Disulfur monoxide: Difference between revisions
white space |
consolidate plausible material |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Disulfur monoxide''' or '''sulfur suboxide''' is an [[inorganic compound]] with formula S<sub>2</sub>O. It is one of the [[lower sulfur oxides]]. It is a colourless gas and condenses to give a pale coloured solid that is unstable at room temperature.<ref name=Steudel>{{cite book|first=R.|last=Steudel|contribution=Sulfur-Rich Oxides S<sub>''n''</sub>O and S<sub>''n''</sub>O<sub>2</sub>|title=Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur-Rich Compounds II|editor-last=Steudel|editor-first=R.|date=2003|publisher=Springer|location=Berlin/Heidelberg|isbn=9783540449515}}</ref> |
'''Disulfur monoxide''' or '''sulfur suboxide''' is an [[inorganic compound]] with formula S<sub>2</sub>O. It is one of the [[lower sulfur oxides]]. It is a colourless gas and condenses to give a pale coloured solid that is unstable at room temperature.<ref name=Steudel>{{cite book|first=R.|last=Steudel|contribution=Sulfur-Rich Oxides S<sub>''n''</sub>O and S<sub>''n''</sub>O<sub>2</sub>|title=Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur-Rich Compounds II|editor-last=Steudel|editor-first=R.|date=2003|publisher=Springer|location=Berlin/Heidelberg|isbn=9783540449515}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | | last1 =Meschi | first1 =D. J. | last2=Myers|first2= R. J.| year = 1959| title = The microwave spectrum, structure, and dipole moment of disulfur monoxide| journal = Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy| volume = 3| issue =1–6 | pages =405–416 | doi = 10.1016/0022-2852(59)90036-0|bibcode = 1959JMoSp...3..405M }}</ref> |
||
==Structure== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
The bond angle S−S−O is 109°.<ref name=Hall77/> According to its microwave spectrum, the S−S−O angle is 117.88° with S−S and S−O bond lengths of 188.4 and 146.5 pm, respectively.<ref>{{cite journal |
|||
| ⚫ | | last1 =Meschi | first1 =D. J. | last2=Myers|first2= R. J.| year = 1959| title = The microwave spectrum, structure, and dipole moment of disulfur monoxide| journal = Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy| volume = 3| issue =1–6 | pages =405–416 | doi = 10.1016/0022-2852(59)90036-0|bibcode = 1959JMoSp...3..405M }}</ref> |
||
==Spectroscopy== |
==Spectroscopy== |
||
Condensed solid S<sub>2</sub>O [[absorption bands|absorbs]] at 420 and 530 nm. These bands have been assigned to decomposition products [[Trisulfur|S<sub>3</sub>]] and [[Tetrasulfur|S<sub>4</sub>]].<ref name=Nav10>{{cite journal|last1=Navizet|first1=Isabelle|last2=Komiha|first2=Najia|last3=Linguerri|first3=Roberto|last4=Chambaud|first4=Gilberte|last5=Rosmus|first5=Pavel|title=On the formation of S<sub>2</sub>O at low energies: An ab initio study|journal=Chemical Physics Letters|date=November 2010|volume=500|issue=4–6|pages=207–210|doi=10.1016/j.cplett.2010.10.012|bibcode = 2010CPL...500..207N }}</ref> |
Condensed solid S<sub>2</sub>O [[absorption bands|absorbs]] at 420 and 530 nm. These bands have been assigned to decomposition products [[Trisulfur|S<sub>3</sub>]] and [[Tetrasulfur|S<sub>4</sub>]].<ref name=Nav10>{{cite journal|last1=Navizet|first1=Isabelle|last2=Komiha|first2=Najia|last3=Linguerri|first3=Roberto|last4=Chambaud|first4=Gilberte|last5=Rosmus|first5=Pavel|title=On the formation of S<sub>2</sub>O at low energies: An ab initio study|journal=Chemical Physics Letters|date=November 2010|volume=500|issue=4–6|pages=207–210|doi=10.1016/j.cplett.2010.10.012|bibcode = 2010CPL...500..207N }}</ref> |
