Half-metal: Difference between revisions
m Open access bot: hdl added to citation with #oabot. |
Removed link for paper that was irrelevant (a theory paper for a compound "CsS" which doesn't exist). Tag: references removed |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Half-metals were first described in 1983, as an explanation for the electrical properties of [[Manganese|Mn]]-based [[Heusler alloy]]s.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=de Groot |first1=R. A. |last2=Mueller |first2=F. M. |last3=Engen |first3=P. G. van |last4=Buschow |first4=K. H. J. |title=New Class of Materials: Half-Metallic Ferromagnets |journal=Physical Review Letters |date=20 June 1983 |volume=50 |issue=25 |pages=2024–2027 |doi=10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.2024 |bibcode=1983PhRvL..50.2024D |url=https://pure.rug.nl/ws/files/3419075/1983PhysRevLettdeGroot.pdf |hdl=11370/e3946f6b-8acb-4e0a-80cf-735506203f25 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
Half-metals were first described in 1983, as an explanation for the electrical properties of [[Manganese|Mn]]-based [[Heusler alloy]]s.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=de Groot |first1=R. A. |last2=Mueller |first2=F. M. |last3=Engen |first3=P. G. van |last4=Buschow |first4=K. H. J. |title=New Class of Materials: Half-Metallic Ferromagnets |journal=Physical Review Letters |date=20 June 1983 |volume=50 |issue=25 |pages=2024–2027 |doi=10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.2024 |bibcode=1983PhRvL..50.2024D |url=https://pure.rug.nl/ws/files/3419075/1983PhysRevLettdeGroot.pdf |hdl=11370/e3946f6b-8acb-4e0a-80cf-735506203f25 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
||
Some notable half-metals are [[chromium(IV) oxide]], [[magnetite]], and [[lanthanum strontium manganite]] (LSMO),<ref name=COEY02/> as well as [[chromium arsenide]]. Half-metals have attracted some interest for their potential use in [[spintronics]]. |
Some notable half-metals are [[chromium(IV) oxide]], [[magnetite]], and [[lanthanum strontium manganite]] (LSMO),<ref name=COEY02/> as well as [[chromium arsenide]]. Half-metals have attracted some interest for their potential use in [[spintronics]]. |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 21:27, 3 May 2022
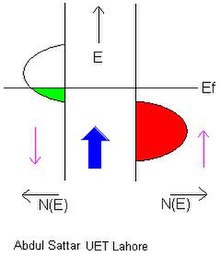
A half-metal is any substance that acts as a conductor to electrons of one spin orientation, but as an insulator or semiconductor to those of the opposite orientation. Although all half-metals are ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic), most ferromagnets are not half-metals. Many of the known examples of half-metals are oxides, sulfides, or Heusler alloys.[1]
In half-metals, the valence band for one spin orientation is partially filled while there is a gap in the density of states for the other spin orientation. This results in conducting behavior for only electrons in the first spin orientation. In some half-metals, the majority spin channel is the conducting one while in others the minority channel is.[citation needed]
Half-metals were first described in 1983, as an explanation for the electrical properties of Mn-based Heusler alloys.[2]
Some notable half-metals are chromium(IV) oxide, magnetite, and lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO),[1] as well as chromium arsenide. Half-metals have attracted some interest for their potential use in spintronics.
References
- ^ a b Coey, J.M.D.; Venkatesan, M. (2002). "Half-metallic ferromagnetism: Example of CrO2". Journal of Applied Physics. 91 (10): 8345–50. Bibcode:2002JAP....91.8345C. doi:10.1063/1.1447879.
- ^ de Groot, R. A.; Mueller, F. M.; Engen, P. G. van; Buschow, K. H. J. (20 June 1983). "New Class of Materials: Half-Metallic Ferromagnets" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 50 (25): 2024–2027. Bibcode:1983PhRvL..50.2024D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.50.2024. hdl:11370/e3946f6b-8acb-4e0a-80cf-735506203f25.
Further reading
- Guezlane, M; Baaziz, H; El Haj Hassan, F; Charifi, Z; Djaballah, Y (2016). "Electronic, magnetic and thermal properties of Co2CrxFe1−xX (X=Al, Si) Heusler alloys: First-principles calculations". Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 414: 219–26. Bibcode:2016JMMM..414..219G. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.04.056.
- Son, Young-Woo; Cohen, Marvin L; Louie, Steven G (2006). "Half-metallic graphene nanoribbons". Nature. 444 (7117): 347–9. arXiv:cond-mat/0611600. Bibcode:2006Natur.444..347S. doi:10.1038/nature05180. PMID 17108960. S2CID 52851642.
- http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~ah566/research/half_metals.html[full citation needed][permanent dead link]
- http://www.tcd.ie/Physics/People/Michael.Coey/oxsen/newsletter/january98/halfmeta.htm[full citation needed]


