Nanumea: Difference between revisions
tag with {{Bare URL PDF}} |
IdiotSavant (talk | contribs) m →History: - link rot cleanup |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
The rich [[Tuvaluan mythology|mythical history of Nanumea]] describes a settlement led by an explorer/adventurer and warrior from the south named Tefolaha. Some accounts say Tefolaha and his crew came from [[Tonga]], others name [[Samoa]], but whether these names refer to today's Tonga and Samoa is not certain. Tefolaha, traditional accounts say, found the island of Nanumea populated by two women, Pai and Vau, whom it was believed had formed it from baskets of sand. Tefolaha wagered with them for the island and eventually won it through trickery, whereupon Pai and Vau departed.<ref name="GSS1">{{cite web| last = Samuels | first = George Siosi | work= The Loop |title= Tales From Nanumea: Pai & Vau (Animation) |url= http://www.theloop.com.au/siosism/portfolio/tales-from-nanumea-pai-vau/36952 | access-date=15 February 2015}}</ref> Tefolaha's sons and daughters are today the founding ancestors of leading families and the seven chiefly lineages of Nanumea. Today's population also traces descent from crew members who arrived with Tefolaha, and from later visitors from the far distant and more recent past. Nanumean traditions describe the islets, [[Temotufoliki|Motu Foliki]], [[Lefogaki|Lafogaki]] and [[Teatua a Taepoa|Te Afua-a-Taepoa]], as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha.<ref name="TAH7">{{cite book |author=Taulu Isako |editor-first1=Hugh |editor-last1=Laracy |title= Tuvalu: A History |year= 1983 |publisher= Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu |pages=49|chapter=Chapter 7 – Nanumea }}</ref> |
The rich [[Tuvaluan mythology|mythical history of Nanumea]] describes a settlement led by an explorer/adventurer and warrior from the south named Tefolaha. Some accounts say Tefolaha and his crew came from [[Tonga]], others name [[Samoa]], but whether these names refer to today's Tonga and Samoa is not certain. Tefolaha, traditional accounts say, found the island of Nanumea populated by two women, Pai and Vau, whom it was believed had formed it from baskets of sand. Tefolaha wagered with them for the island and eventually won it through trickery, whereupon Pai and Vau departed.<ref name="GSS1">{{cite web| last = Samuels | first = George Siosi | work= The Loop |title= Tales From Nanumea: Pai & Vau (Animation) |url= http://www.theloop.com.au/siosism/portfolio/tales-from-nanumea-pai-vau/36952 | access-date=15 February 2015}}</ref> Tefolaha's sons and daughters are today the founding ancestors of leading families and the seven chiefly lineages of Nanumea. Today's population also traces descent from crew members who arrived with Tefolaha, and from later visitors from the far distant and more recent past. Nanumean traditions describe the islets, [[Temotufoliki|Motu Foliki]], [[Lefogaki|Lafogaki]] and [[Teatua a Taepoa|Te Afua-a-Taepoa]], as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha.<ref name="TAH7">{{cite book |author=Taulu Isako |editor-first1=Hugh |editor-last1=Laracy |title= Tuvalu: A History |year= 1983 |publisher= Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu |pages=49|chapter=Chapter 7 – Nanumea }}</ref> |
||
The legendary, miraculous spear Kaumaile came with the hero Tefolaha to Nanumea. He fought with a {{convert|1.8|m|abbr=on}} long weapon on the islands of Samoa and Tonga. As Tefolaha died, "Kaumaile" went to his heirs, then to his heirs and on and on - 23 generations. The wood from the spear was radiocarbon dated to 880 years BP or AD 1070.<ref>http://www.nanumea.net/PDF%20files%20used%20in%20NEA%20website/Kaumaile%20Radiocarbon%20Dating%20Results,%202pp%20combined.pdf |
