YugabyteDB: Difference between revisions
m line breaks |
m fixed line breaks |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| founder = Kannan Muthukkaruppan, Karthik Ranganathan, Mikhail Bautin |
| founder = Kannan Muthukkaruppan, Karthik Ranganathan, Mikhail Bautin |
||
| hq_location = [[Silicon Valley]], USA |
| hq_location = [[Silicon Valley]], USA |
||
| key_people = Kannan Muthukkaruppan<br><small>(Co-Founder & President,< |
| key_people = Kannan Muthukkaruppan<br><small>(Co-Founder & President,<br> Product Development)</small><br> Karthik Ranganathan<br><small>(Co-Founder & CTO)</small><br> Mikhail Bautin<br><small>(Co-Founder &<br>Software Architect)</small><br> Bill Cook<br><small>(CEO)</small> |
||
| services = Commercial database management systems |
| services = Commercial database management systems |
||
Revision as of 14:11, 30 December 2021
 | |
| Original author(s) | Kannan Muthukkaruppan, Karthik Ranganathan, Mikhail Bautin |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Yugabyte, Inc. |
| Initial release | 2016 |
| Stable release | 2.8 (Stable) 2.11 (Development) / November 18, 2021 November 23, 2021 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Linux RedHat 7.x and derivatives |
| Platform | Bare Metal, Virtual Machine, Docker, Kubernetes and various container management platroms |
| Available in | English |
| Type | RDBMS |
| License | Apache 2.0 |
| Website | www |
| Company type | Private |
|---|---|
| Industry | Software |
| Founded | 2016 |
| Founder | Kannan Muthukkaruppan, Karthik Ranganathan, Mikhail Bautin |
| Headquarters | Silicon Valley, USA |
Key people | Kannan Muthukkaruppan (Co-Founder & President, Product Development) Karthik Ranganathan (Co-Founder & CTO) Mikhail Bautin (Co-Founder & Software Architect) Bill Cook (CEO) |
| Services | Commercial database management systems |
| Website | www |
YugabyteDB is a high-performance distributed SQL database for cloud-native applications, developed by Yugabyte.[1]
History
Yugabyte was founded by ex-Facebook engineers Kannan Muthukkaruppan, Karthik Ranganathan, and Mikhail Bautin. At Facebook, they were part of the team that built and operated Cassandra and HBase[2]. The team scaled the data platform for massive real-time workloads such as Facebook Messenger and Facebook’s Operational Data Store from millions to billions of users in just a few years[3].
The founders came together in February 2016 to build YugabyteDB, believing that the trends they experienced at Facebook – microservices, containerization, high availability, geographic distribution, APIs, and open-source – were relevant to all businesses, especially as they move from on-premise to cloud-native operations[4].
YugabyteDB was initially available in two editions: community and enterprise. In July 2019, Yugabyte open sourced previously commercial features and launched YugabyteDB as 100% open-source under the Apache 2.0 license.
Yugabyte launched Yugabyte Cloud, a fully managed database-as-a-service offering of YugabyteDB, in September 2021[5]. Yugabyte Cloud combines the power of distributed SQL with the ease of use of a cloud database management system.
Yugabyte closed a $188 Million Series C funding round on October 28, 2021, bringing their valuation to over $1.3bn[6]. The round was led by Sapphire Ventures, and included participation from Alkeon Capital, Meritech Capital Partners, and Wells Fargo Strategic Capital, and existing investors Lightspeed Venture Partners, 8VC, Dell Technologies Capital, Wipro Ventures.
Features
YugabyteDB combines enterprise-grade relational database capabilities with a cloud-native architecture, horizontal scalability, and resilience.
YugabyteDB is code compatible with PostgreSQL, reusing PostgreSQL’s query layer to achieve a high degree of compatibility with existing PostgreSQL applications.
YugabyteDB delivers a comprehensive set of advanced RDBMS features like triggers, functions, stored procedures, strong secondary indexes, and distributed ACID transactions.
YugabyteDB offers comprehensive and flexible deployment options in geo-distributed environments allowing operators to use synchronous and asynchronous data replication and geo-partitioning to achieve desired consistency, resilience, performance, and compliance objectives.
YugabyteDB enables organizations to maintain a robust security posture with built-in controls such as LDAP authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), data encryption at rest and in transit (TLS), audit logging, and column-level permissions.
Architecture
YugabyteDB is a Distributed SQL database that is strongly transactionally consistent across failure zones (i.e. ACID compliance] as demonstrated by Jepsen testing[7]. In CAP Theorem terms YugabyteDB is a Consistent/Partition Tolerant (CP) database.
YugabyteDB has two layers, a storage engine known as DocDB and the Yugabyte Query Layer.
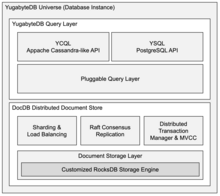
DocDB
The storage engine consists of a customized RocksDB combined with sharding and load balancing algorithms for the data. In addition, the Raft consensus algorithm controls the replication of data between the nodes. There is also a distributed transaction manager and Multiversion concurrency control (MVCC) to support distributed transactions.
The engine also exploits a Hybrid Logical Clock[8] that combines coarsely-synchronized physical clocks with Lamport clocks to track causal relationships.
The DocDB layer is not directly accessible by users.
YugabyteDB Query Layer
Yugabyte has a pluggable query layer that abstracts the query layer from the storage layer below. There are currently two APIs that can access the database:
YCQL is a Cassandra-like API based around v3.10 and re-written in C++. YCQL is accessed via standard Cassandra drivers using the native protocol port of 9042. In addition to the 'vanilla' Cassandra components, YCQL is augmented with the following features:
- Transactional consistency - unlike Cassandra, Yugabyte YCQL is transactional.
- JSON data types supported natively
- Tables can have secondary indexes
YSQL is a PostgreSQL code-compatible API based around v11.2. YSQL is accessed via standard PostgreSQL drivers using native protocols. It exploits the native PostgreSQL code for the query layer and replaces the storage engine with calls to the pluggable query layer. This re-use means that Yugabyte supports many features, including:
- Triggers & Stored Procedures
- PostgreSQL extensions that operate in the query layer
- Native JSONB support
Currently, data written to either API is not accessible via the other API
The security model for accessing the system is inherited from the API, so access controls for YSQL look like PostgreSQL, and YCQL looks like Cassandra access controls.
See also
References
- ^ "YugabyteDB System Properties". DB-Engines. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "Karthik Ranganathan". Dataversity. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "YugaByte Raises $8M in Series A Funding". FINSMES. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "Yugabyte expands its fully managed enterprise cloud service with $188M". VentureBeat. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "Yugabyte Delivers Effortless Distributed SQL With Cloud Database-as-a-Service". BusinessWire. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "Yugabyte Closes $188 Million Series C Funding Round Bringing Valuation to Over $1.3B". BusinessWire. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "YugaByte DB 1.3.1". Jepsen.io. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
- ^ "Hybrid Clock". Martin Fowler. Retrieved December 30, 2021.
