Eurozone: Difference between revisions
MetalManeMc (talk | contribs) Flag template Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Tag: Reverted |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
| |
| |
||
| BE |
| BE |
||
|- |
|||
| [[Bulgaria]] |
|||
| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| [[Bulgarian lev|Lev]] |
|||
| |
|||
| BG |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Cyprus]] |
| [[Cyprus]] |
||
| Line 98: | Line 108: | ||
| {{small|''Northern Cyprus''}}<ref group="lower-alpha">The self-declared ''Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus'' is not recognised by the EU and uses the [[Turkish lira]]. However the euro does circulate widely.{{citation needed|date=May 2018}}</ref> |
| {{small|''Northern Cyprus''}}<ref group="lower-alpha">The self-declared ''Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus'' is not recognised by the EU and uses the [[Turkish lira]]. However the euro does circulate widely.{{citation needed|date=May 2018}}</ref> |
||
| CY |
| CY |
||
|- |
|||
| [[Czechia]] |
|||
| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| align="right"| |
|||
| [[Czech koruna|Koruna]] |
|||
| |
|||
| CZ |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Estonia]] |
| [[Estonia]] |
||
Revision as of 11:08, 17 May 2021
| Policy of | European Union |
|---|---|
| Type | Monetary union |
| Currency | Euro |
| Established | 1 January 1999 |
| Members | |
| Governance | |
| Political control | Eurogroup |
| Group president | Paschal Donohoe |
| Issuing authority | European Central Bank |
| ECB president | Christine Lagarde |
| Statistics | |
| Area | 2,753,828 km2 |
| Population | 342,409,476[1] |
| Density | 124/km2 |
| GDP (Nominal) | $12.712 trillion[2] |
| Interest rate | -0.50%[3] |
| Inflation | 0.2%[4] |
| Unemployment(2020) | 8.6%[5] |
| Trade balance | €362 billion trade surplus[6] |
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
|
|
The eurozone, officially called the euro area,[7] is a monetary union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender. The monetary authority of the eurozone is the Eurosystem. Eight members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them will be obliged to adopt the euro in the future.
The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Spain. Other EU states (except for Denmark) are obliged to join once they meet the criteria to do so.[8] No state has left, and there are no provisions to do so or to be expelled.[9] Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City have formal agreements with the EU to use the euro as their official currency and issue their own coins.[10][11][12] Kosovo and Montenegro have adopted the euro unilaterally,[13] but these countries do not officially form part of the eurozone and do not have representation in the European Central Bank (ECB) or in the Eurogroup.[14]
The ECB, which is governed by a president and a board of the heads of national central banks, sets the monetary policy of the zone. The principal task of the ECB is to keep inflation under control. Though there is no common representation, governance or fiscal policy for the currency union, some co-operation does take place through the Eurogroup, which makes political decisions regarding the eurozone and the euro. The Eurogroup is composed of the finance ministers of eurozone states, but in emergencies, national leaders also form the Eurogroup.
Since the financial crisis of 2007–2008, the eurozone has established and used provisions for granting emergency loans to member states in return for enacting economic reforms.[citation needed] The eurozone has also enacted some limited fiscal integration: for example, in peer review of each other's national budgets. The issue is political and in a state of flux in terms of what further provisions will be agreed for eurozone change.
Territory
European Union member states
In 1998, eleven member states of the European Union had met the euro convergence criteria, and the eurozone came into existence with the official launch of the euro (alongside national currencies) on 1 January 1999. Greece qualified in 2000, and was admitted on 1 January 2001 before physical notes and coins were introduced on 1 January 2002, replacing all national currencies. Between 2007 and 2015, seven new states acceded.
| State | Adopted | Population[1] 2019 |
Nominal GNI 2019 (USD, millions)[15] |
Relative GNI of total, nominal |
GNI per capita nominal, 2019 (USD)[16] |
Pre-euro currency |
Exceptions | ISO code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 1999-01-01[17] | 8,858,775 | 456,779 | 3.18% | 51,460 | Schilling | AT | |
| Belgium | 1999-01-01[17] | 11,467,923 | 551,595 | 4.18% | 48,030 | Franc | BE | |
| Bulgaria | Lev | BG | ||||||
| Cyprus | 2008-01-01[18] | 875,898 | 24,628 | 0.18% | 27,710 | Pound | Northern Cyprus[a] | CY |
| Czechia | Koruna | CZ | ||||||
| Estonia | 2011-01-01[19] | 1,324,820 | 30,856 | 0.20% | 23,260 | Kroon | EE | |
| Finland | 1999-01-01[17] | 5,517,919 | 276,085 | 2.08% | 50,010 | Markka | FI | |
