Evolution of the French colonial empire: Difference between revisions
BrazilAlan20 (talk | contribs) |
BrazilAlan20 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
* [[Tobago]] (1666–1667, 1781–1793, 1802–1803) |
* [[Tobago]] (1666–1667, 1781–1793, 1802–1803) |
||
* [[Falkland Islands]] (1504, 1701, 1764–1767) |
* [[Falkland Islands]] (1504, 1701, 1764–1767) |
||
* [[Turks and Caicos Islands]] (1783) |
|||
* [[Montserrat]] (1666, 1712) |
|||
==In Africa== |
==In Africa== |
||
Revision as of 21:50, 12 January 2022
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2022) |
The French colonial empire was the set of territories outside Europe that were under French rule from the 16th century to the late 1980s. From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire stretched from a total area at its peak in 1680 to over 10,000,000 square kilometres (3,900,000 sq mi), the second largest empire in the world at the time behind only the Spanish Empire. In terms of land area, the Second French colonial empire extended to over 13,500,000 square kilometres (5,200,000 sq mi) at its peak in 1936, the second largest in the world at the time, which accounted for 10% of the world's land area. The total land area of the first and second French colonial empire combined reached 24,000,000 square kilometres (9,300,000 sq mi).

This is a list of all territories that were part of the French colonial empires in the last 500 years, either entirely or in part, either under French sovereignty or as mandate or protectorate. When only a part of the country was under French rule, that part is listed in parentheses after the country. When there are no parentheses, it means the whole country was formerly part of any one of the French colonial empires. Countries listed are those where French sovereignty applied effectively. Areas that were only claimed, but not effectively controlled (such as Manhattan or Western Australia) are not listed.
The following is a list of all countries that were part of the French colonial empires in the last 500 years, either entirely or in part, either under French sovereignty or as mandate.

In the Americas

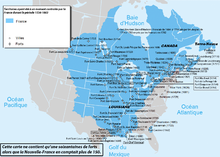


North America
- Present-day Dominican Republic (1795–1809)
- Canada
- New France (1534–1763), and nearby lands:
- Present-day United States
- The Fort Saint Louis (Texas) (1685–1689)
- Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands (1650–1733)
- Fort Caroline in French Florida (occupation by Huguenots) (1562–1565)
- Vincennes and Fort Ouiatenon in Indiana
- French Louisiana (23.3% of the current territory)[citation needed] (1764–1804) (sold by Napoleon I) (also see: Louisiana (New Spain))
- Lower Louisiana
- Upper Louisiana
- Louisiana (New France) (1672–1764)
- Present-day Brazil
- France Équinoxiale (Bay of São Luis) (1610–1615)
- The island of Saint Alexis (1531)
- The Territory of Amapá (1897) (disputed Franco-Brazilian territory resolved in favour of Brazil)[1]
- The city of Viçosa-Ceará (Territory of Ibiapaba) (1590–1604)
- France Antarctique, to Fort Coligny ( Rio de Janeiro Bay; intended as a haven for Huguenots) (1555–1567)
- Île Delphine's island (1736–1737)
- Haiti (1627–1804)
- Present-day Suriname
- Tapanahony (District of Sipaliwini) (Controversial Franco-Dutch in favour of the Netherlands) (25.8% of the current territory) (1814)
- Îles des Saintes (1648–present)
- Marie-Galante (1635–present)
- la Désirade (1635–present)
- Guadeloupe (1635–present)
- Martinique (1635–present)
- French Guiana (1604–present)
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon (1604–1713, 1763–present)
- Collectivity of Saint Martin (1624–present)
- Saint Barthélemy (1648–1784, 1878–present)
- Clipperton Island (1858–present)
- Dominica (1625–1763, 1778–1783)
- Nevis (1782–1784)
- Grenada (1650–1762, 1779–1783)
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (1719–1763, 1779–1783)
- Saint Christopher Island (1628–1690, 1698–1702, 1706, 1782–1783)
- Antigua (briefly in 1666)
- Saint Lucia (1650–1723, 1756–1778, 1784–1803)
- Present-day Guyana (1782–1784)
- Tobago (1666–1667, 1781–1793, 1802–1803)
- Falkland Islands (1504, 1701, 1764–1767)
- Turks and Caicos Islands (1783)
- Montserrat (1666, 1712)
In Africa

