Uintatherium: Difference between revisions
Princeton Expedition history |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
==Discovery== |
==Discovery== |
||
Fossils of ''Uintatherium'' were first discovered in the Bridger Basin near Fort Bridger by Lieutenant W. N. Wann in September of 1870 and were later described as a new species of [[Megacerops|''Titanotherium'',]] ''Titanotherium anceps'', by [[Othniel Charles Marsh|Othniel Marsh]] in 1871<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. The specimen (YPM 11030) only consisted of several skull pieces, including the right parietal horn, and fragmentary postcrania<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. The following year, Marsh and Joseph Leidy collected in the Eocene Beds near Fort Bridger while Edward Cope, Marsh's competitor, excavated in the Washakie Basin. In August of 1872, Leidy named ''Uintatherium robustum'' based on a posterior skull and partial mandibles (ANSP 12607)<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref><ref name=":1">Leidy, Joseph (1872a) On some new species of |
[[File:Rs-11415 1024x1024.jpg|thumb|Restoration of Edward Cope's proboscidean ''Loxolophodon'' theory from 1873.|left]]Fossils of ''Uintatherium'' were first discovered in the Bridger Basin near Fort Bridger by Lieutenant W. N. Wann in September of 1870 and were later described as a new species of [[Megacerops|''Titanotherium'',]] ''Titanotherium anceps'', by [[Othniel Charles Marsh|Othniel Marsh]] in 1871<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. The specimen (YPM 11030) only consisted of several skull pieces, including the right parietal horn, and fragmentary postcrania<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. The following year, Marsh and Joseph Leidy collected in the Eocene Beds near Fort Bridger while Edward Cope, Marsh's competitor, excavated in the Washakie Basin. In August of 1872, Leidy named ''Uintatherium robustum'' based on a posterior skull and partial mandibles (ANSP 12607)<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref><ref name=":1">Leidy, Joseph (1872a) On some new species of |
||
fossil mammalia from Wyoming: Acad. Nat. |
fossil mammalia from Wyoming: Acad. Nat. |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Sci. Philadelphia Proc, 1872, p. 240-242.</ref>. 18 days after the description of ''Uintatherium'', Cope and Marsh both named new genera of Uinta Dinoceratans, Cope naming ''Loxolophodon'' in his "garbled" telegram<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Cope|first=Edward|date=1872|title=Telegram describing extinct Proboscidians from Wyoming|journal=Paleontological Bulletin|volume=5}}</ref> and Marsh dubbed ''Tinoceras''<ref name=":3">{{Cite journal|last=Anonymous|date=1885-03-01|title=Professor Marsh's monography of the dinocerata|url=https://www.ajsonline.org/content/s3-29/171/173|journal=American Journal of Science|language=en|volume=s3-29|issue=171|pages=173–204|doi=10.2475/ajs.s3-29.171.173|issn=0002-9599}}</ref>. Due to ''Uintatherium'' being named first, Cope and Marsh's genera are synonymous with ''Uintatherium''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Cope described 2 genera his telegram, ''Loxolophodon'' and ''Eobasileus''<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Cope|first=Edward|date=1872|title=Telegram describing extinct Proboscidians from Wyoming|journal=Paleontological Bulletin|volume=5}}</ref><ref name=":4">Cope, E. D. (1873). On the Short Footed Ungulata of the Eocene of Wyoming. ''Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society'', ''13''(90), 38-74.</ref> '','' the latter is currently considered separate from ''Uintatherium''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. ''Tinoceras'' was a new genus made for ''Titanotherium anceps'' by Marsh<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Several days later, Marsh erected the genus ''Dinoceras''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref><ref name=":3" />''.'' ''Dinoceras'' and ''Tinoceras'' would receive several additional species by Marsh throughout the 1870s and 1880s, many based on fragmentary material<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Several complete skulls were found by Cope and Marsh crews, leading to theories like Cope's proboscidean assessment<ref name=":4">Cope, E. D. (1873). On the Short Footed Ungulata of the Eocene of Wyoming. ''Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society'', ''13''(90), 38-74.