The legendary, miraculous spear Kaumaile came with the hero Tefolaha to Nanumea. He fought with a {{convert|1.8|m|abbr=on}} long weapon on the islands of Samoa and Tonga. As Tefolaha died, "Kaumaile" went to his heirs, then to his heirs and on and on - 23 generations. The wood from the spear was radiocarbon dated to 880 years BP or AD 1070.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nanumea.net/PDF%20files%20used%20in%20NEA%20website/Kaumaile%20Radiocarbon%20Dating%20Results,%202pp%20combined.pdf |title=Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Result |publisher=GNS Science |date=9 February 2007 |access-date=19 March 2022}}</ref> The wood is from the species [[Casuarina equisetifolia]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/mensch/suedsee-speer-hamburger-forscher-bestimmt-holzart-a-971945.html|title=Südsee-Speer: Hamburger Forscher bestimmt Holzart}}</ref> |
||
The first recorded sighting of Nanumea by Europeans was by Spanish naval officer [[Francisco Antonio Mourelle|Francisco Mourelle de la Rúa]] who sailed past it on 5 May 1781 with frigate ''La Princesa'', when attempting a southern crossing of the Pacific from the Philippines to [[New Spain]]. He charted Nanumea as ''San Augustin''.<ref name=autogenerated1>Keith S. Chambers & Doug Munro, ''The Mystery of Gran Cocal: European Discovery and Mis-Discovery in Tuvalu'', 89(2) (1980) ''[[The Journal of the Polynesian Society]]'', 167-198</ref><ref>Laumua Kofe, Palagi and Pastors, ''Tuvalu: A History'', Ch. 15, (USP / Tuvalu government)</ref> In 1809, Captain Patterson in the brig ''Elizabeth'' sighted Nanumea while passing through the northern Tuvalu waters on a trading voyage from Port Jackson, Sydney, Australia to China.<ref name=autogenerated1 /> |
The first recorded sighting of Nanumea by Europeans was by Spanish naval officer [[Francisco Antonio Mourelle|Francisco Mourelle de la Rúa]] who sailed past it on 5 May 1781 with frigate ''La Princesa'', when attempting a southern crossing of the Pacific from the Philippines to [[New Spain]]. He charted Nanumea as ''San Augustin''.<ref name=autogenerated1>Keith S. Chambers & Doug Munro, ''The Mystery of Gran Cocal: European Discovery and Mis-Discovery in Tuvalu'', 89(2) (1980) ''[[The Journal of the Polynesian Society]]'', 167-198</ref><ref>Laumua Kofe, Palagi and Pastors, ''Tuvalu: A History'', Ch. 15, (USP / Tuvalu government)</ref> In 1809, Captain Patterson in the brig ''Elizabeth'' sighted Nanumea while passing through the northern Tuvalu waters on a trading voyage from Port Jackson, Sydney, Australia to China.<ref name=autogenerated1 /> |
||
Revision as of 02:20, 19 March 2022
Nanumea | |
|---|---|
 Nanumea atoll from space | |
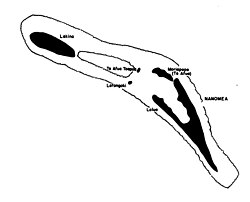 Map of the island | |
Location in Tuvalu | |
| Coordinates: 05°39′55″S 176°06′45″E / 5.66528°S 176.11250°E | |
| Country | Tuvalu |
| Area | |
• Total | 3.9 km2 (1.5 sq mi) |
| Population (2017) | |
• Total | 512 |
| • Density | 130/km2 (340/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166 code | ISO416TV-NMA |
Nanumea is the northwesternmost atoll in the Polynesian nation of Tuvalu,[1] a group of nine coral atolls and islands spread over about 400 miles (640 km) of Pacific Ocean just south of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Nanumea is 4 km2 (1.5 sq mi) with a population of 512 people (2017 census).[2]
Geography
Located along one edge of the so-called Polynesian triangle, Nanumea lies just south of the Gilbert Islands, which are Micronesian in language and culture. Nanumea is a classic atoll, a series of low islets sitting on a coral reef shelf surrounding a lagoon. About 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) long by 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) wide in overall size, the dry land area is about 3.9 square kilometres (1.5 sq mi). The two largest islets Nanumea and Lakena, which comprise 90% of the dry land area of the atoll.[3]
Since the early 1990s, the use of nets and spearing has been prohibited in all parts of the lagoon and the Nanumea Conservation Area was established in 2006.[4] The Nanumea Conservation Area covers about 2 square kilometres (0.77 sq mi) of the central lagoon and consists of about 10% of the reef area of the atoll, including marine habitats and 2 islets. A survey of the conservation zone was conducted in 2010.[5][6]
