Ethyl cyanoacrylate: Difference between revisions
Added in Category:Sweet-smelling chemicals |
|||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
==Applications== |
==Applications== |
||
Ethyl cyanoacrylate is used for gluing various materials. It is also used in medicine, for [[liquid bandage]]s and for [[surgical suture|suture]]-less surgery, but it is used less often than the less toxic [[Butyl cyanoacrylate|''n''-butyl]] and [[octyl cyanoacrylate]]s. Off-the-shelf consumer glues are unsuitable for medical applications, as they are not medical-grade, which means their solvent and cyanoacrylate formulations have not been evaluated and optimized to reduce toxicity and prevent foreign body reactions, as would be the case with medical cyanoacrylates<ref>http://www.miracleglue.com/wounds.htm</ref> |
Ethyl cyanoacrylate is used for gluing various materials. It is also used in medicine, for [[liquid bandage]]s and for [[surgical suture|suture]]-less surgery, but it is used less often than the less toxic [[Butyl cyanoacrylate|''n''-butyl]] and [[octyl cyanoacrylate]]s. Off-the-shelf consumer glues are unsuitable for medical applications, as they are not medical-grade, which means their solvent and cyanoacrylate formulations have not been evaluated and optimized to reduce toxicity and prevent foreign body reactions, as would be the case with medical cyanoacrylates<ref>http://www.miracleglue.com/wounds.htm</ref> |
||
In Forensics, Cyanoacrylate Ester has also been found to have excellent non-destructive impressioning abilities, which are especially important when lifting fingerprints from delicate evidence items, or when the prints could not be lifted using traditional means such as fingerprinting powder. The procedure involves heating the acrylate in a sealed chamber. Its fumes then seek out deposited proteins that form into a white, stable, and clear print outlines. The resulting prints could be used as is or enhanced further by staining them with darker pigments.<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5514188/</ref><ref>https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329210209_The_Effect_of_Cyanoacrylate_Fuming_on_Subsequent_Protein_Stain_Enhancement_of_Fingermarks_in_Blood</ref> |
|||
After curing, the resulting resin softens at temperatures above {{Cvt|150|C|}}. The service temperature of the joint is {{Cvt|-54|to|82|C}}. Its [[dielectric constant]] at 1 [[MegaHertz|megahertz]] is 3.33.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.palmlabsadhesives.com/technical_data.htm |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2008-12-08 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20081208044317/http://www.palmlabsadhesives.com/technical_data.htm |archivedate=2008-12-08 }}</ref> |
After curing, the resulting resin softens at temperatures above {{Cvt|150|C|}}. The service temperature of the joint is {{Cvt|-54|to|82|C}}. Its [[dielectric constant]] at 1 [[MegaHertz|megahertz]] is 3.33.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.palmlabsadhesives.com/technical_data.htm |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2008-12-08 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20081208044317/http://www.palmlabsadhesives.com/technical_data.htm |archivedate=2008-12-08 }}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 05:08, 14 June 2021
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl 2-cyanoprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Ethyl 2-cyanoacrylate; ECA; Ethyl alpha-cyanoacrylate; 910EM; ace-ee; CN2; CN4; Cemedine 3000rs; Krazy glue; Permabond 105 : Permabond 200; Super glue; Pro grip 4000; TK 200; TK 201; Cyanolite 201; Cyanacrine; Cyano-Veneer
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.628 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1993 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 125.127 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL |
| Melting point | −22 °C (−8 °F; 251 K) |
| Boiling point | 54 to 56 °C (129 to 133 °F; 327 to 329 K) at 3 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 83 °C (181 °F; 356 K) |
Threshold limit value (TLV)
|
0.2 ppm |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
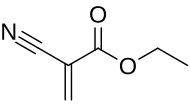
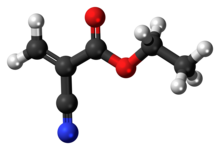
Ethyl cyanoacrylate (ECA), a cyanoacrylate ester, is an ethyl ester of 2-cyano-2-propenoic acid. It is a colorless liquid with low viscosity and a faint sweet smell in pure form. It is the main component of cyanoacrylate glues and can be encountered under many trade names.[1] It is soluble in acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, nitromethane, and methylene chloride.[2] ECA polymerizes rapidly in presence of moisture.
Production
Ethyl cyanoacrylate is prepared by the condensation of formaldehyde with ethyl cyanoacetate:
- CH
2(C≡N)CO
2Et + CH
2O → H
2C
2Et + H
2O
This exothermic reaction affords the polymer, which is subsequently sintered, thermally "cracked" to give the monomer. Alternatively, it can be prepared by the ethoxycarbonylation of cyanoacetylene.[1]
Applications
Ethyl cyanoacrylate is used for gluing various materials. It is also used in medicine, for liquid bandages and for suture-less surgery, but it is used less often than the less toxic n-butyl and octyl cyanoacrylates. Off-the-shelf consumer glues are unsuitable for medical applications, as they are not medical-grade, which means their solvent and cyanoacrylate formulations have not been evaluated and optimized to reduce toxicity and prevent foreign body reactions, as would be the case with medical cyanoacrylates[3]
In Forensics, Cyanoacrylate Ester has also been found to have excellent non-destructive impressioning abilities, which are especially important when lifting fingerprints from delicate evidence items, or when the prints could not be lifted using traditional means such as fingerprinting powder. The procedure involves heating the acrylate in a sealed chamber. Its fumes then seek out deposited proteins that form into a white, stable, and clear print outlines. The resulting prints could be used as is or enhanced further by staining them with darker pigments.[4][5]
After curing, the resulting resin softens at temperatures above 150 °C (302 °F). The service temperature of the joint is −54 to 82 °C (−65 to 180 °F). Its dielectric constant at 1 megahertz is 3.33.[6]
Safety
In the U.S., the threshold limit value for ECA is 0.2 ppm. Heating causes depolymerization of the cured poly-ECA, producing gaseous products which are a strong irritant to the lungs and eyes.
See also
References
- ^ a b Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Takahisa; Shimizu, Noboru; Prescher, Günter; Schwind, Helmut; Weiberg, Otto; Marten, Klaus; Greim, Helmut; Shaffer, Timothy D.; Nandi, Partha (2020). "Acrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 1–21. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_161.pub4. ISBN 9783527303854.
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20090603175358/http://palmlabsadhesives.com/technical_data.htm
- ^ http://www.miracleglue.com/wounds.htm
- ^ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5514188/
- ^ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329210209_The_Effect_of_Cyanoacrylate_Fuming_on_Subsequent_Protein_Stain_Enhancement_of_Fingermarks_in_Blood
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-12-08. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