| France | 1999-01-01[17] | 67,028,048 | 2,846,910 | 22.41% | 42,960 | Franc | New Caledonia[b] French Polynesia[b] Wallis and Futuna[b] |
FR |
| Germany | 1999-01-01[17] | 83,019,214 | 4,038,526 | 31.79% | 42,450 | Mark | DE | |
| Greece | 2001-01-01[20] | 10,722,287 | 211,647 | 1.97% | 19,750 | Drachma | GR | |
| Ireland | 1999-01-01[17] | 4,904,226 | 316,269 | 1.69% | 64,000 | Pound | IE | |
| Italy | 1999-01-01[17] | 60,359,546 | 2,081,972 | 16.91% | 34,530 | Lira | IT | |
| Latvia | 2014-01-01[21] | 1,919,968 | 33,932 | 0.24% | 17,740 | Lats | LV | |
| Lithuania | 2015-01-01[22] | 2,794,184 | 53,162 | 0.36% | 19,080 | Litas | LT | |
| Luxembourg | 1999-01-01[17] | 613,894 | 45,817 | 0.33% | 73,910 | Franc | LU | |
| Malta | 2008-01-01[23] | 493,559 | 14,089 | 0.07% | 28,030 | Lira | MT | |
| Netherlands | 1999-01-01[17] | 17,282,163 | 920,333 | 6.89% | 53,100 | Guilder | Aruba[c] Curaçao[d] Sint Maarten[d] Caribbean Netherlands[e] |
NL |
| Portugal | 1999-01-01[17] | 10,276,617 | 238,204 | 1.75% | 23,200 | Escudo | PT | |
| Slovakia | 2009-01-01[24] | 5,450,421 | 104,778 | 0.76% | 19,210 | Koruna | SK | |
| Slovenia | 2007-01-01[25] | 2,080,908 | 54,169 | 0.38% | 25,940 | Tolar | SI | |
| Spain | 1999-01-01[17] | 46,934,632 | 1,430,766 | 10.75% | 30,390 | Peseta | ES | |
| Eurozone | 341,925,002 | 13,730,527 | 100% | 40,078 | — | — | EZ[f] | |
Dependent territories of EU member states — outside EU
Three of the dependent territories of EU member states not part of the EU have adopted the euro:
- Territorial collectivity of Saint Barthélemy (French territory, with France ensuring eurozone laws are implemented)
- Overseas Collectivity of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon (French territory, with France ensuring eurozone laws are implemented)
- French Southern and Antarctic Lands (French territory, with France ensuring eurozone laws are implemented)
Non-member usage

- European Union member states (special territories not shown)
- 20 in the eurozone5 not in ERM II, but obliged to join the eurozone on meeting the convergence criteria (Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Sweden)
- Non–EU member states
With formal agreement
The euro is also used in countries outside the EU. Four states – Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City —[10][13] have signed formal agreements with the EU to use the euro and issue their own coins. Nevertheless, they are not considered part of the eurozone by the ECB and do not have a seat in the ECB or Euro Group.
Akrotiri and Dhekelia (located on the island of Cyprus) belongs to the United Kingdom, but there are agreements between the UK and Cyprus and between UK and EU about their partial integration with Cyprus and partial adoption of Cypriot law, including the usage of euro in Akrotiri and Dekhelia.
Several currencies are pegged to the euro, some of them with a fluctuation band and others with an exact rate. For example, the West African and Central African CFA francs are pegged exactly at 655.957 CFA to 1 EUR. In 1998, in anticipation of Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union, the Council of the European Union addressed the monetary agreements France had with the CFA Zone and Comoros and ruled that the ECB had no obligation towards the convertibility of the CFA and Comorian francs. The responsibility of the free convertibility remained in the French Treasury.
Other
Kosovo*[g] and Montenegro officially adopted the euro as their sole currency without an agreement and, therefore, have no issuing rights.[13] These states are not considered part of the eurozone by the ECB. However, sometimes the term eurozone is applied to all territories that have adopted the euro as their sole currency.[26][27][28] Further unilateral adoption of the euro (euroisation), by both non-euro EU and non-EU members, is opposed by the ECB and EU.[29]
Historical eurozone enlargements and exchange-rate regimes for EU members
The chart below provides a full summary of all applying exchange-rate regimes for EU members, since the European Monetary System with its Exchange Rate Mechanism and the related new common currency ECU was born on 13 March 1979. The euro replaced the ECU 1:1 at the exchange rate markets, on 1 January 1999. During 1979–1999, the D-Mark functioned as a de facto anchor for the ECU, meaning there was only a minor difference between pegging a currency against ECU and pegging it against the D-mark.
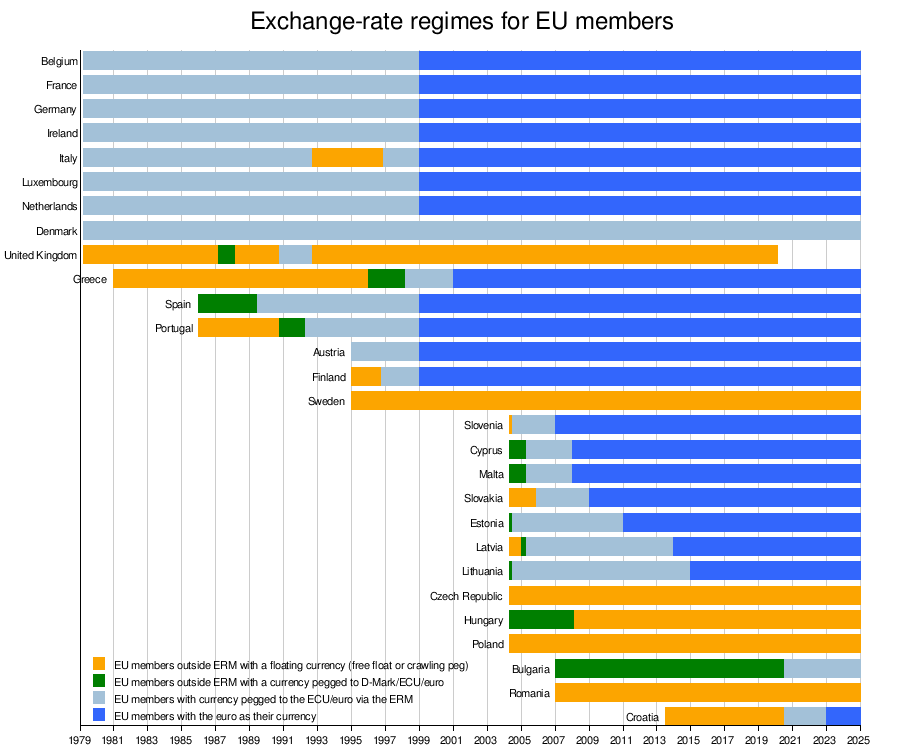
Sources: EC convergence reports 1996-2014, Italian lira, Spanish peseta, Portuguese escudo, Finnish markka, Greek drachma, Sterling
The eurozone was born with its first 11 member states on 1 January 1999. The first enlargement of the eurozone, to Greece, took place on 1 January 2001, one year before the euro had physically entered into circulation. The next enlargements were to states which joined the EU in 2004, and then joined the eurozone on 1 January in the year noted: Slovenia (2007), Cyprus (2008), Malta (2008), Slovakia (2009), Estonia (2011), Latvia (2014), and Lithuania (2015).
