Neurothekeoma: Difference between revisions
m Task 18 (cosmetic): eval 5 templates: del empty params (2×); |
add difference section |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Neurothekeoma2.JPG|thumbnail|Neurothekeoma [[histology]] slide]] |
[[Image:Neurothekeoma2.JPG|thumbnail|Neurothekeoma [[histology]] slide]] |
||
'''Neurothekeoma''' is a benign cutaneous tumor |
'''Neurothekeoma (NT)''' is a rare benign cutaneous tumor, superficial soft tissue tumors that frequently develop on the head and neck. They often occur in the second and early third decades of life and tend to afflict women more frequently than men<ref>Barnhill RL, Mihm MC. Cellular neurothekeoma. A distinctive variant of neurothekeoma mimicking nevomelanocytic tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 Feb;14(2):113-20</ref>. First described by Gallager and Helwig, who proposed the term in order to reflect the presumed origin of the lesion from nerve sheath.<ref name= "helwig">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gallager RL, Helwig EB |title= Neurothekeoma-a benign cutaneous tumor of neural origin |journal=American Journal of Clinical Pathology |volume=74 |issue=6 |pages=759–764 |date=December 1980 |pmid=7446487 |doi=10.1093/ajcp/74.6.759 }}</ref> Microscopically, the lesions described closely resembled the tumor, "nerve sheath myxoma (NSM)", an entity first described by Harkin and Reed.<ref name= "harkin">{{Citation |title= Tumors of the Peripheral Nervous System, in Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, ed: Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 2nd series, fascicle 3 |last= Harkin|first= James C. |author2=Richard J. Reed|year= 1969|publisher= Armed Forces Institute of Pathology|location= Washington, D.C.}}</ref> The latter had, through the years, been variously described as "Bizarre cutaneous neurofibroma",<ref name= "pulitzer">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pulitzer DR, Reed RJ |title=Nerve-sheath myxoma (perineurial myxoma)|journal=American Journal of Dermatopathology |volume=7 |issue=5 |pages=407–421 |date=October 1985 |pmid=4091218 }}</ref> "Myxoma of nerve sheath",<ref name="pulitzer" /> and "Pacinian neurofibroma".<ref name="pulitzer" /> |
||
Clinically, neurothekeomas present as a solitary nodule of the skin.<ref name= "fetsch">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Hallman JR, Lupton GP, Miettinen M |title= Neurothekeoma: an analysis of 178 tumors with detailed immunohistochemical data and long-term patient follow-up information |journal=American Journal of Surgical Pathology |volume=31 |issue=7 |pages=1103–1114 |date=July 2007 |pmid=17592278 |doi=10.1097/pas.0b013e31802d96af|url= https://zenodo.org/record/1234901 }}</ref> The most common sites of occurrence are the head and neck and the extremities.<ref name="fetsch" /> The lesions range in size from about 0.5 cm. to more than 3 cm.<ref name="fetsch" /> The average patient age is about 25 years, but neurothkeomas may occur at any age.<ref name="fetsch" /> Women are affected about more often; the male to female ratio is approximately 1:2.<ref name="fetsch" /> |
Clinically, neurothekeomas present as a solitary nodule of the skin.<ref name= "fetsch">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Hallman JR, Lupton GP, Miettinen M |title= Neurothekeoma: an analysis of 178 tumors with detailed immunohistochemical data and long-term patient follow-up information |journal=American Journal of Surgical Pathology |volume=31 |issue=7 |pages=1103–1114 |date=July 2007 |pmid=17592278 |doi=10.1097/pas.0b013e31802d96af|url= https://zenodo.org/record/1234901 }}</ref> The most common sites of occurrence are the head and neck and the extremities.<ref name="fetsch" /> The lesions range in size from about 0.5 cm. to more than 3 cm.<ref name="fetsch" /> The average patient age is about 25 years, but neurothkeomas may occur at any age.<ref name="fetsch" /> Women are affected about more often; the male to female ratio is approximately 1:2.<ref name="fetsch" /> |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Microscopically, neurothekeoma consists of closely aggregated bundles or fascicles of spindle-shaped cells.<ref name= "lever">{{Citation |chapter= Chapter 35: Tumors of Neural Tissue |title=Lever's Histopathology of the Skin |edition=Ninth |editor=Elder D |display-editors=etal |last= Reed|first= Richard J. |author2=Pulitzer, Donald R.|year= 2008|publisher= Lippincott Raven |location= Philadelphia |isbn= 978-0781773638 }}</ref> The fascicles may or may not have a myxoid background.<ref name="lever" /> |
