|---|
| File:BursaRay logo.png | |
| Overview | |
| Locale | Bursa, Marmara, Turkey |
| Transit type | Rapid transit |
| Number of lines | 2 |
| Number of stations | 38[1] |
| Annual ridership | 91.25 million (2010) |
| Website | Burulaş - Bursaray |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | 24 April 2002 |
| Operator(s) | Burulaş |
| Number of vehicles | 122 cars (total)[2] (48 Siemens Type B80, 30 Bombardier Flexity Swift, 44 Duewag SG2) |
| Technical | |
| System length | 38.9 km (24.2 mi)[1][3] |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge[3] |
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC |
| Average speed | 34 km/h (21 mph) 24 km/h (15 mph) (Line 1 branch)[3] |
| Top speed | 70 km/h (43 mph)[3] 50 km/h (31 mph) (Line 1 branch)[3] |
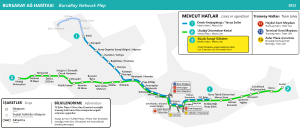
Bursaray (sometimes stylized as BursaRay) is a rapid transit system in the city of Bursa, Marmara Region, Turkey, built in 2000 by TÜVASAŞ, and operated by Burulaş.[4] The name Bursaray is a portmanteau of Bursa, and Ray, the Turkish word for "rail". The Bursaray metro opened for passenger service on 24 April 2002. The metro system presently consists of two lines, which share a main line in the east, and branch into two lines at the western end of the system.
It is planned to expand the Bursaray system to a 50-kilometer (31 mi) network in the future.[citation needed]
History
- 31 Jan 1997: Bursaray contract signed
- 14 Oct 1998: construction begins
- 24 Apr 2002: passenger trial service begins
- 19 Aug 2002: official opening of first line: Şehreküstü - Küçük Sanayi (Hipodrom)
- 02 Jan 2005: construction work begins on BursaRay Phase 1 Stage B
- 06 Apr 2008: extension east from Sehreküstü - Arabayatagi (i.e. BursaRay Phase 1 Stage B enters service)
- 28 Oct 2008: Phase 2 construction work begins
- 24 Dec 2010: extension: Phase 2, Küçük Sanayi (Hipodrom) - Özlüce (2.9 km), enters service
- 19 Sep 2011: extension: Phase 2, Özlüce - Üniversite (3.6 km)
- 15 Dec 2011: extension: Phase 2, Organize Sanayi (1050 Konutlar) - Emek (2.5 km)
- 19 Mar 2014: extension: Phase 3, Arabayatağı - Otosansit (4.4 km)
- 27 Mar 2014: extension: Phase 3, Otosansit - Gürsu (2.0 km)
- 05 Jun 2014: extension: completion of Phase 3, Gürsu - Kestel[5] (1.5 km)
Operations
The Bursaray system is made up of two lines that operate on 38.9 kilometers (24.2 mi) of route, serving 38 stations (7 of which are underground stations).[1][3]
The track gauge is similar to all Turkish metro systems (such as in Istanbul, Ankara, Izmir and Adana); the entire network consists of standard gauge rail of 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in).[3]
Station platforms are 120 meters (390 ft) long, and 92 centimeters (3.02 ft) high; most stations use island platforms.[3]
Rolling stock
A total of 48 cars of the B80 type (27.7-meter (91 ft) long) were delivered by Siemens[2] (in collaboration with the local company TÜVASAŞ). Siemens TS supplied the signalling automation systems and the power supply system.
Later the fleet was enlarged with 30 Bombardier Flexity Swift[2] light rail cars (similar to those on the U5 line on the Frankfurt U-Bahn) from Bombardier. After that, Burulas purchased 44 used 'Sneltram' Duewag SG2 (Duewag T-cars) from Rotterdam;[2] 25 of which were placed in service while the other 19 were used to provide spare parts as needed.
See also
References
- ^ a b c "BURSARAY GÜZERGAHI" [BURSARAY ITINERARY] (in Turkish). Burulaş Bursa Ulaşım Toplu Taşım İşletmeciliği Turizm San. Ve Tic. A.Ş. [Burulaş Bursa Transportation Mass Transit Administration Tourism Industry. Ve Tic. Inc.] Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ a b c d "BursaRay Rotterdam Araçları ve Burulaş (ÖZEL HABER)" [BursaRay Rotterdam Vehicles to Burulaş (SPECIAL NEWS)]. RayHaber (in Turkish). 24 November 2012. Archived from the original on 25 February 2014. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "BURSARAY TEKNİK ÖZELLİKLER" [BURSARAY TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS] (in Turkish). Burulaş Bursa Ulaşım Toplu Taşım İşletmeciliği Turizm San. Ve Tic. A.Ş. [Burulaş Bursa Transportation Mass Transit Administration Tourism Industry. Ve Tic. Inc.] Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ^ "Bursaray: Bursa metro map, Turkey". mapa-metro.com. Retrieved 16 April 2018.
- ^ "BursaRay Kestel etabında son üç istasyon da hizmete açıldı" [BursaRay Kestel extension opens the last three stations]. Cihan (in Turkish). 5 June 2014. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 7 June 2014.
External links
- Bursaray – official site (in Turkish)
- Image of Bursaray
- Map