||
The [[Microwave spectroscopy|microwave spectrum]] of S<sub>2</sub>O has the following rotational parameters: ''A'' = 41915.44 MHz, ''B'' = 5059.07 MHz, and ''C'' = 4507.19 MHz.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cook|first1=Robert L|last2=Winnewisser|first2=Gisbert|last3=Lindsey|first3=D.C|title=The centrifugal distortion constants of disulfur monoxide|journal=Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy|date=May 1973|volume=46|issue=2|pages=276–284|doi=10.1016/0022-2852(73)90042-8|bibcode = 1973JMoSp..46..276C }}</ref> |
The [[Microwave spectroscopy|microwave spectrum]] of S<sub>2</sub>O has the following rotational parameters: ''A'' = 41915.44 MHz, ''B'' = 5059.07 MHz, and ''C'' = 4507.19 MHz.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cook|first1=Robert L|last2=Winnewisser|first2=Gisbert|last3=Lindsey|first3=D.C|title=The centrifugal distortion constants of disulfur monoxide|journal=Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy|date=May 1973|volume=46|issue=2|pages=276–284|doi=10.1016/0022-2852(73)90042-8|bibcode = 1973JMoSp..46..276C }}</ref> |
||
| Line 62: | Line 63: | ||
In the ultraviolet S<sub>2</sub>O has absorption band systems in the ranges 250–340 nm and 190–240 nm. There are bands at 323.5 and 327.8 nm.<ref name=Hall77>{{cite journal|last1=Hallin|first1=K-E. J.|last2=Merer|first2=A. J.|last3=Milton|first3=D. J.|title=Rotational analysis of bands of the 3400 Å system of disulphur monoxide (S<sub>2</sub>O)|journal=Canadian Journal of Physics|date=November 1977|volume=55|issue=21|pages=1858–1867|doi=10.1139/p77-226|bibcode = 1977CaJPh..55.1858H }}</ref> The band in the 315–340 nm range is due to the {{nowrap|C<sup>1</sup>''A''′–X<sup>1</sup>''A''′ (π* ← π)}} transition.<ref name=Zhang95>{{cite journal|last1=Zhang|first1=Qingguo|last2=Dupré|first2=Patrick|last3=Grzybowski|first3=Bartosz|last4=Vaccaro|first4=Patrick H.|title=Laser-induced fluorescence studies of jet-cooled S<sub>2</sub>O: Axis-switching and predissociation effects|journal=The Journal of Chemical Physics|date=1995|volume=103|issue=1|pages=67|doi=10.1063/1.469623|bibcode = 1995JChPh.103...67Z }}</ref> |
In the ultraviolet S<sub>2</sub>O has absorption band systems in the ranges 250–340 nm and 190–240 nm. There are bands at 323.5 and 327.8 nm.<ref name=Hall77>{{cite journal|last1=Hallin|first1=K-E. J.|last2=Merer|first2=A. J.|last3=Milton|first3=D. J.|title=Rotational analysis of bands of the 3400 Å system of disulphur monoxide (S<sub>2</sub>O)|journal=Canadian Journal of Physics|date=November 1977|volume=55|issue=21|pages=1858–1867|doi=10.1139/p77-226|bibcode = 1977CaJPh..55.1858H }}</ref> The band in the 315–340 nm range is due to the {{nowrap|C<sup>1</sup>''A''′–X<sup>1</sup>''A''′ (π* ← π)}} transition.<ref name=Zhang95>{{cite journal|last1=Zhang|first1=Qingguo|last2=Dupré|first2=Patrick|last3=Grzybowski|first3=Bartosz|last4=Vaccaro|first4=Patrick H.|title=Laser-induced fluorescence studies of jet-cooled S<sub>2</sub>O: Axis-switching and predissociation effects|journal=The Journal of Chemical Physics|date=1995|volume=103|issue=1|pages=67|doi=10.1063/1.469623|bibcode = 1995JChPh.103...67Z }}</ref> |
||
The [[harmonic frequency]] for S−S stretching is 415.2 cm<sup>−1</sup>.<ref name=Zhang95/> |
|||
==Synthesis== |
==Synthesis== |
||
| Line 88: | Line 89: | ||
==Reactions== |
==Reactions== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