All new EU members joining the bloc after the signing of the Maastricht Treaty in 1992 are obliged to adopt the euro under the terms of their accession treaties. However, the last of the five economic convergence criteria which need first to be complied with in order to qualify for euro adoption, is the exchange rate stability criterion, which requires having been an ERM-member for a minimum of two years without the presence of "severe tensions" for the currency exchange rate.
In September 2011, a diplomatic source close to the euro adoption preparation talks with the seven remaining new member states who had yet to adopt the euro (Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland and Romania), claimed that the monetary union (eurozone) they had thought they were going to join upon their signing of the accession treaty may very well end up being a very different union entailing much closer fiscal, economic and political convergence. This changed legal status of the eurozone could potentially cause them to conclude that the conditions for their promise to join were no longer valid, which "could force them to stage new referendums" on euro adoption.[30]
| Country | Old unit | Exchange rate (Euro in units of old currency) |
Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | Belgian franc | 40.3399 | 1999 |
| Luxembourg | Luxembourgish franc | 40.3399 | 1999 |
| Germany | Deutsche Mark | 1.95583 | 1999 |
| Spain, Andorra[h] | Spanish peseta | 166.386 | 1999 |
| France, Monaco, Andorra[h] | French franc | 6.55957 | 1999 |
| Ireland | Irish pound | 0.787564 | 1999 |
| Italy, San Marino, Vatican City | Italian lira | 1936.27 | 1999 |
| Netherlands | Dutch guilder | 2.20371 | 1999 |
| Austria | Austrian schilling | 13.7603 | 1999 |
| Portugal | Portuguese escudo | 200.482 | 1999 |
| Finland | Finnish markka | 5.94573 | 1999 |
| Greece | Greek drachma | 340.750 | 2001 |
| Slovenia | Slovenian tolar | 239.640 | 2007 |
| Cyprus | Cypriot pound | 0.585274 | 2008 |
| Malta | Maltese lira | 0.429300 | 2008 |
| Slovakia | Slovak koruna | 30.1260 | 2009 |
| Estonia | Estonian kroon | 15.6466 | 2011 |
| Latvia | Latvian lats | 0.702804 | 2014 |
| Lithuania | Lithuanian litas | 3.45280 | 2015 |
Future enlargement

Eight countries (Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Sweden) are EU members but do not use the euro. Before joining the eurozone, a state must spend at least two years in the European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II). As of September 2020, the Danish central bank, Bulgarian central bank, and Croatian central bank participate in ERM II.
Denmark obtained a special opt-out in the original Maastricht Treaty, and thus is legally exempt from joining the eurozone unless its government decides otherwise, either by parliamentary vote or referendum. The United Kingdom likewise had an opt-out prior to withdrawing from the EU in 2020.
The remaining seven countries are obliged to adopt the euro in future, although the EU has so far not tried to enforce any time plan. They should join as soon as they fulfill the convergence criteria, which include being part of ERM II for two years. Sweden, which joined the EU in 1995 after the Maastricht Treaty was signed, is required to join the eurozone. However, the Swedish people turned down euro adoption in a 2003 referendum and since then the country has intentionally avoided fulfilling the adoption requirements by not joining ERM II, which is voluntary.[31][32] Bulgaria and Croatia joined ERM II on 10 July 2020.[33]
Interest in joining the eurozone increased in Denmark, and initially in Poland, as a result of the 2008 financial crisis. In Iceland, there was an increase in interest in joining the European Union, a pre-condition for adopting the euro.[34] However, by 2010 the debt crisis in the eurozone caused interest from Poland, as well as the Czech Republic, to cool.[35]
Expulsion and withdrawal
In the opinion of journalist Leigh Phillips and Locke Lord's Charles Proctor,[36][37] there is no provision in any European Union treaty for an exit from the eurozone. In fact, they argued, the Treaties make it clear that the process of monetary union was intended to be "irreversible" and "irrevocable".[37] However, in 2009, a European Central Bank legal study argued that, while voluntary withdrawal is legally not possible, expulsion remains "conceivable."[38] Although an explicit provision for an exit option does not exist, many experts and politicians in Europe, have suggested an option to leave the Eurozone should be included in the relevant treaties.[39]
On the issue of leaving the eurozone, the European Commission has stated that "[t]he irrevocability of membership in the euro area is an integral part of the Treaty framework and the Commission, as a guardian of the EU Treaties, intends to fully respect [that irrevocability]."[40] It added that it "does not intend to propose [any] amendment" to the relevant Treaties, the current status being "the best way going forward to increase the resilience of euro area Member States to potential economic and financial crises.[40] The European Central Bank, responding to a question by a Member of the European Parliament, has stated that an exit is not allowed under the Treaties.[41]
Likewise there is no provision for a state to be expelled from the euro.[42] Some, however, including the Dutch government, favour the creation of an expulsion provision for the case whereby a heavily indebted state in the eurozone refuses to comply with an EU economic reform policy.[43]
In a Texas law journal, University of Texas at Austin law professor Jens Dammann has argued that even now EU law contains an implicit right for member states to leave the Eurozone if they no longer meet the criteria that they had to meet in order to join it.[44] Furthermore, he has suggested that, under narrow circumstances, the European Union can expel member states from the eurozone.[45]
University of California, Berkeley professor of Economics and Political Science Barry Eichengreen, argued in 2007 that "Europe’s leap to monetary union was a mistake...compounded by...including [in the union] also...Italy, Spain, Portugal and Greece," and that "although a breakup was not impossible...it was unlikely," given the technical, political and above all economic obstacles. "On the first minute that word got out," Eisengreen argued, "that the [Greek] government was discussing the possibility [of a Grexit] investors would sell their Greek stocks and bonds" and there "would be a full-fledged financial panic... a full-out bank run."[46] In 2011, he still believed the probability of Grexit was "very low" and in case of any bank run "the Greek government would almost certainly receive support for its banks from its European Union partners and the European Central Bank, because, in his view, more financial crises in other European countries are... the last thing that German business wants." As he put it, "the German economic miracle of the last ten years can be summed up in one word: exports. And the country’s export competitiveness has been greatly enhanced by a euro exchange rate that has been kept down at reasonable levels by the fact that Germany shares the currency with other weaker economies."[46]
In Greece's case, one additional obstacle presented by analysts is that if Greece were to replace the euro with a new national currency, this would not be possible to achieve quickly enough. Paper banknotes must be printed and coins minted, which would take about "six months."[47] The changeover, according to a blogger in The Economist, would likely require bank deposits to be converted from euros to the new currency and this prospect could lead to money leaving the country as well as Greek residents withdrawing cash from the banks, causing a bank run and necessitating capital controls.[48] This was not only a blogger statement, as Greece actually had tendencies of bank runs, and capital controls were in effect, without any decision of withdrawal, only media rumours of it.