</ref><ref>Cope, E. D. (1873). On Some of Prof. Marsh's Criticisms. ''The American Naturalist'', ''7''(5), 290-299.</ref>. Due to Cope and Marsh's rivalry, the two would often publish scathing criticisms of each other's work, stating their respective genera were valid<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. The trio would name 25 species now considered synonymous with Marsh's original species, ''Titanotherium anceps'', which was placed in Leidy's genus, ''Uintatherium''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Many additional discoveries of ''Uintatherium'' have occurred, making ''Uintatherium'' one of the best-known and popular American fossil mammals<ref>Wheeler, W. H. (1960). The uintatheres and the Cope-Marsh war. ''Science'', ''131''(3408), 1171-1176.</ref><ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Princeton University launched expeditions to the Eocene beds of Wyoming in the 1870s and 1880s, discovering several partial skulls and naming several species of Uintatheres that are now considered synonyms of ''U. anceps''<ref>Scott, W. B., (1886) On some new forms of the Dinocerata: Am. Jour. Sci., (3) v. 31, p. 303-307.</ref><ref name=":0" />.Major reassesment came in the 1960s by Walter Wheeler who synonymized and re-described many of the ''Uintatherium'' fossils discovered during the 19th century<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. A cast of a ''Uintatherium'' [[skeleton]] is on display at the Utah Field House of Natural History State Park. The skeleton of ''Uintatherium'' is also on display at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington, DC.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Paleobiology | Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History|url=http://paleobiology.si.edu/geotime/main/htmlversion/evidence/eoc_02.html}}</ref> A new species was named based on almost intact skull, ''U. insperatus,'' found in the lower part of the Lushi Formation of the Lushi Basin in [[Henan]] Province, China.<ref name="TongWang" /> |
Sci. Philadelphia Proc, 1872, p. 240-242.</ref>. 18 days after the description of ''Uintatherium'', Cope and Marsh both named new genera of Uinta Dinoceratans, Cope naming ''Loxolophodon'' in his "garbled" telegram<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Cope|first=Edward|date=1872|title=Telegram describing extinct Proboscidians from Wyoming|journal=Paleontological Bulletin|volume=5}}</ref> and Marsh dubbed ''Tinoceras''<ref name=":3">{{Cite journal|last=Anonymous|date=1885-03-01|title=Professor Marsh's monography of the dinocerata|url=https://www.ajsonline.org/content/s3-29/171/173|journal=American Journal of Science|language=en|volume=s3-29|issue=171|pages=173–204|doi=10.2475/ajs.s3-29.171.173|issn=0002-9599}}</ref>. Due to ''Uintatherium'' being named first, Cope and Marsh's genera are synonymous with ''Uintatherium''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Cope described 2 genera his telegram, ''Loxolophodon'' and ''Eobasileus''<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Cope|first=Edward|date=1872|title=Telegram describing extinct Proboscidians from Wyoming|journal=Paleontological Bulletin|volume=5}}</ref><ref name=":4">Cope, E. D. (1873). On the Short Footed Ungulata of the Eocene of Wyoming. ''Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society'', ''13''(90), 38-74.</ref> '','' the latter is currently considered separate from ''Uintatherium''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. ''Tinoceras'' was a new genus made for ''Titanotherium anceps'' by Marsh<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Several days later, Marsh erected the genus ''Dinoceras''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref><ref name=":3" />''.'' ''Dinoceras'' and ''Tinoceras'' would receive several additional species by Marsh throughout the 1870s and 1880s, many based on fragmentary material<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Several complete skulls were found by Cope and Marsh crews, leading to theories like Cope's proboscidean assessment<ref name=":4">Cope, E. D. (1873). On the Short Footed Ungulata of the Eocene of Wyoming. ''Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society'', ''13''(90), 38-74.</ref><ref>Cope, E. D. (1873). On Some of Prof. Marsh's Criticisms. ''The American Naturalist'', ''7''(5), 290-299.