Halogenation: Difference between revisions
new intro | Alter: template type. Add: issue, volume, journal, isbn, pages, year, title, chapter, authors 1-2. Formatted dashes. | Use this tool. Report bugs. | #UCB_Gadget |
lede |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{for|the addition of chlorine, hypochlorite, etc. to drinking water|Water chlorination}} |
{{for|the addition of chlorine, hypochlorite, etc. to drinking water|Water chlorination}} |
||
In [[chemistry]], '''halogenation''' is a [[chemical reaction]] that entails the introduction of one or more [[halogen]]s into a [[chemical compound|compound]]. Halide-containing compounds are |
In [[chemistry]], '''halogenation''' is a [[chemical reaction]] that entails the introduction of one or more [[halogen]]s into a [[chemical compound|compound]]. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs.<ref>{{cite book |doi=10.1002/9780470771723.ch3|chapter=Formation of Carbon-Halogen Bonds|title=Halides, Pseudo-Halides and Azides: Part 2 (1983)|year=1983|last1=Hudlicky|first1=Milos|last2=Hudlicky|first2=Tomas|pages=1021–1172|isbn=9780470771723|editor1=S. Patai|editor2=Z. Rappoport|series=PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups}}</ref> This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. ''This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens (F<sub>2</sub>, Cl<sub>2</sub>, Br<sub>2</sub>, I<sub>2</sub>).'' Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for the purpose of introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. [[thionyl chloride]]. |
||
==Organic chemistry== |
==Organic chemistry== |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===Free radical halogenation === |
===Free radical halogenation === |
||
Halogenation of saturated hydrocarbons typically requires free radical pathways. The regiochemistry of the halogenation of alkanes is |
Halogenation of saturated hydrocarbons is a substitution reaction. The reaction typically requires free radical pathways. The regiochemistry of the halogenation of alkanes is largely determined by the relative weakness of the C–H bonds. This trend is reflected by the faster reaction at tertiary and secondary positions. |
||
Fluorinations with elemental fluorine (F<sub>2</sub>) are particularly exothermic, so much so that highly specialised conditions and apparatus are required. The method [[electrochemical fluorination]] generates small amounts of elemental fluorine in situ from [[hydrogen fluoride]]. The method avoid the hazards of handling fluorine gas. Many commercially important organic compounds are fluorinated using this technology. Aside from F<sub>2</sub> and its electrochemically generated equivalent, [[cobalt(III) fluoride]] is used as sources of fluorine radicals. |
Fluorinations with elemental fluorine (F<sub>2</sub>) are particularly exothermic, so much so that highly specialised conditions and apparatus are required. The method [[electrochemical fluorination]] generates small amounts of elemental fluorine in situ from [[hydrogen fluoride]]. The method avoid the hazards of handling fluorine gas. Many commercially important organic compounds are fluorinated using this technology. Aside from F<sub>2</sub> and its electrochemically generated equivalent, [[cobalt(III) fluoride]] is used as sources of fluorine radicals. |
||
| Line 16: | Line 15: | ||
Free radical chlorination is used for the industrial production of some solvents:<ref name=Ullmann>{{Ullmann|doi=10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2}}</ref> |
Free radical chlorination is used for the industrial production of some solvents:<ref name=Ullmann>{{Ullmann|doi=10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2}}</ref> |
||
:CH<sub>4</sub> + Cl<sub>2</sub> → CH<sub>3</sub>Cl + HCl |
:CH<sub>4</sub> + Cl<sub>2</sub> → CH<sub>3</sub>Cl + HCl |
||
Rearrangement often accompany such free radical reactions. |
|||
Naturally |
Naturally-occuring organobromine compounds are usually produced by free-radical pathway catalyzed by the enzyme [[bromoperoxidase]]. The reaction requires bromide in combination with oxygen as an oxidant. The oceans are estimated to release 1–2 million tons of bromoform and 56,000 tons of bromomethane annually.<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1039/a900201d|title=The diversity of naturally occurring organobromine compounds|year=1999|last1=Gribble|first1=Gordon W.|journal=Chemical Society Reviews|volume=28|issue=5|pages=335–346}}</ref> |
