Love (band): Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|American rock group}} |
{{short description|American rock group}} |
||
{{About|the American rock band|the Japanese pop duo|Love (Japanese band) |
{{About|the American rock band|the Japanese pop duo|Love (Japanese band)}} |
||
{{confuse|1==Love}} |
|||
{{Infobox musical artist |
{{Infobox musical artist |
||
| name = Love |
| name = Love |
||
Revision as of 03:13, 16 June 2021
Love | |
|---|---|
![Love in 1967 (L-R: Johnny Echols, Bryan MacLean, Arthur Lee [top], Ken Forssi, Michael Stuart)](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c3/LOVE60s.png/250px-LOVE60s.png) | |
| Background information | |
| Also known as | Love Revisited |
| Origin | Los Angeles, California, U.S. |
| Genres | |
| Years active |
|
| Members |
|
| Past members | See members section |
| Website | love-revisited |
Love was an American psychedelic and folk-rock band formed in Los Angeles in 1965. Led by Arthur Lee, Love was one of the first racially diverse American rock bands. Their style drew from an eclectic range of sources including hard rock, blues, jazz, flamenco, and orchestral pop.[5]
While finding only modest success on the music charts, peaking in 1966 with their Top 40 hit "7 and 7 Is", Love would come to be praised by critics as their third album, Forever Changes (1967), became generally regarded as one of the best albums of the 1960s. It was added to the Library of Congress's National Recording Registry in 2011.[6]
History
Formation and early years
Singer/multi-instrumentalist Arthur Lee, who was originally from Memphis, Tennessee but had lived in Los Angeles since the age of five, had been recording since 1963 with his bands the LAG's and Lee's American Four. He wrote and produced the single "My Diary" for Rosa Lee Brooks in 1964, which featured Jimi Hendrix on guitar.[7] The Sons Of Adam, which included future Love drummer Michael Stuart, recorded the Lee composition "Feathered Fish". After attending a performance by the Byrds, Lee decided to form a band that joined the newly minted folk-rock sound of the Byrds to his primarily rhythm and blues style.[8]
Singer/guitarist Bryan MacLean, who had met Lee when he was working as a roadie for The Byrds, joined Lee's new band, which was first called the Grass Roots. MacLean had also been playing in bands around Los Angeles since about 1963.[9][10] Also joining the band was another Memphis native, lead guitarist Johnny Echols, and drummer Don Conka. A short time later, Conka was replaced by Alban "Snoopy" Pfisterer. Love's first bassist, Johnny Fleckenstein, went on to join the Standells in 1967. Fleckenstein was replaced by Ken Forssi (formerly of a post-"Wipe Out" lineup of The Surfaris).[11] Upon the appearance of another group called The Grass Roots, Lee changed the name of the new band to Love.[8]
Love started playing the Los Angeles clubs in April 1965 and became a popular local attraction, while gaining the attention of the Rolling Stones and the Yardbirds.[11] The band lived communally in a house called "the Castle" and their first two albums included photographs shot in the garden of that house.[12]
