Flag of Barbados: Difference between revisions
CzarJobKhaya (talk | contribs) m →Historical flags: Chronological |
ce |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[File:Barbados Flag - Montréal (43347249922).jpg|thumb|Barbados flag at Carifiesta 2018, [[Montreal]]]] |
[[File:Barbados Flag - Montréal (43347249922).jpg|thumb|Barbados flag at Carifiesta 2018, [[Montreal]]]] |
||
The |
The '''flag of Barbados''' was designed by Grantley Prescod and was officially adopted to represent the nation of [[Barbados]] on 30 November 1966, the island's first [[Independence Day]]. It was raised for the first time by Lieutenant Hartley Dottin of the [[Barbados Regiment]]. |
||
== Design == |
== Design == |
||
Revision as of 06:25, 4 July 2022
 | |
| The Broken Trident | |
| Use | National flag, civil and state ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | 30 November 1966 |
| Design | A vertical triband of ultramarine (hoist-side and fly-side) and gold with the black trident-head centred on the gold band. |
| Designed by | Grantley Prescod |
 | |
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A red cross on a white field, the national flag in the canton |

The flag of Barbados was designed by Grantley Prescod and was officially adopted to represent the nation of Barbados on 30 November 1966, the island's first Independence Day. It was raised for the first time by Lieutenant Hartley Dottin of the Barbados Regiment.
Design
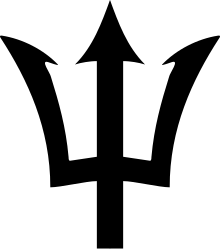
It consists of a triband of two bands of ultramarine, which are said to stand for the ocean surrounding the country and the sky, separated by a golden middle band, which represents the sand. A black trident head, commonly called the broken trident, is centred in the golden band, and the fact that the staff is missing is significant. The trident symbol was taken from Barbados' colonial badge, where the trident of Poseidon is shown with Britannia holding it. The broken lower part symbolises a symbolic break from its status as a colony.[1] The three points of the trident represent the three principles of democracy: 1) government of the people, 2) government for the people, and 3) government by the people.[2]
The design of the flag was created by Grantley W. Prescod and was chosen from an open competition arranged by the Barbados government. Over a thousand entries were received.[3]
The official British Standard colour code numbers for the flag are: Ultramarine —BCC 148, Gold — BS O/002.[4]
Other flags
-
Standard of the President of Barbados
-
Standard of the Prime Minister of Barbados
Historical flags
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1870–1966 | Flag of the Colony of Barbados | A Blue Ensign with an emblem of Barbados. |
 |
1958–1962 | Flag of the West Indies Federation | Known as "Sun and Seas Flag"[5] — A blue field with four white horizontal wavy bars (the top pair of bars being parallel and the lower pair also parallel) and an orange sun in the centre. |
 |
1966–2021 | Royal Standard of Barbados | A bearded fig tree (with the leaves coloured blue) in the centre and a Pride of Barbados flower in each of the top corners on a yellow field. A blue disc of the letter "E" crowned surrounded by a garland of gold roses defaces the flag. |
 |
1966–2021 | Standard of the Governor-General of Barbados | A crowned lion standing on a crown, on a blue field, with the words "Barbados" |
See also
References
- ^ Flag of Barbados, Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Barbados). Archived from original on 13 November 2011. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ "Barbados". Flags Of The World. Retrieved 2021-02-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Government of Barbados National Flag". Barbados.gov.bb. 12 November 2003. Archived from the original on 28 April 2010. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ CHAPTER 300A NATIONAL EMBLEMS AND NATIONAL ANTHEM OF BARBADOS (REGULATION), World Intellectual Property Office (WIPO)
- ^ Princess Opens New Parliament (1958), YouTube