</ref>. Due to Cope and Marsh's rivalry, the two would often publish scathing criticisms of each other's work, stating their respective genera were valid<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. The trio would name 25 species now considered synonymous with Marsh's original species, ''Titanotherium anceps'', which was placed in Leidy's genus, ''Uintatherium''<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Many additional discoveries of ''Uintatherium'' have occurred, making ''Uintatherium'' one of the best-known and popular American fossil mammals<ref>Wheeler, W. H. (1960). The uintatheres and the Cope-Marsh war. ''Science'', ''131''(3408), 1171-1176.</ref><ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. Princeton University launched expeditions to the Eocene beds of Wyoming in the 1870s and 1880s, discovering several partial skulls and naming several species of Uintatheres that are now considered synonyms of ''U. anceps''<ref>Scott, W. B., (1886) On some new forms of the Dinocerata: Am. Jour. Sci., (3) v. 31, p. 303-307.</ref><ref name=":0" />.Major reassesment came in the 1960s by Walter Wheeler who synonymized and re-described many of the ''Uintatherium'' fossils discovered during the 19th century<ref name=":0">Wheeler, W. H. (1961). [http://images.peabody.yale.edu/publications/bulletin/Bulletin14_1961.pdf Revision of the uintatheres]. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.</ref>. A cast of a ''Uintatherium'' [[skeleton]] is on display at the Utah Field House of Natural History State Park. The skeleton of ''Uintatherium'' is also on display at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington, DC.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Paleobiology | Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History|url=http://paleobiology.si.edu/geotime/main/htmlversion/evidence/eoc_02.html}}</ref> A new species was named based on almost intact skull, ''U. insperatus,'' found in the lower part of the Lushi Formation of the Lushi Basin in [[Henan]] Province, China.<ref name="TongWang" /> |
||
[[File:Rs-11415 1024x1024.jpg|thumb|Restoration of Edward Cope's proboscidean ''Loxolophodon'' theory from 1873.|left]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist|2}} |
{{Reflist|2}} |
||
Revision as of 20:45, 31 January 2022
| Uintatherium Temporal range: Eocene,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Cast of the skeleton, French National Museum of Natural History in the Paris | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Dinocerata |
| Family: | †Uintatheriidae |
| Subfamily: | †Uintatheriinae |
| Genus: | †Uintatherium Leidy, 1872 |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Genus synonymy
Synonyms of U. anceps
| |

Uintatherium ("Beast of the Uinta Mountains") is an extinct genus of herbivorous mammal that lived during the Eocene epoch. Two species are currently recognized: U. anceps from the United States during the Early to Middle Eocene (56–38 million years ago) and U. insperatus of Middle to Late Eocene (48–34 million years ago) China.[1]
Description
Uintatherium was a large browsing animal. With a length of about 4 m (13 ft), a height of 1.70 m (5.6 ft), and a weight up to 2 tonnes, it was similar to today's rhinoceros, both in size and in shape.[2] Its legs were robust to sustain the weight of the animal and were equipped with hooves.[3] Moreover, a Uintathere's sternum was made up of horizontal segments, unlike today's rhinos, which have compressed vertical segments.[4]
Skull
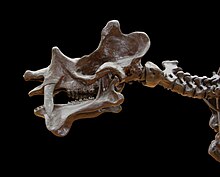
Its most unusual feature was the skull, which is both large and strongly built, but simultaneously flat and concave: this feature is rare and, apart from some brontotheres, not regularly characteristic of any other known mammal. Its cranial cavity was exceptionally small due to the walls of the cranium being exceedingly thick. The weight of the skull was mitigated by numerous sinuses permeating the walls of the cranium, like those in an elephant's skull.
The large upper canine teeth might have served as formidable defensive weapons, and superficially resembled those of saber-toothed cats. Sexually dimorphic, the teeth were larger in males than in females. However, they also might have used them to pluck the aquatic plants from marshes that seem to have comprised their diet.
The skulls of the males bore six prominent knob-like ossicones that grew from the frontal region of the skull. The function of these structures is unknown. They may have been of use in defense and/or sexual display.