S<sub>2</sub>O disproportionates to [[trisulfur]] and [[sulfur dioxide]]: |
|||
:2 S<sub>2</sub>O → S<sub>3</sub> + SO<sub>2</sub> |
:2 S<sub>2</sub>O → "S<sub>3</sub>" + SO<sub>2</sub> |
||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
Revision as of 11:37, 30 July 2021
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
sulfur suboxide; sulfuroxide;
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| S2O | |
| Molar mass | 80.1294 g/mol[1] |
| Appearance | colourless gas or dark red solid[2] |
| Structure | |
| bent | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
toxic |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Trisulfur SO Ozone SO2 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Disulfur monoxide or sulfur suboxide is an inorganic compound with formula S2O. It is one of the lower sulfur oxides. It is a colourless gas and condenses to give a pale coloured solid that is unstable at room temperature.[3]
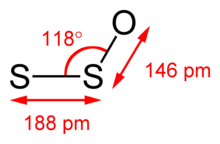
Structure
The bond angle S−S−O is 109°.[4] According to its microwave spectrum, the S−S−O angle is 117.88° with S−S and S−O bond lengths of 188.4 and 146.5 pm, respectively.[5]
Spectroscopy
Condensed solid S2O absorbs at 420 and 530 nm. These bands have been assigned to decomposition products S3 and S4.[6]
The microwave spectrum of S2O has the following rotational parameters: A = 41915.44 MHz, B = 5059.07 MHz, and C = 4507.19 MHz.[7]
In the ultraviolet S2O has absorption band systems in the ranges 250–340 nm and 190–240 nm. There are bands at 323.5 and 327.8 nm.[4] The band in the 315–340 nm range is due to the C1A′–X1A′ (π* ← π) transition.[8]
The harmonic frequency for S−S stretching is 415.2 cm−1.[8]
Synthesis
Historical
Disulfur monoxide was discovered by Peter W. Schenk in 1933.[3] with a glow discharge though sulfur vapour and sulfur dioxide. He discovered that the gas could survive for hours at single digit pressures of mercury in clean glass, but it decomposed near 30 mmHg (4 kPa). Schenk assigned the formula as SO and called it sulfur monoxide. In 1956, D. J. Meschi and R. J. Myers established the formula as S2O.[9]
Preparation
The reaction of thionyl chloride with silver(I) sulfide:
- SOCl2 + Ag2S → 2 AgCl + S2O
Also 5,6-di-tert-butyl-2,3,7-trithiabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene 2-endo-7-endo-dioxide when heated can form S2O.[10] It reacts with diazoalkanes to form dithiirane 1-oxides.[11]

It also arises via thermal decomposition of sulfur dioxide in a glow discharge.[12]
Occurrence
Volcanism
S2O can be found coming from volcanoes on Io. It can form between 1% and 6% when hot 100-bar S2 and SO2 gas erupts from volcanoes. It is believed that Pele on Io is surrounded by solid S2O.[13]
Combustion
It can be formed by many methods, including combustion of sulfur vapour in a deficiency of oxygen. It arises by oxidizing sulfur with copper(II) oxide:[14]
- 3 S8 + 12 CuO → 12 CuS + 4 S2O + 4 SO2
As a ligand
Disulfur monoxide occurs as a ligand bound to transition metals. One example is OsCl(NO)(PPh3)2(η2-S2O). These complexes are closely related to transition metal sulfur dioxide complexes.
Reactions
On decomposition at room temperature it forms SO2 via the formation of polysulfur oxides.[12]
- 2 S2O → "S3" + SO2
Further reading
- Possible biological occurrence: Iverson, W. P. (26 May 1967). "Disulfur monoxide: production by Desulfovibrio". Science. 156 (3778): 1112–1114. Bibcode:1967Sci...156.1112I. doi:10.1126/science.156.3778.1112. PMID 6024190.