The largest villages are Haumaefa with 187 people (2012) and Lolua with 187 people (2012).[2] The junior school is Kaumaile Primary School. There are scattered households across the lagoon from Nanumea village at Matagi and on Motu Foliki, and on the southeastern tip of Lakena islet. The two largest islets, comprising over 90% of the dry land area of the atoll, are Nanumea and Lakena. In addition there are three much smaller islets, Motu Foliki, Lafogaki and Te Afua-a-Taepoa spread around the encircling reef flat. There are 2 mangrove forests, a small patch to the south of Nanumea and another on the islet of Lakena.[7]
The pulaka pits are located on Lakena,[8] as the Nanumeans want the main island of Nanumea to remain mosquito free. Pulaka is grown in large pits of composted soil below the water table.[9]
In 2011, the kou leafworm (Ethmia nigroapicella) had a devastating impact on Nanumea by stripping the leaves of the Kanava trees (Cordia subcordata), ( beach cordia). The Kanava trees provide coastal protection, wind shelter, shade and are habitats for sea birds. The flowers of the Kanava are also locally prized.[10]
In March 2015 Nanumea suffered damage to houses, crops and infrastructure as the result of storm surges caused by Cyclone Pam.[11][12]
Climate crisis
In 2016 the Tuvalu National Council for Women worked with the Green Climate Fund to enable women from the islands of Nanumea and Nanumaga to be part of talks about climate crisis. One their key issues was the additional burden of social care than women take on in the aftermath of natural disasters.[13]
Language and cultural links
Nanumeans are Polynesians. The Nanumean dialect of the Tuvaluan language is closely related to other west Polynesian languages, including the Tongan language, Tokelauan, Samoan, and the languages of the Polynesian outliers.[14] Although the eight Tuvalu communities have distinctive accents and some distinctive vocabulary, the dialects of Tuvalu are mutually intelligible to Tuvalu speakers with the exception of the language of Nui atoll, whose inhabitants speak a dialect of the Gilbertese language (with the exception of small children, most Tuvaluans from Nui also speak Tuvaluan).[14][15] With this exception, Tuvaluan is universally understood and spoken in Tuvalu. English is also spoken, especially in Tuvalu's capital, and is one of the official languages of the central government.[14]
History

The rich mythical history of Nanumea describes a settlement led by an explorer/adventurer and warrior from the south named Tefolaha. Some accounts say Tefolaha and his crew came from Tonga, others name Samoa, but whether these names refer to today's Tonga and Samoa is not certain. Tefolaha, traditional accounts say, found the island of Nanumea populated by two women, Pai and Vau, whom it was believed had formed it from baskets of sand. Tefolaha wagered with them for the island and eventually won it through trickery, whereupon Pai and Vau departed.[16] Tefolaha's sons and daughters are today the founding ancestors of leading families and the seven chiefly lineages of Nanumea. Today's population also traces descent from crew members who arrived with Tefolaha, and from later visitors from the far distant and more recent past. Nanumean traditions describe the islets, Motu Foliki, Lafogaki and Te Afua-a-Taepoa, as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha.[17]
The legendary, miraculous spear Kaumaile came with the hero Tefolaha to Nanumea. He fought with a 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) long weapon on the islands of Samoa and Tonga. As Tefolaha died, "Kaumaile" went to his heirs, then to his heirs and on and on - 23 generations. The wood from the spear was radiocarbon dated to 880 years BP or AD 1070.[18] The wood is from the species Casuarina equisetifolia.[19]