- French Morocco (1912–1956) (protectorate) (89% of the current territory) (now Morocco)
- French Algeria (1830–1962)
- French Lybia (1943–1951) (Lybia)
- French Tunisia (1881–1956) (protectorate) (Tunisia)
- Ivory Coast (1843–1960)
- Dahomey or French Dahomey (now Benin) (1883–1960)
- Independent of Dahomey, under French protectorate in 1889
- Porto-Novo (protectorate) (1863–1865, 1882)
- Cotonou (protectorate) (1868)
- French Sudan (now Mali) (1883–1960)
- Senegambia and Niger (1902–1904)
- Guinea or French Guinea (1891–1958)
- Mauritania (1902–1960)
- Adrar emirate (protectorate) (1909)
- The Taganit confederation's emirate (protectorate) (1905)
- Brakna confederation's emirate (protectorate)
- Emirate of Trarza (protectorate) (1902)
- Niger (1890–1960)
- Sultanate of Damagaram (Zinder) (protectorate) (1899)
- Senegal (1677–1960)
- French Upper Volta (now Burkina Faso) (1896–1960)
- French Togoland (1918–1960) (formerly a German colony, mandate became a French colony) (now Togo)
- Nigeria
- The Enclaves of Forcados and Badjibo (territory under a lease of 30 years) (1900–1927)
- The Emirate of Muri (Northeast of Nigeria) (1892–1893)
- Gambia
- Albreda (1681–1857)
- Kunta Kinteh Island (1695–1697, 1702)
- Chad (1900–1960)
- Oubangui-Chari (currently Central African Republic) (1905–1960)
- Dar al Kuti (protectorate) (1897) (in 1912 its sultanate was suppressed by the French)
- Sultanate of Bangassou (protectorate) (1894)
- Present-day The Republic of Congo, then French Congo (1875–1960)
- Gabon (1839–1960)
- French Cameroon (91% of current Cameroon) (1918–1960) (formerly a German colony, Mandate, Protectorate then French Colony)
- São Tomé and Príncipe (1709)
East Africa and Indian Ocean
- Madagascar (1896–1960)
- Kingdom of Imerina (protectorate) (1896)
- Isle de France (1715–1810) (now Mauritius)
- Djibouti (French Somaliland) (the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas) (French Somalia) (1862–1977)
- French Egypt (1798–1801, 1858–1882, 1956)
- Mayotte (1841–present)
- Seychelles (1756–1810)
- Chagos Archipelago (1721–1745, 1768–1814)
- The Scattered Islands (Banc du Geyser, Bassas da India, Europa Island, Juan de Nova Island, Glorioso Islands, Tromelin Island)
- Comoros (1866–1975)
- Réunion (1710–present)
In Asia
This section needs additional citations for verification. (March 2018) |
- French Indochina
- French Indochinese Union (1887–1954)
- Laos (protectorate) (1893–1953)
- Cambodia (protectorate) (1863–1953)
- Vietnam
- Cochinchina (Southern Vietnam) (1858–1949)
- Annam (protectorate) (Central Vietnam) (1883–1949)
- Tonkin (protectorate) (Northern Vietnam) (1884–1949)
- State of Vietnam (1949–1954)
- Spratly Islands (1933–1939)
- Paracel Islands (1933–1939)
- Some territories in the eastern part of Thailand (independent state, but after Franco-Siamese War in 1893, Thailand has lost 3 provinces during the next 15 years)
- Chanthaburi Province (1893-1904)
- Trat Province (1904-1907)
- Dan Sai District (in the area of the Loei Province:1903-1907)
- French Indochinese Union (1887–1954)
- India and Sri Lanka
- French India
- French Establishments of India, composed of Pondichéry (1765–1954); Karikal (1725–1954); Mahé (1721–1954) Yanaon (1723–1954); Chandernagor (1673–1952)
- French India
- Taiwan
- The city/port of Keelung (1884–1885)
- Pescadores Islands (1885)
- Basilan (1845)
- China
- The territory of Kouang-Tchéou-Wan, a dependency of French Indochina) (1898–1945)
- The foreign concessions : French Concession of Shanghai (1849–1946), Tianjin (1860–1946) and Hankou (1898–1946)
- The Spheres of French influence officially recognized by China on the provinces of Yunnan, Guangxi, Hainan, Guangdong
- Shamian Island (1859–1949) (a fifth of the island)
- Palestine
- Syria or French Syria (1920–1946) (French Mandate of Syria)
- Alawite State (1920–1936)
- State of Aleppo (1920–1924)
- State of Jabal Druze (1921–1936)
- State of Damascus (1920–1924)
- Sanjak of Alexandretta (now part of Turkey)
- State of Greater Lebanon (now it is Lebanon) (1920–1946)
- Lebanon or French Lebanon (1920–1946) (French Mandate of Lebanon)
- Mount Lebanon (An international protocol fixes the autonomy of the mount Lebanon under the protection of France)[2]
- Yemen
- Cheikh Saïd (Some French atlases and history books claimed the territory was French, but France never occupied it and never claimed jurisdiction or sovereignty over the territory, which therefore was never French, remaining under Turkish, then Yemeni control.[3])
In Oceania
- French Polynesia
- Society Islands (became a French protectorate in 1843 and a colony in 1880)
- Tuamotu Archipelago
- Marquesas Islands (under French control in 1870, and later incorporated into the territory of French Polynesia)
- Gambier Islands
- Mangareva (protectorate) (1844/1871)
- Austral Islands
- Rurutu (Austral Islands) (protectorate) (1858–1889)[4]
- Papua New Guinea
- New Ireland (1880–1882) (attempt at colonization, unofficial)
- New Caledonia
- Hawaiian Islands (1837) (at the beginning of French presence there; however, the United States persuaded the local Queen to negotiate with them instead, by means of the strength of a company of U.S. Marines)
- Hawaii (1849) (French invasion of Honolulu)
- The New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
- French protectorate (1887–1906)
- Anglo-French condominium (1906–1980)
- Australia
- Dirk Hartog Island (1772) (made an unofficial annexation for all Australia)[5][6][7]
- Wallis and Futuna (1887–present)
- Kingdom of Uvea (Wallis and Futuna) (declared to be a protectorate by King of Uvea and Captain Mallet in 1842. Officially in a treaty becomes a French protectorate in 1887 until annexed in 1917)
- Kingdom of Sigave (signed a treaty establishing a French protectorate in 1888 until annexed in 1917)
- Kingdom of Alo (Wallis and Futuna) (signed a treaty establishing a French protectorate in 1888 until annexed in 1917)
In Antarctica