Microscopically, neurothekeoma consists of closely aggregated bundles or fascicles of spindle-shaped cells.<ref name= "lever">{{Citation |chapter= Chapter 35: Tumors of Neural Tissue |title=Lever's Histopathology of the Skin |edition=Ninth |editor=Elder D |display-editors=etal |last= Reed|first= Richard J. |author2=Pulitzer, Donald R.|year= 2008|publisher= Lippincott Raven |location= Philadelphia |isbn= 978-0781773638 }}</ref> The fascicles may or may not have a myxoid background.<ref name="lever" /> |
||
Since the time of their first description, it has been reported that neurothekeomas are likely not of nerve sheath origin, as implied by the term.<ref name= "fetsch" /> Consequently, neurothekeoma and nerve sheath myxoma are likely not related histogenetically, although they are similar in appearance and in behavior.<ref name="fetsch" />Based mostly on the quantity of myxoid matrix present, neurothekeomas can have a variety of histologic characteristics, including myxoid, cellular, or mixed-type. The myxoid variety of neurothekeoma has inadvertently included nerve sheath myxoma because to similarity in clinical presentation and histology. However, it appears that the neurothekeoma that Barnhill and Mihm reported in 1990 is a a separate and distinct entity from true nerve sheath myxoma<ref>Almeida TFA, Verli FD, Dos Santos CRR, Falci SGM, Almeida LY, Almeida LKY, Mesquita ATM, León JE. Multiple Desmoplastic Cellular Neurothekeomas in Child: Report of the First Oral Case and Review of the Literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2018 Mar;12(1):75-81.</ref>.It has been proposed that neurothekeomas are derived from fibrohistiocytic cells rather than the peripheral nerve sheath.<ref>Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Hallman JR, Lupton GP, Miettinen M. Neurothekeoma: an analysis of 178 tumors with detailed immunohistochemical data and long-term patient follow-up information. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Jul;31(7):1103-14.</ref><ref name= "Hornick">Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Cellular neurothekeoma: detailed characterization in a series of 133 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Mar;31(3):329-40.</ref><ref>Page RN, King R, Mihm MC, Googe PB. Microphthalmia transcription factor and NKI/C3 expression in cellular neurothekeoma. Mod Pathol. 2004 Feb;17(2):230-4.</ref><ref>Yun SJ, Park HS, Lee JB, Kim SJ, Lee SC, Won YH. Myxoid Cellular Neurothekeoma: A New Entity of S100-Negative, CD68-Positive Myxoid Neurothekeoma. Ann Dermatol. 2014 Aug;26(4):510-3.</ref>Despite having a different histologic appearance, neurothekeoma does not respond with the S100 protein while nerve sheath myxoma does (myxoid, mixed, or cellular). |
|||
Since the time of their first description, it has been reported that neurothekeomas are likely not of nerve sheath origin, as implied by the term.<ref name= "fetsch" /> Consequently, neurothekeoma and nerve sheath myxoma are likely not related histogenetically, although they are similar in appearance and in behavior.<ref name="fetsch" /> |
|||
== Difference from nerve sheath myxoma== |
|||
A rare neuro-ectodermal tumor known as a benign nerve sheath myxoma (NSM) was originally identified in 1969<ref name="harkin" />. In contrast, a cellular variation known as Neurothekeoma (NT) was characterized in 1980 by Gallager and Helwig<ref name="helwig" />. Later on, it was common to use both Neurothekeoma (NT) and nerve sheath myxoma (NSM) interchangeably.<ref>A.M. Cimino-Mathews, Peripheral nerve sheath tumors, Surgical Pathol. 4 (2011) 761–782</ref><ref>K.M. Benbenisty, A. Andea, J. Metcalf, et al., Atypical cellular neurothekeoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery, Dermatol. Surg. 32 (2006) 582–587</ref>In 2011, Sheth et al. used microarray analysis to distinguish between Neurothekeoma and Nerve Sheath Myxoma based on the genetic expression of the cells<ref>S. Sheth, X. Li, S. Binder, S.M. Dry, Differential gene expression profiles of neurothekeomas and nerve sheath myxomas by microarray analysis, Mod. Pathol. 24 (2011) 343–354.</ref>. NSM is more frequent among young people without gender preference. Between 30 and 40 years of age is when the incidence peaks<ref>I. Ahmed, J. Rawat, S. Singh, A. Sharma, A. Pandey, M. Goel, Neurothekeoma: a sacrococcygeal tumor in a child, J. Pediatr. Surg. 45 (2010) 1037–1039.</ref>. The head and neck are rarely affected by the tumor, which is more usually seen in the upper limb<ref> S.A. Fanto, E. Fanto, Neurothekeoma of the median nerve: case report, J. Hand Surg. 37A (2012) 1184–1186.</ref>. Young women are twice as likely as males to get NT, and it usually affects the head and neck rather than the hands<ref name="Hornick" />. While NT can afflict females from infancy to old age with a peak incidence in the twenties, NSM has a peak incidence in the fourth decade<ref>P.W. Allen, Myxoma is not a single entity: a review of the concept of myxoma, Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 4 (2000) 99–123</ref>. |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 02:05, 13 July 2022