Signed to Elektra Records as the label's first rock act,[13] the band scored a minor hit single in 1966 with their version of Burt Bacharach and Hal David's "My Little Red Book". Their first album, Love, was released in March 1966. The album sold moderately well and reached No. 57 on the Billboard 200 chart.[8] The single "7 and 7 Is", released in July 1966, gained notice for the exceptional guitar work of Johnny Echols and proto-punk style drumming of Pfisterer. The single became Love's highest-charting single at No. 33 in the Billboard Hot 100.[8] Two more members were added around this time, Tjay Cantrelli (real name John Barbieri) on woodwinds and Michael Stuart on drums. Pfisterer, never a confident drummer, switched to harpsichord.[11] Elektra's art director, William S. Harvey, designed a distinctive logo for the band, "four cartoonish letters with exaggerated, curvaceous serifs", incorporating male and female symbols.[14]
Forever Changes era

Love's second album, Da Capo, was released in November 1966 and included "7 and 7 Is" as well as the subsequent singles "She Comes in Colors" and "¡Que Vida!".[15] It marked the experimental direction Arthur wanted to take. With the seven member lineup for DaCapo, shortly after this album, Cantrelli and Pfisterer left the band, leaving it as a five-piece once again.[8] Their third album Forever Changes was released in November 1967 and was co-produced by Bruce Botnick.[16] The album displayed a softer and more avant-garde approach for the band.[17] By this time, tension arose between Arthur Lee and Bryan MacLean, who wanted more of his songs on the album.[10] The band recorded the album in only 64 hours, though many professional session players were utilized, including some who replaced the actual band members in some songs.[18] Writer Richard Meltzer, in his book The Aesthetics of Rock, commented on Love's "orchestral moves", "post-doper word contraction cuteness", and Lee's vocal style that serves as a "reaffirmation of Johnny Mathis".[19] Forever Changes included one hit single, MacLean's "Alone Again Or". By this stage, Love were far more popular in the UK, where the album reached No. 24, than in their home country, where it could only reach No. 154.[8] Forever Changes has since received recognition as one of the greatest rock albums of all time, appearing on Rolling Stone magazine's list of The 500 Greatest Albums of All Time,[20] being inducted into the Grammy Hall of Fame, and added to the Library of Congress's National Recording Registry in 2011.[21]
Later years
For unclear reasons, Bryan MacLean left the band after Forever Changes[9] (though one possible issue was a solo deal that he had signed with Elektra[22]), while Lee dismissed all the other members.[11] MacLean later reemerged as a Contemporary Christian artist.[9] Johnny Echols and Ken Forssi succumbed to drug addiction and crime, and disappeared from the music scene;[23] and drummer Michael Stuart also retired from music.[12] Echols eventually moved to New York and became an in-demand studio musician.[24]
Arthur Lee, as the only remaining member, convened a new lineup of Love with Jay Donnellan (soon replaced by Gary Rowles) on guitar, Frank Fayad on bass, and George Suranovich on drums. This lineup played in a blues rock style, as opposed to the folk-rock and psychedelic styles of the band's previous incarnation. The new line-up never garnered the widespread acceptance or acclaim of the original group.[11] Three albums were released by various permutations of this lineup: Four Sail (1969), Out Here (1969), and False Start (1970).[8] The last featured a guest appearance by Jimi Hendrix.[25] Another album by this incarnation of the band was recorded in 1971, but the material was not released until 2009 on the compilation album Love Lost.[26] Arthur Lee released the solo album Vindicator in 1972.[27] Another lost Love album titled Black Beauty was recorded in 1973 by a new lineup featuring guitarist Melvan Whittington, bassist Robert Rozelle, and drummer Joe Blocker, but Arthur Lee's record label went out of business before it was released. The album was finally released by High Moon Records in 2012.[28] The final official Love album, Reel to Real (1974), was recorded by Lee and session musicians.[29]