The first recorded sighting of Nanumea by Europeans was by Spanish naval officer Francisco Mourelle de la Rúa who sailed past it on 5 May 1781 with frigate La Princesa, when attempting a southern crossing of the Pacific from the Philippines to New Spain. He charted Nanumea as San Augustin.[20][21] In 1809, Captain Patterson in the brig Elizabeth sighted Nanumea while passing through the northern Tuvalu waters on a trading voyage from Port Jackson, Sydney, Australia to China.[20]
From 1879 to 1881 Alfred Restieaux was the resident trader on Nanumea.[22][23] 19th century resident Palagi traders also included: Tom Day (c.1872)[24] and Jack Buckland (c.1895). The population of Nanumea from 1860 to 1900 is estimated to be between 500[25] and 650 people.[26]
Nanumea Post Office opened around 1919.[27]

Donald Gilbert Kennedy, the resident District Officer in the administration of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony from 1932 to 1938, describe the construction of paopao and of the variations of single-outrigger canoes that had been developed on Vaitupu and Nanumea.[28]
During World War II the American forces built Nanumea Airfield and the people moved to live on Lakena.[29] USS LST-203 was grounded on the reef at Nanumea on 2 October 1943 in order to land equipment. The rusting hull of the ship remains on the reef.[30] The 'American Passage' was blasted through the reef by a Naval Construction Battalion (Seabees), who were assisted by local divers. This passage improved access to Nanumea. B-24 Liberator aircraft of 30th Bombardment Group flew from Nanumea Airfield. After the war the airfield was dismantled and the land returned to its owners, however as the coral base was compacted to make the runway the land now provides poor ground for growing coconuts.[29]
On Nanumea, tender boats, which go out to the inter-island ships, run through the 'American Passage' and offload passengers and cargo at a small wharf within the protected lagoon.[31]
Governance and connection to other Nanumean communities
Nanumea's local government consists of a chiefly council (Falekaupule) representing the seven chiefly lines which trace descent from the founder, Tefolaha, or from other key settlers, and an elected high chief (Pulefenua). The island also elects and sends two representatives to the Tuvalu national parliament based in the capital, Funafuti.
While Nanumea atoll remains the homeland for all Nanumeans, there are increasingly large populations of Nanumean residents in the capital, Funafuti, in New Zealand (especially Auckland and Wellington), and in Australia and other Pacific locations. These expatriate populations are well-organized, have active elected leadership councils, and keep in close touch with doings in Nanumea itself.
General election, 2019
Maatia Toafa and Satini Manuella were not returned to parliament at the 2019 general election. Ampelosa Manoa Tehulu and Timi Melei were elected to represent Nanumea.[32]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonpartisan | Maatia Toafa | 219 | 13.6 | |
| Nonpartisan | Satini Manuella | 198 | 12.3 | |
| Nonpartisan | Ampelosa Manoa Tehulu |
603 | 37.4 | |
| Nonpartisan | Timi Melei |
327 | 20.3 | |
| Nonpartisan | Tipelu Kauani | 266 | 16.5 | |
Identity

Nanumean identity and pride is demonstrated in many ways, from the distinctive intonation pattern and vocabulary of its version of Tuvaluan to celebrations including its unique Po o Tefolaha, part of a long holiday covering Christmas, New Year and some weeks beyond. These "Big Days" (Po Lahi) celebrations, marked with noon feasts in the island's community hall, the aahiga or maneapa,[33] feature a marathon round of the competitive ball game Ano, pitting the two village sides, Haumaefa and Lolua, against each other. On 8 January each year, the island's conversion to Christianity over a century ago is commemorated in the Po o Tefolaha, Tefolaha's Day. Po Lahi is celebrated in Nanumea itself and by many Nanumean communities overseas, including those in Funafuti, Fiji, Auckland, Wellington, Tarawa, Australia and other locations.