Administration and representation

The monetary policy of all countries in the eurozone is managed by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Eurosystem which comprises the ECB and the central banks of the EU states who have joined the eurozone. Countries outside the eurozone are not represented in these institutions. Whereas all EU member states are part of the European System of Central Banks (ESCB), non EU member states have no say in all three institutions, even those with monetary agreements such as Monaco. The ECB is entitled to authorise the design and printing of euro banknotes and the volume of euro coins minted, and its president is currently Christine Lagarde.
The eurozone is represented politically by its finance ministers, known collectively as the Eurogroup, and is presided over by a president, currently Paschal Donohoe. The finance ministers of the EU member states that use the euro meet a day before a meeting of the Economic and Financial Affairs Council (Ecofin) of the Council of the European Union. The Group is not an official Council formation but when the full EcoFin council votes on matters only affecting the eurozone, only Euro Group members are permitted to vote on it.[49][50][51]
Since the global financial crisis of 2007–2008, the Euro Group has met irregularly not as finance ministers, but as heads of state and government (like the European Council). It is in this forum, the Euro summit, that many eurozone reforms have been decided upon. In 2011, former French President Nicolas Sarkozy pushed for these summits to become regular and twice a year in order for it to be a 'true economic government'.
Reform
In April 2008 in Brussels, future European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker suggested that the eurozone should be represented at the IMF as a bloc, rather than each member state separately: "It is absurd for those 15 countries not to agree to have a single representation at the IMF. It makes us look absolutely ridiculous. We are regarded as buffoons on the international scene".[52] In 2017 Juncker stated that he aims to have this agreed by the end of his mandate in 2019.[53] However, Finance Commissioner Joaquín Almunia stated that before there is common representation, a common political agenda should be agreed upon.[52]
Leading EU figures including the commission and national governments have proposed a variety of reforms to the eurozone's architecture; notably the creation of a Finance Minister, a larger eurozone budget, and reform of the current bailout mechanisms into either a "European Monetary Fund" or a eurozone Treasury. While many have similar themes, details vary greatly.[54][55][56][57]
Economy

Comparison table
| Population | GDP(Nominal)a | |
|---|---|---|
| 328 million | $20.8 trillion | |
| 1400 million | $14.9 trillion | |
| 342 million | $12.7 trillion |
| Economy | Nominal GDP (billions in USD) - Peak year as of 2020
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (01) United States (Peak in 2019) | |||||||||
| (02) China (Peak in 2020) | |||||||||
| (03) |
|||||||||
| (04) Japan (Peak in 2012) | |||||||||
| (05) United Kingdom (Peak in 2007) | |||||||||
| (06) India (Peak in 2019) | |||||||||
| (07) Brazil (Peak in 2011) | |||||||||
| (08) Russia (Peak in 2013) | |||||||||
| (09) Canada (Peak in 2013) | |||||||||
| (10) Korea (Peak in 2018) | |||||||||
| (11) Australia (Peak in 2012) | |||||||||
| (12) Mexico (Peak in 2014) | |||||||||
| (13) Indonesia (Peak in 2019) | |||||||||
| (14) Turkey (Peak in 2013) | |||||||||
| (15) Saudi Arabia (Peak in 2018) | |||||||||
| (16) Switzerland (Peak in 2019) | |||||||||
| (17) Argentina (Peak in 2017) | |||||||||
| (18) Taiwan (Peak in 2020) | |||||||||
| (19) Poland (Peak in 2018) | |||||||||
| (20) Sweden (Peak in 2013) | |||||||||
|
The 20 largest economies in the world including Eurozone as a single entity, by Nominal GDP (2020) at their peak level of GDP in billions US$. The values for EU members that are not also eurozone members are listed both separately and as part of the EU.[59] | |||||||||
Inflation
HICP figures from the ECB, taken from May of each year:
|
|
|
|