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, there were various attempts to reunite the original Love lineup. At the suggestion of late-period guitarist John Sterling, Arthur Lee and Bryan MacLean reunited for one show in 1978, which was recorded and released as Love Live in 1980.[11] Material from Out Here plus four previously unreleased live tracks was released as Studio/Live in 1982.[11] Arthur Lee was largely inactive in the 1980s and only made sporadic onstage appearances with pick-up bands.[7]
Lee reemerged in 1992 with a new album titled Five String Serenade, released under the name Arthur Lee & Love.[30] The album's title track was later covered by Mazzy Star.[31] Lee then returned to semi-regular performing, often backed by the band Baby Lemonade.[32] In 1995, Rhino Records released the compilation Love Story, a two-disc set with extensive liner notes which chronicled the band's 1966–1972 period.[33]
Ken Forssi, bassist for the classic Love lineup, died of a suspected brain tumor at age 54 on January 5, 1998.[23] Bryan MacLean died of a heart attack at age 52 on December 25, 1998 while having dinner with a young fan who was researching a book about Love.[34] Arthur Lee was in prison when both of these former bandmates died.[35]
Reformation and reunions
After spending six years in prison from 1995 to 2001 for firearms offenses, Lee began touring under the name Love with Arthur Lee, with the members of Baby Lemonade rounding out the lineup.[36] In 2002 Michael Stuart (now known as Michael Stuart-Ware), the drummer on the Love albums Da Capo and Forever Changes, wrote the acclaimed book Behind the Scenes on the Pegasus Carousel with the Legendary Rock Group Love.[37]

Johnny Echols joined Lee's latest group for a special Forever Changes 35th Anniversary performance in the spring of 2003 and again for tours in 2004 and 2005.[33] Due to Arthur Lee's battle with acute myeloid leukemia, the details of which were not known by the band at the time, he could not participate in the final tour in 2005. Since no one knew of his illness, Lee's decision to forgo the final tour was met with confused reactions.[7] The remaining members of the band, led by Echols, continued to perform without Lee, under the name The Love Band.[33]
Michael Stuart-Ware and Johnny Echols performed with Baby Lemonade at Hollywood's Whisky A Go-Go on June 28, 2006 in a benefit concert for Arthur Lee. The show included guest appearances by Robert Plant and Nils Lofgren. Lee died of acute myeloid leukemia on August 3, 2006 at age 61.[7]
In 2009, a reformed version of Love, featuring Johnny Echols, members of Baby Lemonade, and Probyn Gregory of the Wondermints, toured the United States and Canada. Michael Stuart-Ware was listed as a member of this act for a time in 2009. The group continued to tour sporadically in the following years under the name The Love Band featuring Johnny Echols.[38] This group completed its farewell tour of the UK in 2019.[39]