- Cyclic disulfur monoxide: Lo, Wen-Jui; Wu, Yu-Jong; Lee, Yuan-Pern (September 2003). "Ultraviolet Absorption Spectrum of Cyclic S2O in Solid Ar". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 107 (36): 6944–6947. Bibcode:2003JPCA..107.6944L. doi:10.1021/jp034563j.
- Discovery of S2O: Schenk, Peter W. (18 March 1933). "Über das Schwefelmonoxyd" [On sulfur monoxide]. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (in German). 211 (1–2): 150–160. doi:10.1002/zaac.19332110117.
References
- ^ a b c "Disulfur monoxide". NIST. 2008.
- ^ Hapke, B.; Graham, F. (May 1989). "Spectral properties of condensed phases of disulfur monoxide, polysulfur oxide, and irradiated sulfur". Icarus. 79 (1): 47. Bibcode:1989Icar...79...47H. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(89)90107-3.
- ^ a b Steudel, R. (2003). "Sulfur-Rich Oxides SnO and SnO2". In Steudel, R. (ed.). Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur-Rich Compounds II. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer. ISBN 9783540449515.
- ^ a b Hallin, K-E. J.; Merer, A. J.; Milton, D. J. (November 1977). "Rotational analysis of bands of the 3400 Å system of disulphur monoxide (S2O)". Canadian Journal of Physics. 55 (21): 1858–1867. Bibcode:1977CaJPh..55.1858H. doi:10.1139/p77-226.
- ^ Meschi, D. J.; Myers, R. J. (1959). "The microwave spectrum, structure, and dipole moment of disulfur monoxide". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 3 (1–6): 405–416. Bibcode:1959JMoSp...3..405M. doi:10.1016/0022-2852(59)90036-0.
- ^ Cook, Robert L; Winnewisser, Gisbert; Lindsey, D.C (May 1973). "The centrifugal distortion constants of disulfur monoxide". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 46 (2): 276–284. Bibcode:1973JMoSp..46..276C. doi:10.1016/0022-2852(73)90042-8.
- ^ a b Zhang, Qingguo; Dupré, Patrick; Grzybowski, Bartosz; Vaccaro, Patrick H. (1995). "Laser-induced fluorescence studies of jet-cooled S2O: Axis-switching and predissociation effects". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 103 (1): 67. Bibcode:1995JChPh.103...67Z. doi:10.1063/1.469623.
- ^ Meschi, David J.; Myers, Rollie J. (30 July 1956). "Disulfur Monoxide. I. Its Identification as the Major Constituent in Schenk's "Sulfur Monoxide"". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 78 (24): 6220. doi:10.1021/ja01605a002.
- ^ Nakayama, J.; Aoki, S.; Takayama, J.; Sakamoto, A.; Sugihara, Y.; Ishii, A. (28 July 2004). "Reversible disulfur monoxide (S2O)-forming retro-Diels–Alder reaction. disproportionation of S2O to trithio-ozone (S3) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) and reactivities of S2O and S3". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 126 (29): 9085–9093. doi:10.1021/ja047729i. PMID 15264842.
- ^ Ishii, A.; Kawai, T.; Tekura, K.; Oshida, H.; Nakayama, J. (18 May 2001). "A Convenient Method for the Generation of a Disulfur Monoxide Equivalent and Its Reaction with Diazoalkanes to Yield Dithiirane 1-Oxides". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 40 (10): 1924–1926. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20010518)40:10<1924::AID-ANIE1924>3.0.CO;2-F. PMID 11385674.
- ^ a b Cotton and Wilkinson (1966). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Treatise. p. 540.
- ^ Zolotov, Mikhail Yu.; Fegley, Bruce (9 March 1998). "Volcanic Origin of Disulfur Monoxide (S2O) on Io" (PDF). Icarus. 133 (2): 293. Bibcode:1998Icar..133..293Z. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.5930.
- ^ Satyanarayana, S. R.; Vasudeva Murthy, A. R. (1964). "Reactions with Disulphur monoxide Solutions Obtained by the Reduction of Cupric Oxide by Elemental Sulphur" (PDF). Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Section A. 59 (4).