A widely recognized symbol of Nanumean identity and unity is the fighting spear, "Kaumaile."[34][35] Said to have been brought with him by the island's founder, Tefolaha, Kaumaile was used to defeat invaders to Nanumea, most notably by Lapi to defeat a giant, Tuulaapoupou.[36] Recent carbon dating tests have shown that the Kaumaile spear is over 800 years old.[37]
Prominent local people
Lady Naama Maheu Latasi (died 16 March 2012) was the first woman to be elected to the Parliament of Tuvalu, was elected from the constituency of Nanumea.[38]
Maatia Toafa (born 1 May 1954) was the Prime Minister of Tuvalu 2004–2006 and continues to represent Nanumea in the Parliament of Tuvalu. He served as the Minister of Finance and Economic Development in the Sopoaga Ministry (2013-2019).[39]
Willy Telavi (born 28 January 1954) was first elected to parliament in 2006 and was appointed Home Affairs Minister in the Government of Apisai Ielemia. He was re-elected in 2010 and became the Prime Minister of Tuvalu on 24 December 2010. His term of prime minister ended on 2 August 2013.[40] He resigned from Parliament in August 2014.[41][42]
Literature
Chambers, Keith S. and Anne 2001 Unity of Heart: Culture and Change in a Polynesian Atoll Society. Prospect Hts, Illinois: Waveland Press (ISBN 1-57766-166-4)
Chambers, Anne 1984 Nanumea. (No. 6 in Atoll Economy: Social Change in Kiribati and Tuvalu.) Canberra: Australian National University, Development Studies Centre (ISBN 0-86784-457-4)
Chambers, Keith S. 1984 Heirs of Tefolaha: Tradition and Social Organization in Nanumea, a Polynesian Atoll Community. PhD Dissertation, Anthropology, University of California, Berkeley (pub. by University Microfilms, Ann Arbor, Michigan)
Laracy, Hugh (editor) 1983 Tuvalu: a History. Suva: University of the South Pacific, Institute of Pacific Studies and Extension Services, and Funafuti: Ministry of Social Services. [21 chapters, maps, photos, appendices. Chapters written by Tuvaluan authors]
External links
- TALES FROM NANUMEA: PAI & VAU, animation by George Siosi Samuels, Cultural Animator
- TALES FROM NANUMEA: THE DEFEAT OF TULAAPOUPOU, animation by George Siosi Samuels, Cultural Animator
- Nanumea.Net—A Website for the People of Nanumea
- Images and further information on the Kaumaile spear from Nanumea.net
- TuvaluIslands.com
References
- ^ "Maps of Tuvalu". Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- ^ a b "Population of communities in Tuvalu". Thomas Brinkhoff. 2017. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- ^ FCG ANZDEC Ltd (7 August 2020). Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment - Nanumaga and Nanumea (Report). The Pacific Community. p. 45. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ FCG ANZDEC Ltd (7 August 2020). Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment - Nanumaga and Nanumea (Report). The Pacific Community. p. 74. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ Sandrine Job, Dr. Daniela Ceccarelli (December 2012). "Tuvalu Marine Life Scientific Report" (PDF). an Alofa Tuvalu project with the Tuvalu Fisheries Department. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- ^ Sandrine Job, Dr. Daniela Ceccarelli (December 2011). "Tuvalu Marine Life Synthesis Report" (PDF). an Alofa Tuvalu project with the Tuvalu Fisheries Department. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- ^ FCG ANZDEC Ltd (7 August 2020). Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment - Nanumaga and Nanumea (Report). The Pacific Community. p. 79. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ FCG ANZDEC Ltd (7 August 2020). Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment - Nanumaga and Nanumea (Report). The Pacific Community. p. 64. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ Taulu Isako (1983). "Chapter 7 – Nanumea". In Laracy, Hugh (ed.). Tuvalu: A History. Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu. pp. 55–56.
- ^ FCG ANZDEC Ltd (7 August 2020). Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment - Nanumaga and Nanumea (Report). The Pacific Community. p. 76. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ "Tuvalu: Tropical Cyclone Pam Situation Report No. 2 (as of 30 March 2015)". Relief Web. 30 March 2015. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ^ "Tuvalu situation update: Securing health from disastrous impacts of cyclone Pam in Tuvalu". Relief Web/World health Organisation – Western Pacific Region. 3 April 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ FP015: Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project (PDF). Green Climate Fund.