On June 25, 2019, The New York Times Magazine listed Love among hundreds of artists whose material was reportedly destroyed in the 2008 Universal fire.[40]
Influence
Today, Love's critical reputation exceeds the limited success they experienced during their time;[11] their 1967 album Forever Changes is held in particularly high regard and often appears on lists of the best rock albums of all time.[41] During their late-1960s heyday, the Rolling Stones and the Doors were known to be Love fans.[12] Many modern bands influenced by psychedelic rock list Love as a major inspiration,[42] such as Primal Scream,[43] The Stone Roses,[44] and The Jesus and Mary Chain.[43] Robert Plant cites Forever Changes as one of his favorite albums.[45]
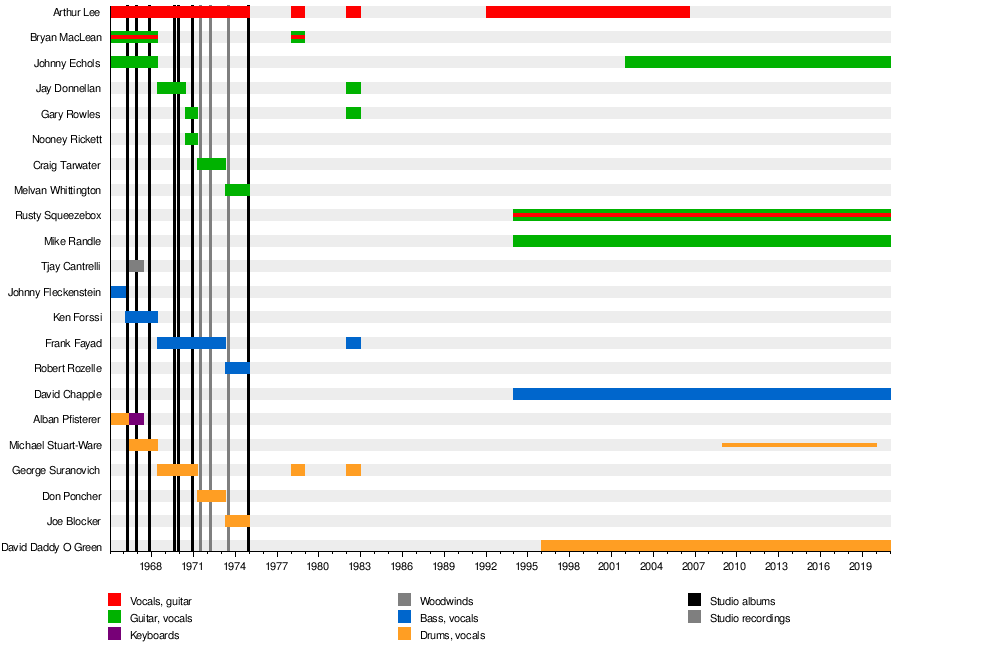
Members
Current members
classic lineup members are in bold
- Johnny Echols – lead guitar (1965–68, 2002–Present)
- Rusty Squeezebox – guitar, vocals (1994–Present)
- Mike Randle – guitar (1994–Present)
- David "Daddy O" Green – drums (1994–Present)
- David Chapple – bass guitar (1996–Present)
Former members
classic lineup members are in bold
- Arthur Lee – songwriter, vocals, guitar, piano, percussion, harmonica (1965–75, 1978, 1982, 1992–2006; died 2006)
- Bryan MacLean – songwriter, rhythm guitar, vocals (1965–68, 1978; died 1998)
- Alban "Snoopy" Pfisterer – drums, organ, harpsichord (1965–67)
- Larry Pincock – drums (1965–1966; died 2012)
- Johnny "Fleck" Fleckenstein – bass guitar (1965–1966, died 2017[46])
- Don Conka – drums (1965; died 2004)
- Ken Forssi – bass guitar (1966–68; died 1998)
- Michael Stuart-Ware – drums (1966–68, special guest from 2009)
- Tjay Cantrelli (born John Barberis) – woodwind (1966–67; died 1985)
- Frank Fayad – bass guitar, backing vocal (1968–73, 1982; died 2014)
- George Suranovich – drums, backing vocal (1968–70, 1978, 1982; died 1990)
- Jay Donnellan – lead guitar (1968–69, 1982)
- Drachen Theaker – drums (1968–69; died 1992)
- Gary Rowles – lead guitar (1969–71, 1982)
- Nooney Rickett – guitars (1969–71)
- Paul Martin – guitars (1969)
- Don Poncher – drums (1971–1973)
- Craig Tarwater – guitar (1971–1973)
- Melvan Whittington – guitar (1973–1975; died 2015)
- Robert Rozelle – bass (1973–1975)
- Joe Blocker – drums (1973–1975)
- Probyn Gregory – multiple instruments (2009)
- Justin Polimeni – drums (1992-1993)
- Bobby Beausoleil - guitar
Timeline
Discography
- Love (1966)
- Da Capo (1966)
- Forever Changes (1967)
- Four Sail (1969)
- Out Here (1969)
- False Start (1970)
- Reel to Real (1974)
- Love Lost (2009, compilation)
- Black Beauty (2012, compilation)
References
- ^ Prince, Patrick (31 March 2011). "New label to release Love's 'Black Beauty'". Goldmine. Retrieved 17 September 2016.
- ^ Unterberger, Richie. "Love – Artist Biography". AllMusic. All Media Network. Retrieved October 28, 2016.
- ^ Einarson, John (2001). Desperados: The Roots of Country Rock. Cooper Square Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-8154-1065-2.
- ^ SPIN Media LLC (October 2006). SPIN. SPIN Media LLC. p. 52. ISSN 0886-3032.
- ^ "Love > Charts & Awards". AllMusic. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- ^ "Forever Changes". www.etsu.edu. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b c d Sullivan, James (2006-08-04). "Arthur Lee (1945-2006)". Rolling Stone. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b c d e f g Strong, Martin C. (2000). The Great Rock Discography (5th ed.). Edinburgh: Mojo Books. pp. 585–586. ISBN 1-84195-017-3.