Interest rates
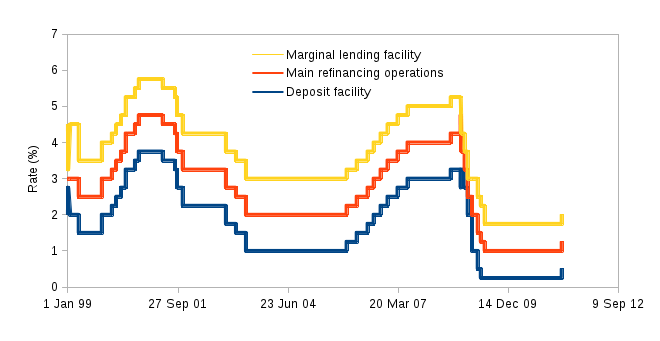
Interest rates for the eurozone, set by the ECB since 1999. Levels are in percentages per annum. Between June 2000 and October 2008, the main refinancing operations were variable rate tenders, as opposed to fixed rate tenders. The figures indicated in the table from 2000 to 2008 refer to the minimum interest rate at which counterparties may place their bids.[3]
| Date | Deposit facility |
Main refinancing operations |
Marginal lending facility |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1999-01-01 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.50 |
| 1999-01-04[i] | 2.75 | 3.00 | 3.25 |
| 1999-01-22 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.50 |
| 1999-04-09 | 1.50 | 2.50 | 3.50 |
| 1999-11-05 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 |
| 2000-02-04 | 2.25 | 3.25 | 4.25 |
| 2000-03-17 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 4.50 |
| 2000-04-28 | 2.75 | 3.75 | 4.75 |
| 2000-06-09 | 3.25 | 4.25 | 5.25 |
| 2000-06-28 | 3.25 | 4.25 | 5.25 |
| 2000-09-01 | 3.50 | 4.50 | 5.50 |
| 2000-10-06 | 3.75 | 4.75 | 5.75 |
| 2001-05-11 | 3.50 | 4.50 | 5.50 |
| 2001-08-31 | 3.25 | 4.25 | 5.25 |
| 2001-09-18 | 2.75 | 3.75 | 4.75 |
| 2001-11-09 | 2.25 | 3.25 | 4.25 |
| 2002-12-06 | 1.75 | 2.75 | 3.75 |
| 2003-03-07 | 1.50 | 2.50 | 3.50 |
| 2003-06-06 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 |
| 2005-12-06 | 1.25 | 2.25 | 3.25 |
| 2006-03-08 | 1.50 | 2.50 | 3.50 |
| 2006-06-15 | 1.75 | 2.75 | 3.75 |
| 2006-08-09 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 |
| 2006-10-11 | 2.25 | 3.25 | 4.25 |
| 2006-12-13 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 4.50 |
| 2007-03-14 | 2.75 | 3.75 | 4.75 |
| 2007-06-13 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 |
| 2008-07-09 | 3.25 | 4.25 | 5.25 |
| 2008-10-08 | 2.75 | 4.75 | |
| 2008-10-09 | 3.25 | 4.25 | |
| 2008-10-15 | 3.25 | 3.75 | 4.25 |
| 2008-11-12 | 2.75 | 3.25 | 3.75 |
| 2008-12-10 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.00 |
| 2009-01-21 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 |
| 2009-03-11 | 0.50 | 1.50 | 2.50 |
| 2009-04-08 | 0.25 | 1.25 | 2.25 |
| 2009-05-13 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 1.75 |
| 2011-04-13 | 0.50 | 1.25 | 2.00 |
| 2011-07-13 | 0.75 | 1.50 | 2.25 |
| 2011-11-09 | 0.50 | 1.25 | 2.00 |
| 2011-12-14 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 1.75 |
| 2012-07-11 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 1.50 |
| 2013-05-08 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| 2013-11-13 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 2014-06-11 | -0.10 | 0.15 | 0.40 |
| 2014-09-10 | -0.20 | 0.05 | 0.30 |
| 2015-12-09 | -0.30 | 0.05 | 0.30 |
| 2016-03-16 | -0.40 | 0.00 | 0.25 |
Public debt
The following table states the ratio of public debt to GDP in percent for eurozone countries given by EuroStat.[60] The euro convergence criterion is 60%.
| Country | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurozone | 64.9 | 69.6 | 80.2 | 85.8 | 87.7 | 90.7 | 92.6 | 92.8 | 90.9 | 90.1 | 87.7 | 85.8 |
| Austria | 64.7 | 68.7 | 79.7 | 82.4 | 82.2 | 81.9 | 91.3 | 84.0 | 86.2 | 83.6 | 78.4 | 74.0 |
| Belgium | 87.0 | 93.2 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 102.3 | 104.8 | 105.5 | 107.0 | 106.0 | 105.7 | 103.1 | 100.0 |
| Cyprus | 53.5 | 45.5 | 53.9 | 56.3 | 65.8 | 80.3 | 104.0 | 109.1 | 108.9 | 107.1 | 97.5 | 100.6 |
| Estonia | 3.7 | 4.5 | 7.0 | 6.6 | 5.9 | 9.8 | 10.2 | 10.6 | 9.7 | 9.4 | 9.0 | 8.4 |
| Finland | 34.0 | 32.6 | 41.7 | 47.1 | 48.5 | 53.6 | 56.2 | 59.8 | 63.1 | 63.1 | 61.4 | 59.0 |
| France | 64.3 | 68.8 | 79.0 | 81.7 | 85.2 | 90.6 | 93.4 | 94.9 | 95.8 | 96.5 | 97.0 | 98.4 |
| Germany | 63.7 | 65.5 | 72.4 | 81.0 | 78.3 | 81.1 | 78.7 | 75.6 | 71.2 | 68.1 | 64.1 | 61.9 |
| Greece | 103.1 | 109.4 | 126.7 | 146.2 | 172.1 | 161.9 | 178.4 | 180.2 | 176.9 | 180.8 | 178.6 | 181.2 |
| Ireland | 23.9 | 42.4 | 61.8 | 86.8 | 109.1 | 119.9 | 119.9 | 104.2 | 93.8 | 72.8 | 68.0 | 63.6 |
| Italy | 99.8 | 106.2 | 112.5 | 115.4 | 116.5 | 126.5 | 132.5 | 135.4 | 132.7 | 132 | 131.8 | 134.8 |