Discovery

Fossils of Uintatherium were first discovered in the Bridger Basin near Fort Bridger by Lieutenant W. N. Wann in September of 1870 and were later described as a new species of Titanotherium, Titanotherium anceps, by Othniel Marsh in 1871[5]. The specimen (YPM 11030) only consisted of several skull pieces, including the right parietal horn, and fragmentary postcrania[5]. The following year, Marsh and Joseph Leidy collected in the Eocene Beds near Fort Bridger while Edward Cope, Marsh's competitor, excavated in the Washakie Basin. In August of 1872, Leidy named Uintatherium robustum based on a posterior skull and partial mandibles (ANSP 12607)[5][6]. Another specimen discovered by Leidy's crews consisting of a canine was named Uintamastix atrox and was thought to have been a saber-toothed and carnivorous[5][6]. 18 days after the description of Uintatherium, Cope and Marsh both named new genera of Uinta Dinoceratans, Cope naming Loxolophodon in his "garbled" telegram[7] and Marsh dubbed Tinoceras[8]. Due to Uintatherium being named first, Cope and Marsh's genera are synonymous with Uintatherium[5]. Cope described 2 genera his telegram, Loxolophodon and Eobasileus[7][9] , the latter is currently considered separate from Uintatherium[5]. Tinoceras was a new genus made for Titanotherium anceps by Marsh[8][5]. Several days later, Marsh erected the genus Dinoceras[5][8]. Dinoceras and Tinoceras would receive several additional species by Marsh throughout the 1870s and 1880s, many based on fragmentary material[8][5]. Several complete skulls were found by Cope and Marsh crews, leading to theories like Cope's proboscidean assessment[9][10]. Due to Cope and Marsh's rivalry, the two would often publish scathing criticisms of each other's work, stating their respective genera were valid[5]. The trio would name 25 species now considered synonymous with Marsh's original species, Titanotherium anceps, which was placed in Leidy's genus, Uintatherium[5]. Many additional discoveries of Uintatherium have occurred, making Uintatherium one of the best-known and popular American fossil mammals[11][5]. Princeton University launched expeditions to the Eocene beds of Wyoming in the 1870s and 1880s, discovering several partial skulls and naming several species of Uintatheres that are now considered synonyms of U. anceps[12][5].Major reassesment came in the 1960s by Walter Wheeler who synonymized and re-described many of the Uintatherium fossils discovered during the 19th century[5]. A cast of a Uintatherium skeleton is on display at the Utah Field House of Natural History State Park. The skeleton of Uintatherium is also on display at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington, DC.[13] A new species was named based on almost intact skull, U. insperatus, found in the lower part of the Lushi Formation of the Lushi Basin in Henan Province, China.[1]
References
- ^ a b Tong, Yongsheng; Wang Jingwen (July 1981). "A SKULL OF UINTATHERIUM FROM HENAN" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. XIX (3): 208–214.
- ^ "Ice Age Mammals - EnchantedLearning.com".
- ^ Joseph Leidy (1873). "Contribution to the extinct vertebrate fauna of the Western Territories". Geological Survey of the Territories. 1.
- ^ Restoration of Dinoceras mirabile by Charles Othniel Marsh
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Wheeler, W. H. (1961). Revision of the uintatheres. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University.
- ^ a b Leidy, Joseph (1872a) On some new species of fossil mammalia from Wyoming: Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadelphia Proc, 1872, p. 240-242.
- ^ a b Cope, Edward (1872). "Telegram describing extinct Proboscidians from Wyoming". Paleontological Bulletin. 5.
- ^ a b c d Anonymous (1885-03-01). "Professor Marsh's monography of the dinocerata". American Journal of Science. s3-29 (171): 173–204. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-29.171.173. ISSN 0002-9599.
- ^ a b Cope, E. D. (1873). On the Short Footed Ungulata of the Eocene of Wyoming. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society, 13(90), 38-74.
- ^ Cope, E. D. (1873). On Some of Prof. Marsh's Criticisms. The American Naturalist, 7(5), 290-299.
- ^ Wheeler, W. H. (1960). The uintatheres and the Cope-Marsh war. Science, 131(3408), 1171-1176.
- ^ Scott, W. B., (1886) On some new forms of the Dinocerata: Am. Jour. Sci., (3) v. 31, p. 303-307.
- ^ "Paleobiology | Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History".
Further reading
- Academy of Natural Sciences
- National Park Service
- Wood, Horace Elmer 1923, The problem of the Uintatherium molars, Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History ; v. 48, article 18
- Fossil Evidence - Eocene: Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History