- ^ a b c "Bryan MacLean | Biography & History". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b Tobler, John (1999-01-02). "Bryan Maclean obituary". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Love | Biography & History". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b c February 2016, Max Bell19. "The Man Who Inspired Hendrix: The Crazy World Of Arthur Lee & Love". Classic Rock Magazine. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Love's Main Man Looks Back on the '60s, Man : Arthur Lee, leader of Elektra's first rock band, talks about the Doors, the Byrds and Mick Jagger". Los Angeles Times. 1993-08-26. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Jim K. Davies, "Love", Band Logo Jukebox. Retrieved 25 June 2020
- ^ "Da Capo - Love | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Unterberger, Richie. "Bruce Botnick Interview". Richieunterberger.com. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
- ^ "Forever Changes - Love | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Forever Changes by Love album review | Classic Rock Review". Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Meltzer, Richard (1987). The Aesthetics Of Rock. Hachette Books. ISBN 0306802872.
- ^ "The 500 Greatest Albums of All Time". Rolling Stone (Special Issue). 40 | Forever Changes – Love. November 2003. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- ^ "Love, Dead in National Recording Registry". psychedelicsight.com. Retrieved 23 May 2012.
- ^ "LOVE STORY - Record Collector Magazine". recordcollectormag.com. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b Scribner, Sara (1999-03-25). "Love hurts". Dallas Observer. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Breznikar, Klemen (December 29, 2017). "Love interview with Johnny Echols". It's Psychedelic Baby! Magazine. Archived from the original on January 2, 2018. Retrieved February 18, 2020.
- ^ "False Start - Love | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Love Lost - Love | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Vindicator - Arthur Lee | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Love: Black Beauty Review". pastemagazine.com. 2014-11-11. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Reel to Real - Love | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Five String Serenade - Arthur Lee | Song Info". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "So Tonight That I Might See - Mazzy Star | Songs, Reviews, Credits". AllMusic. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Love Backing Band Splits With Arthur Lee". Billboard. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b c "Love - Interview with Johnny Echols". www.pennyblackmusic.co.uk. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ "Obituary: Bryan MacLean". The Independent. 1999-01-01. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Greenwald, Matthew (2001-12-12). "Love's Arthur Lee to Be Free". Rolling Stone. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Greenwald, Matthew (2002-08-09). "Arthur Lee's New Love". Rolling Stone. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ James, Falling (2010-07-28). "Book Review: "Forever Changes: Arthur Lee and the Book of Love," by John Einarson". LA Weekly. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Lyng, Eoghan (2019-01-21). "A Piece of Love: An Interview with Johnny Echols". Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Simon Godley, "Farewell UK Tour from The Love Band featuring Johnny Echols", GodIsInTheTV, 11 December 2018. Retrieved 5 July 2019
- ^ Rosen, Jody (25 June 2019). "Here Are Hundreds More Artists Whose Tapes Were Destroyed in the UMG Fire". The New York Times. Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- ^ Jeff Weiss (8 November 2017). "Love's Forever Changes May Be the Greatest Album Ever Made in L.A." laweekly.com.
- ^ Goodman, Dean; Reuters (2006-08-09). "Arthur Lee, influential musician in the band Love, dies". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
{{cite web}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Hodgkinson, Will (2008-05-18). "Soundtrack of my life: Bobby Gillespie". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Guardian Staff (2009-03-15). "Flashback: March 1989: The Stone Roses". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ Rolling Stone Magazine (May 5, 2005). "Q&A: Robert Plant". Retrieved 2009-04-19.
- ^ "Larry Tamblyn". Facebook.com. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
External links
- Official site of Arthur Lee
- Fan Love site by Torben Skott
- Complete Love discography – With track listings, personnel and lyrics.
- The Boston Phoenix July 2008
- Acid rock music groups
- Elektra Records artists
- Folk rock groups from California
- Harvest Records artists
- Blue Thumb Records artists
- Musical groups established in 1965
- Musical groups disestablished in 1996
- Musical groups reestablished in 2002
- Musical groups disestablished in 2005
- Musical groups reestablished in 2009
- Musical groups from Los Angeles
- Psychedelic pop music groups
- Psychedelic rock music groups from California
- RSO Records artists
- Freak scene
- Freak artists