| Latvia | 8.0 | 18.6 | 36.6 | 47.5 | 42.8 | 42.2 | 40.0 | 41.6 | 36.4 | 40.6 | 40.1 | 36.4 |
| Lithuania | 15.9 | 14.6 | 29.0 | 36.2 | 37.2 | 39.7 | 38.7 | 40.5 | 42.7 | 40.1 | 39.7 | 34.1 |
| Luxembourg | 7.7 | 15.4 | 16.0 | 20.1 | 19.1 | 22.0 | 23.7 | 22.7 | 21.4 | 20.8 | 23.0 | 21.0 |
| Malta | 62.3 | 61.8 | 67.8 | 67.6 | 69.9 | 65.9 | 65.8 | 61.6 | 63.9 | 57.6 | 50.8 | 45.8 |
| Netherlands | 42.7 | 54.7 | 56.5 | 59.0 | 61.7 | 66.3 | 67.7 | 67.9 | 65.1 | 61.8 | 56.7 | 52.4 |
| Portugal | 68.4 | 75.6 | 83.6 | 96.2 | 111.4 | 129.0 | 131.4 | 132.9 | 129.0 | 130.1 | 125.7 | 122.2 |
| Slovakia | 30.1 | 28.6 | 41.0 | 43.3 | 43.3 | 51.8 | 54.7 | 53.6 | 52.9 | 51.8 | 50.9 | 49.4 |
| Slovenia | 22.8 | 21.8 | 36.0 | 40.8 | 46.6 | 53.6 | 70.0 | 80.3 | 83.2 | 78.5 | 73.6 | 70.4 |
| Spain | 35.6 | 39.7 | 52.7 | 60.1 | 69.5 | 86.3 | 95.8 | 100.7 | 99.2 | 99.0 | 98.3 | 97.6 |
Fiscal policies

The primary means for fiscal coordination within the EU lies in the Broad Economic Policy Guidelines which are written for every member state, but with particular reference to the 19 current members of the eurozone. These guidelines are not binding, but are intended to represent policy coordination among the EU member states, so as to take into account the linked structures of their economies.
For their mutual assurance and stability of the currency, members of the eurozone have to respect the Stability and Growth Pact, which sets agreed limits on deficits and national debt, with associated sanctions for deviation. The Pact originally set a limit of 3% of GDP for the yearly deficit of all eurozone member states; with fines for any state which exceeded this amount. In 2005, Portugal, Germany, and France had all exceeded this amount, but the Council of Ministers had not voted to fine those states. Subsequently, reforms were adopted to provide more flexibility and ensure that the deficit criteria took into account the economic conditions of the member states, and additional factors.
The Fiscal Compact[61][62] (formally, the Treaty on Stability, Coordination and Governance in the Economic and Monetary Union),[63] is an intergovernmental treaty introduced as a new stricter version of the Stability and Growth Pact, signed on 2 March 2012 by all member states of the European Union (EU), except the Czech Republic, the United Kingdom,[64] and Croatia (subsequently acceding the EU in July 2013). The treaty entered into force on 1 January 2013 for the 16 states which completed ratification prior of this date.[65] As of 1 April 2014, it had been ratified and entered into force for all 25 signatories.
Olivier Blanchard suggests that a fiscal union in the EZ can mitigate devastating effects of the single currency on the EZ peripheral countries. But he adds that the currency bloc will not work perfectly even if a fiscal transfer system is built, because, he argues, the fundamental issue about competitiveness adjustment is not tackled. The problem is, since the EZ peripheral countries do not have their own currencies, they are forced to adjust their economies by decreasing their wages instead of devaluation.[66]
Bailout provisions
The financial crisis of 2007–2008 prompted a number of reforms in the eurozone. One was a U-turn on the eurozone's bailout policy that led to the creation of a specific fund to assist eurozone states in trouble. The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) and the European Financial Stability Mechanism (EFSM) were created in 2010 to provide, alongside the International Monetary Fund (IMF), a system and fund to bail out members. However the EFSF and EFSM were temporary, small and lacked a basis in the EU treaties. Therefore, it was agreed in 2011 to establish a European Stability Mechanism (ESM) which would be much larger, funded only by eurozone states (not the EU as a whole as the EFSF/EFSM were) and would have a permanent treaty basis. As a result of that its creation involved agreeing an amendment to TEFU Article 136 allowing for the ESM and a new ESM treaty to detail how the ESM would operate. If both are successfully ratified according to schedule, the ESM would be operational by the time the EFSF/EFSM expire in mid-2013.