- ^ a b c Besnier, Niko (2000). Tuvaluan: A Polynesian Language of the Central Pacific. London: Routledge.
- ^ "Tuvaluan (Te 'gana Tūvalu)". Omniglot. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- ^ Samuels, George Siosi. "Tales From Nanumea: Pai & Vau (Animation)". The Loop. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ^ Taulu Isako (1983). "Chapter 7 – Nanumea". In Laracy, Hugh (ed.). Tuvalu: A History. Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu. p. 49.
- ^ "Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Result" (PDF). GNS Science. 9 February 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2022.
- ^ "Südsee-Speer: Hamburger Forscher bestimmt Holzart".
- ^ a b Keith S. Chambers & Doug Munro, The Mystery of Gran Cocal: European Discovery and Mis-Discovery in Tuvalu, 89(2) (1980) The Journal of the Polynesian Society, 167-198
- ^ Laumua Kofe, Palagi and Pastors, Tuvalu: A History, Ch. 15, (USP / Tuvalu government)
- ^ Resture, Alfred. "Alfred Restieaux Manuscripts – Part 2". Jane Resture. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ Munro, Doug (1980). "Tom De Wolf's Pacific Venture: The Life History of a Commercial Enterprise in Samoa". Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ Hayter, Lieut, Francis, Logbook & Journal, H.M.S. Basilisk, January 1871-1873, Pacific Manuscripts Bureau
- ^ Richard Bedford, Barrie Macdonald & Doug Monro, Population Estimates for Kiribati and Tuvalu (1980) 89(1) Journal of the Polynesian Society 199
- ^ W.F. Newton, The Early Population of the Ellice Islands, 76(2) (1967) The Journal of the Polynesian Society, 197-204.
- ^ Premier Postal History. "Post Office List". Premier Postal Auctions. Retrieved 5 July 2013.
- ^ Kennedy, Donald (1931). "The Ellice Islands Canoe Journal of the Polynesian Society Memoir no. 9". Journal of the Polynesian Society: 71–100.
- ^ a b Melei Telavi (1983). "Chapter 18 - War". In Laracy, Hugh (ed.). Tuvalu: A History. Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu. p. 143.
- ^ Bartsch, Bill. "War Relics in Tuvalu and Kiribati" (PDF). South Pacific Bulletin (1975). Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- ^ FCG ANZDEC Ltd (7 August 2020). Tuvalu Coastal Adaptation Project: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment - Nanumaga and Nanumea (Report). The Pacific Community. p. 91. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- ^ Tahana, Jamie (10 September 2019). "Tuvalu elections: large turnover for new parliament". Radio New Zealand. Retrieved 10 September 2019.
- ^ Lambert, Sylvester M. "Meeting house on Nanumea, Tuvalu, called the aahiga or maneapa". Special Collections & Archives, UC San Diego. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ^ Chambers, Keith S.; Chambers, Anne (2001). Unity of Heart: Culture and Change in a Polynesian Atoll Society. Prospect Hts, Illinois: Waveland Press. ISBN 1-57766-166-4.
- ^ More about the Kaumaile
- ^ Samuels, George Siosi. "Tales From Nanumea: The Defeat of Tulaapoupou (Animation)". The Loop. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ^ Nanumea Website
- ^ "The first elected female Member of Parliament in Tuvalu, Lady Sapeta Naama Maheu Laatasi, laid to rest in Funafuti" (PDF). Tuvalu Philatelic Bureau Newsletter (TPB: 01/2012). 2 May 2012.
- ^ "Enele Sopoaga Sworn-in Today as Tuvalu's New PM". Islands Business. 5 August 2013. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
- ^ Cooney, Campbell (4 August 2013). "Tuvalu parliament elects new prime minister". Australia News Network. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
- ^ "Former Tuvalu PM quits parliament". Radio New Zealand International. 26 August 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ^ "Tuvalu to hold by-election after MP resignation". Radio Australia. 25 August 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.