||
The [[iodoform reaction]], which involves degradation of methyl ketones, proceeds by the free-radical iodination. |
The [[iodoform reaction]], which involves degradation of methyl ketones, proceeds by the free-radical iodination. |
||
==== Addition of halogens to alkenes and alkynes ==== |
==== Addition of halogens to alkenes and alkynes ==== |
||
Unsaturated compounds, especially [[alkenes]] and [[alkynes]], add halogens: |
Unsaturated compounds, especially [[alkenes]] and [[alkynes]], ''add'' halogens: |
||
:RCH=CHR′ + X<sub>2</sub> → RCHX–CHXR′ |
:RCH=CHR′ + X<sub>2</sub> → RCHX–CHXR′ |
||
The addition of halogens to alkenes proceeds via intermediate [[halonium ion]]s. In special cases, such intermediates have been isolated.<ref>{{cite journal | journal = [[Chem. Commun.]] | year = 1998 | pages = 927–928 | doi = 10.1039/a709063c | title = X-Ray structure of bridged 2,2′-bi(adamant-2-ylidene) chloronium cation and comparison of its reactivity with a singly bonded chloroarenium cation |author1=T. Mori |author2=R. Rathore | issue = 8 }}</ref> |
The addition of halogens to alkenes proceeds via intermediate [[halonium ion]]s. In special cases, such intermediates have been isolated.<ref>{{cite journal | journal = [[Chem. Commun.]] | year = 1998 | pages = 927–928 | doi = 10.1039/a709063c | title = X-Ray structure of bridged 2,2′-bi(adamant-2-ylidene) chloronium cation and comparison of its reactivity with a singly bonded chloroarenium cation |author1=T. Mori |author2=R. Rathore | issue = 8 }}</ref> |
||
| Line 47: | Line 45: | ||
In the [[Hunsdiecker reaction]], from carboxylic acids are converted to the chain-shortened halide. The carboxylic acid is first converted to its silver salt, which is then oxidized with halogen: |
In the [[Hunsdiecker reaction]], from carboxylic acids are converted to the chain-shortened halide. The carboxylic acid is first converted to its silver salt, which is then oxidized with halogen: |
||
:RCO<sub>2</sub>Ag + Br<sub>2</sub> → RBr + CO<sub>2</sub> + AgBr |
:RCO<sub>2</sub>Ag + Br<sub>2</sub> → RBr + CO<sub>2</sub> + AgBr |
||
The [[Sandmeyer reaction]] is used to give aryl halides from [[diazonium salt]]s, which are obtained from [[aniline]]s. In the [[Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation]], carboxylic acids are alpha-halogenated. |
|||
In [[oxychlorination]], the combination of hydrogen chloride and oxygen serves as the equivalent of chlorine, as illustrated by this route to dichloroethane: |
|||
:2 HCl + CH<sub>2</sub>=CH<sub>2</sub> + {{1/2}} O<sub>2</sub> → ClCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Cl + H<sub>2</sub>O |
|||
==Inorganic chemistry== |
==Inorganic chemistry== |
||
Revision as of 22:44, 16 May 2021
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs.[1] This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2). Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for the purpose of introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.
Organic chemistry
Several pathways exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, including free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate determines the pathway. The facility of halogenation is influenced by the halogen. Fluorine and chlorine are more electrophilic and are more aggressive halogenating agents. Bromine is a weaker halogenating agent than both fluorine and chlorine, while iodine is the least reactive of them all. The facility of dehydrohalogenation follows the reverse trend: iodine is most easily removed from organic compounds, and organofluorine compounds are highly stable.
Free radical halogenation
Halogenation of saturated hydrocarbons is a substitution reaction. The reaction typically requires free radical pathways. The regiochemistry of the halogenation of alkanes is largely determined by the relative weakness of the C–H bonds. This trend is reflected by the faster reaction at tertiary and secondary positions.
Fluorinations with elemental fluorine (F2) are particularly exothermic, so much so that highly specialised conditions and apparatus are required. The method electrochemical fluorination generates small amounts of elemental fluorine in situ from hydrogen fluoride. The method avoid the hazards of handling fluorine gas. Many commercially important organic compounds are fluorinated using this technology. Aside from F2 and its electrochemically generated equivalent, cobalt(III) fluoride is used as sources of fluorine radicals.