In February 2016, the UK secured further confirmation that countries that do not use the Euro would not be required to contribute to bailouts for Eurozone countries.[67]
Peer review
In June 2010, a broad agreement was finally reached on a controversial proposal for member states to peer review each other's budgets prior to their presentation to national parliaments. Although showing the entire budget to each other was opposed by Germany, Sweden and the UK, each government would present to their peers and the Commission their estimates for growth, inflation, revenue and expenditure levels six months before they go to national parliaments. If a country was to run a deficit, they would have to justify it to the rest of the EU while countries with a debt more than 60% of GDP would face greater scrutiny.[68]
The plans would apply to all EU members, not just the eurozone, and have to be approved by EU leaders along with proposals for states to face sanctions before they reach the 3% limit in the Stability and Growth Pact. Poland has criticised the idea of withholding regional funding for those who break the deficit limits, as that would only impact the poorer states.[68] In June 2010 France agreed to back Germany's plan for suspending the voting rights of members who breach the rules.[69] In March 2011 was initiated a new reform of the Stability and Growth Pact aiming at straightening the rules by adopting an automatic procedure for imposing of penalties in case of breaches of either the deficit or the debt rules.[70][71]
Criticism
Nobel prize-winning economist James Tobin thought that the euro project would not succeed without making drastic changes to European institutions, pointing out the difference between the US and the eurozone.[72] Concerning monetary policies, the US central bank FRB aims at both growth and reducing unemployment, while the ECB tends to give its first priority to price stability under the Bundesbank's supervision. As the price level of the currency bloc is kept low, the unemployment level of the region has become higher than that of US since 1982.[72]
When it comes to fiscal policies, 12 percent of the US federal budget is used for transfers to states and local governments. Also, when a state has financial or economic difficulties, a fair amount of money is automatically transferred to the state. The US government does not impose restrictions on state budget policies. This is different from the fiscal policies of the eurozone, where Treaty of Maastricht requires each eurozone member country to run its budget deficit smaller than 3 percent of its GDP.[72]
In February 2019, a study from the Centre for European Policy concluded that while some countries had gained from adopting the euro, several countries were poorer than they would have been had they not adopted it, with France and Italy being particularly affected. The authors argued that this was down to its effect on competitiveness; usually countries would devalue their currencies to make their exports cheaper on the world market but this was not possible due to the common currency.[73]
Economic policemen
In 1997, Arnulf Baring expressed concern that the European Monetary Union would make Germans the most hated people in Europe. Baring suspected the possibility that the people in Mediterranean countries would regard Germans and the currency bloc as economic policemen.[74]
See also
- Greek withdrawal from the eurozone
- List of acronyms associated with the eurozone crisis
- List of people associated with the eurozone crisis
- Sixpack (European Union law)
- Special member state territories and the European Union
- Economic and Monetary Union
- Capital Markets Union
- Banking Union
Notes
- ^ The self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus is not recognised by the EU and uses the Turkish lira. However the euro does circulate widely.[citation needed]
- ^ a b c French Pacific territories use the CFP franc, which is pegged to the euro.(1 franc = 0.00838 euro)
- ^ Aruba is part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, but not the EU. It uses the Aruban florin, which is pegged to the US dollar.(1 dollar = 1.79 florins)
- ^ a b Currently uses the Netherlands Antillean guilder and had planned to introduce the Caribbean guilder in 2014, although the change has been delayed. "FAQ - Central Bank". Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 16 May 2014. both are pegged to the US dollar.(1 dollar = 1.79 guilder)
- ^ Uses the US Dollar.
- ^ EZ is not assigned, but is reserved for this purpose, in ISO-3166-1.
- ^ Template:Kosovo-note
- ^ a b Andorra got a formal agreement on euro usage in 2011
- ^ The ECB announced on 22 December 1998 that, between 4 and 21 January 1999, there would be a narrow corridor of 50 base points interest rates for the marginal lending facility and the deposit facility in order to help the transition to the ECB's interest regime.
References
- ^ a b "Total population as of 1 January 2020. Euro area (19 countries)". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu.
- ^ https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2020/October/weo-report?a=1&c=163,&s=NGDPD,&sy=2019&ey=2025&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1
- ^ a b Key ECB interest rates Archived 11 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine, ECB
- ^ HICP – all items – annual average inflation rate Eurostat
- ^ Harmonised unemployment rate by gender – total Eurostat
- ^ https://www.reuters.com/article/eurozone-economy-currentaccount/euro-zone-2019-current-account-surplus-steady-at-31-gdp-ecb-idUSF9N2AB003
- ^ "Countries, languages, currencies". Interinstitutional style guide. the EU Publications Office. Retrieved 2 February 2009.
The euro area Archived 6 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine, European Central Bank - ^ "Who can join and when?". European Commission - European Commission. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ Fox, Benjamin (1 February 2013). "Dutch PM: Eurozone needs exit clause". EUobserver.com. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ^ a b "Agreements on monetary relations (Monaco, San Marino, the Vatican and Andorra)". European Communities. 30 September 2004. Retrieved 12 September 2006.
- ^ "The government announces a contest for the design of the Andorran euros". Andorra Mint. 19 March 2013. Archived from the original on 22 August 2013. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ "Nouvelles d'Andorre" (in French). 1 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2013.
- ^ a b c "The euro outside the euro area". Europa (web portal). Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ A glossary Archived 14 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine issued by the ECB defines "euro area", without mention of Monaco, San Marino, or the Vatican.
- ^ "GNI, Atlas method (current US$) | Data | Table". Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 23 June 2016.
- ^ "GNI per capita, Atlas method (current US$) | Data". Archived from the original on 28 October 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "COUNCIL DECISION of 3 May 1998 in accordance with Article 109j(4) of the Treaty". Official Journal of the European Union. L (139/30). 11 May 1998. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 10 July 2007 in accordance with Article 122(2) of the Treaty on the adoption by Cyprus of the single currency on 1 January 2008". Official Journal of the European Union. L (186/29). 18 July 2007. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 13 July 2010 in accordance with Article 140(2) of the Treaty on the adoption by Estonia of the euro on 1 January 2011". Official Journal of the European Union. L (196/24). 28 July 2010. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 19 June 2000 in accordance with Article 122(2) of the Treaty on the adoption by Greece of the single currency on 1 January 2001". Official Journal of the European Union. L (167/19). 7 July 2000. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 9 July 2013 on the adoption by Latvia of the euro on 1 January 2014". Official Journal of the European Union. L (195/24). 18 July 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 23 July 2014 on the adoption by Lithuania of the euro on 1 January 2015". Official Journal of the European Union. L (228/29). 31 July 2014. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 10 July 2007 in accordance with Article 122(2) of the Treaty on the adoption by Malta of the single currency on 1 January 2008". Official Journal of the European Union. L (186/32). 18 July 2007. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 8 July 2008 in accordance with Article 122(2) of the Treaty on the adoption by Slovakia of the single currency on 1 January 2009". Official Journal of the European Union. L (195/24). 24 July 2008. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "COUNCIL DECISION of 11 July 2006 in accordance with Article 122(2) of the Treaty on the adoption by Slovenia of the single currency on 1 January 2007". Official Journal of the European Union. L (195/25). 15 July 2006. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "European Foundation Intelligence Digest". Europeanfoundation.org. Archived from the original on 26 August 2007. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ^ "Euro used as legal tender in non-EU nations". International Herald Tribune. 1 January 2007. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- ^ "Europe, The eurozone's 13th member". BBC News. 11 December 2001. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ^ "Unilateral Euroization By Iceland Comes With Real Costs And Serious Risks". Lawofemu.info. 15 February 2008. Archived from the original on 14 March 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "New EU members to break free from euro duty". Euractiv.com. 13 September 2011. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- ^ "Sverige sa nej till euron" (in Swedish). Swedish Parliament. 28 August 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2014.