- French Southern and Antarctic Lands (TAAF)
- Crozet Islands (24 January 1772[8]– present)
- Kerguelen Islands (13 February 1772[9]– present)
- Île Amsterdam (in 1843 but abandoned) (1892–present)
- Île Saint-Paul (in 1843 but abandoned) (1892–present)
- Adélie Land (1840–present) (sheltering one of two French Bases in Antarctica, the other one being Franco-Italian (that borders with the Australian Antarctic Territory on both sides and divides that in two)
See also
References
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2011-02-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "BnF - Voyage en Orient". expositions.bnf.fr. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ^ Cheikh Saïd - The territory of Cheikh Saïd was acquired in 1868 by a French company. It is for that reason that it was formerly shown with the French colours on certain atlases. In fact, Cheikh Saïd has been occupied by the Turks since 1870, and by the Yemenis since the First World War., Dictionnaire encyclopédique Quillet, (1985 ed.).
- ^ "Drapeau de Rurutu - Tahiti Heritage". www.tahitiheritage.pf. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ^ "Consulter le sujet - L'Australie serait-elle française ?!... • [Forums". Francedownunder.com. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ^ Godard, Philippe; Kerros, Tugdual de; Margot, Odette; Stanbury, Myra; Baxter, Sue; Western Australian Museum; Godard, Phillippe; De Kerros, Tugdual; Margot, Odette; Stanbury, Myra; Baxter, Sue (2008), 1772 : the French annexation of New Holland : the tale of Louis de Saint Aloürn, Western Australian Museum, ISBN 978-1-920843-98-4
- ^ Philippe Godard, Tugdual de Kerros 2002, "Louis de Saint Aloüarn, un marin breton à la conquête des terres australes", Les Portes du large, Saint-Jacques-de-la-Lande, 331-336
- ^ "TAAF". Taaf.fr. Archived from the original on 2012-01-20. Retrieved 2012-01-10.
- ^ "Kerguelen – yves trémarec – james cook – asia – hillsborough – rhodes". Kerguelen-voyages.com. Archived from the original on 2013-10-02.