Free radical chlorination is used for the industrial production of some solvents:[2]
- CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
Naturally-occuring organobromine compounds are usually produced by free-radical pathway catalyzed by the enzyme bromoperoxidase. The reaction requires bromide in combination with oxygen as an oxidant. The oceans are estimated to release 1–2 million tons of bromoform and 56,000 tons of bromomethane annually.[3]
The iodoform reaction, which involves degradation of methyl ketones, proceeds by the free-radical iodination.
Addition of halogens to alkenes and alkynes
Unsaturated compounds, especially alkenes and alkynes, add halogens:
- RCH=CHR′ + X2 → RCHX–CHXR′
The addition of halogens to alkenes proceeds via intermediate halonium ions. In special cases, such intermediates have been isolated.[4]

Structure of a bromonium ion
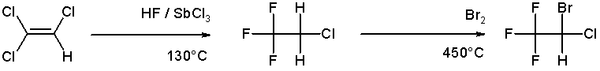
Bromination is more selective than chlorination because the reaction is less exothermic. Illustrative bromination of an alkene is the route to the anesthetic halothane from trichloroethylene:[5]
Iodination can be effected by the addition of iodine to alkenes. The reaction, which conveniently proceeds with the discharge of the color of I2, is the basis of the analytical method called the iodine number, which is used to measure the degree of unsaturation for fats.
Halogenation of aromatic compounds
Chlorination and bromination
Aromatic compounds are subject to electrophilic halogenation:[6]
- RC6H5 + X2 → HX + RC6H4X
This reaction typically works well for chlorine and bromine. Often a Lewis acidic catalyst is used, such as ferric bromide. Industrial halogenations are often effected by treating the arome with halogen in the presence of iron metal. the halogen reacts with iron, generating the ferric halide catalyst.[7]
Fluorination
Because fluorine is very reactive, the protocol described above would not be efficient as the aromatic molecule would react destructively with F2. Therefore, other methods, such as the Balz–Schiemann reaction, must be used to prepare fluorinated aromatic compounds.
Iodination
Iodinations can be conducted with hydrogen iodide in the presence of an oxidising agent that generates I2.
Other halogenation methods
In the Hunsdiecker reaction, from carboxylic acids are converted to the chain-shortened halide. The carboxylic acid is first converted to its silver salt, which is then oxidized with halogen:
- RCO2Ag + Br2 → RBr + CO2 + AgBr
Inorganic chemistry
All elements aside from argon, neon, and helium form fluorides by direct reaction with fluorine. Chlorine is slightly more selective, but still reacts with most metals and heavier nonmetals. Following the usual trend, bromine is less reactive and iodine least of all. Of the many reactions possible, illustrative is the formation of gold(III) chloride by the chlorination of gold. The chlorination of metals is usually not very important industrially since the chlorides are more easily made from the oxides and the hydrogen halide. Where chlorination of inorganic compounds is practiced on a relatively large scale is for the production of phosphorus trichloride and sulfur monochloride.[8]
See also
- Dehalogenation
- Haloalkane (Alkyl halide)
- Halogenoarene (Aryl halide)
- Free radical halogenation
- Haloketone
- Electrophilic substitution
References
- ^ Hudlicky, Milos; Hudlicky, Tomas (1983). "Formation of Carbon-Halogen Bonds". In S. Patai; Z. Rappoport (eds.). Halides, Pseudo-Halides and Azides: Part 2 (1983). PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups. pp. 1021–1172. doi:10.1002/9780470771723.ch3. ISBN 9780470771723.
- ^ Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Gribble, Gordon W. (1999). "The diversity of naturally occurring organobromine compounds". Chemical Society Reviews. 28 (5): 335–346. doi:10.1039/a900201d.
- ^ T. Mori; R. Rathore (1998). "X-Ray structure of bridged 2,2′-bi(adamant-2-ylidene) chloronium cation and comparison of its reactivity with a singly bonded chloroarenium cation". Chem. Commun. (8): 927–928. doi:10.1039/a709063c.
- ^ Synthesis of Essential Drugs, Ruben Vardanyan, Victor Hruby; Elsevier 2005 ISBN 0-444-52166-6
- ^ Illustrative procedure for chlorination of an aromatic compound: Edward R. Atkinson, Donald M. Murphy, and James E. Lufkin (1951). "dl-4,4′,6,6′-Tetrachlorodiphenic Acid". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 4, p. 872. - ^ Organic chemistry by Jonathan Clayden, Nick Grieves, Stuart Warren, Oxford University Press
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.