- ^ "Information on ERM II". European Commission. 22 December 2009. Retrieved 16 January 2010.
- ^ "Bulgaria, Croatia take vital step to joining euro". Reuters. 10 July 2020. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- ^ Dougherty, Carter (1 December 2008). "Buffeted by financial crisis, countries seek euro's shelter". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 2 December 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Czechs, Poles cooler to euro as they watch debt crisis". Reuters. 16 June 2010. Retrieved 18 June 2010.
- ^ "Brussels: No one can leave the euro" by Leigh Phillips, EUobserver, 8 September 2011
- ^ a b "The Eurozone crisis – the final stage?" by Charles Proctor, Locke Lord, 15 May 2012
- ^ "Withdrawal and Expulsion from the EU and EMU : Some reflections" by Phoebus Athanassiou, Principal Legal Counsel with the Directorate-General for Legal Service, ECB, 2009
- ^ "German advisory council calls for exit option in the eurozone" by Daniel Tost, EurActiv, 29 July 2015
- ^ a b Text of response by Olli Rehn, European Commissioner for Economic and Monetary Affairs and the Euro, on behalf of the European Commission, to question submitted by Claudio Morganti, Member of the European Parliament, 22 June 2012
- ^ Text of message by Mario Draghi, ECB, to Claudio Morganti, Member of the European Parliament, 6 November 2012
- ^ Athanassiou, Phoebus (December 2009) Withdrawal and Expulsion from the EU and EMU, Some Reflections (PDF), European Central Bank. Retrieved 8 September 2011
- ^ Phillips, Leigh. "EUobserver / Netherlands: Indebted states must be made 'wards' of the commission or leave euro". Euobserver.com. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ Dammann, Jens (10 February 2012). "The Right to Leave the Eurozone". U of Texas Law, Public Law Research Paper. 2013. 48 (2). SSRN 2262873.
- ^ Dammann, Jens (26 August 2015). "Paradise Lost: Can the European Union Expel Countries from the Eurozone". Vanderbilt Journal of Transnational Law. 2016. 49 (2). SSRN 2827699.
- ^ a b Eichengreen, Barry (23 July 2011)Can the Euro Area Hit the Rewind Button? (PDF), University of California. Retrieved 8 September 2011
- ^ Wallop, Harry (29 May 2012). "De La Rue silent on deal to print Drachma". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Take the money and run". The Economist. 28 January 2015. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ Treaty of Lisbon (Provisions specific to member states whose currency is the euro), EurLex Archived 27 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "An economic government for the eurozone?" (PDF). Federal Union. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ^ Protocols, Official Journal of the European Union
- ^ a b Elitsa Vucheva (15 April 2008). "Eurozone countries should speak with one voice, Juncker says". EU Observer. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ^ "Commission wants single eurozone seat at IMF plan adopted by end of mandate", Euractiv, 7 December 2017
- ^ "Macron is right — the eurozone needs a finance minister", Financial Times, 28 September 2017
- ^ Europe should have its own economy and finance minister, says EC, theguardian 6 December 2017
- ^ "Large number of EU finance ministers want euro zone budget: Dijsselbloem", Reuters, 6 November 2017
- ^ "Spain urges sweeping reforms on eurozone to correct flaws", Financial Times, 14 June 2017
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.imf.org.
- ^ Figures from the October 2020 update of the International Monetary Fund's World Economic Outlook Database. [1]
- ^ "General government gross debt - annual data (table code: teina225)". Eurostat. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Nicholas Watt (31 January 2012). "Lib Dems praise David Cameron for EU U-turn". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 5 February 2012.
- ^ "The fiscal compact ready to be signed". European Commission. 31 January 2012. Archived from the original on 22 October 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2012.
- ^ "Referendum to be held on Fiscal Treaty". RTÉ News. 28 February 2012.
- ^ "EU summit: All but two leaders sign fiscal treaty". BBC News. 2 March 2012. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- ^ "Fiscal compact enters into force 21/12/2012 (Press: 551, Nr: 18019/12)" (PDF). European Council. 21 December 2012. Retrieved 21 December 2012.
- ^ Fiscal union will never fix a dysfunctional eurozone, warns ex-IMF chief Blanchard Mehreen Khan, The Daily Telegraph (London), 10 October 2015
- ^ "European Council meeting (18 and 19 February 2016) – Conclusions". European Commission. Retrieved 14 May 2016.
- ^ a b EU agrees controversial peer review of national budgets, EU Observer
- ^ Willis, Andrew (15 June 2010) Merkel: Spain can access aid if needed, EU Observer
- ^ "Council reaches agreement on measures to strengthen economic governance" (PDF). Retrieved 18 May 2011.
- ^ Jan Strupczewski (15 March 2011). "EU finmins adopt tougher rules against debt, imbalance". Uk.finance.yahoo.com. Yahoo! Finance. Retrieved 18 May 2011.[dead link]
- ^ a b c J. Tobin, Policy Opinions, 31 (2001)
- ^ Nicole Ng, "CEP study: Germans gain most from euro introduction", Deutsche Welle, 25/02/19, accessed 05/03/19
- ^ This Prediction about the Euro Deserves a ‘Nostradamus Award’ W. Richter, Wolf Street, 16 July 2015