Neurothekeoma (NT) is a rare benign cutaneous tumor, superficial soft tissue tumors that frequently develop on the head and neck. They often occur in the second and early third decades of life and tend to afflict women more frequently than men[1]. First described by Gallager and Helwig, who proposed the term in order to reflect the presumed origin of the lesion from nerve sheath.[2] Microscopically, the lesions described closely resembled the tumor, "nerve sheath myxoma (NSM)", an entity first described by Harkin and Reed.[3] The latter had, through the years, been variously described as "Bizarre cutaneous neurofibroma",[4] "Myxoma of nerve sheath",[4] and "Pacinian neurofibroma".[4]
Clinically, neurothekeomas present as a solitary nodule of the skin.[5] The most common sites of occurrence are the head and neck and the extremities.[5] The lesions range in size from about 0.5 cm. to more than 3 cm.[5] The average patient age is about 25 years, but neurothkeomas may occur at any age.[5] Women are affected about more often; the male to female ratio is approximately 1:2.[5]
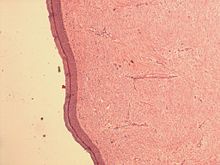
Microscopically, neurothekeoma consists of closely aggregated bundles or fascicles of spindle-shaped cells.[6] The fascicles may or may not have a myxoid background.[6]
Since the time of their first description, it has been reported that neurothekeomas are likely not of nerve sheath origin, as implied by the term.[5] Consequently, neurothekeoma and nerve sheath myxoma are likely not related histogenetically, although they are similar in appearance and in behavior.[5]Based mostly on the quantity of myxoid matrix present, neurothekeomas can have a variety of histologic characteristics, including myxoid, cellular, or mixed-type. The myxoid variety of neurothekeoma has inadvertently included nerve sheath myxoma because to similarity in clinical presentation and histology. However, it appears that the neurothekeoma that Barnhill and Mihm reported in 1990 is a a separate and distinct entity from true nerve sheath myxoma[7].It has been proposed that neurothekeomas are derived from fibrohistiocytic cells rather than the peripheral nerve sheath.[8][9][10][11]Despite having a different histologic appearance, neurothekeoma does not respond with the S100 protein while nerve sheath myxoma does (myxoid, mixed, or cellular).
Difference from nerve sheath myxoma
A rare neuro-ectodermal tumor known as a benign nerve sheath myxoma (NSM) was originally identified in 1969[3]. In contrast, a cellular variation known as Neurothekeoma (NT) was characterized in 1980 by Gallager and Helwig[2]. Later on, it was common to use both Neurothekeoma (NT) and nerve sheath myxoma (NSM) interchangeably.[12][13]In 2011, Sheth et al. used microarray analysis to distinguish between Neurothekeoma and Nerve Sheath Myxoma based on the genetic expression of the cells[14]. NSM is more frequent among young people without gender preference. Between 30 and 40 years of age is when the incidence peaks[15]. The head and neck are rarely affected by the tumor, which is more usually seen in the upper limb[16]. Young women are twice as likely as males to get NT, and it usually affects the head and neck rather than the hands[9]. While NT can afflict females from infancy to old age with a peak incidence in the twenties, NSM has a peak incidence in the fourth decade[17].
See also
- List of cutaneous conditions
- List of histologic stains that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions
- Myxoid tumor
References
- ^ Barnhill RL, Mihm MC. Cellular neurothekeoma. A distinctive variant of neurothekeoma mimicking nevomelanocytic tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 Feb;14(2):113-20
- ^ a b Gallager RL, Helwig EB (December 1980). "Neurothekeoma-a benign cutaneous tumor of neural origin". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 74 (6): 759–764. doi:10.1093/ajcp/74.6.759. PMID 7446487.
- ^ a b Harkin, James C.; Richard J. Reed (1969), Tumors of the Peripheral Nervous System, in Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, ed: Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 2nd series, fascicle 3, Washington, D.C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology
- ^ a b c Pulitzer DR, Reed RJ (October 1985). "Nerve-sheath myxoma (perineurial myxoma)". American Journal of Dermatopathology. 7 (5): 407–421. PMID 4091218.
- ^ a b c d e f g Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Hallman JR, Lupton GP, Miettinen M (July 2007). "Neurothekeoma: an analysis of 178 tumors with detailed immunohistochemical data and long-term patient follow-up information". American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 31 (7): 1103–1114. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31802d96af. PMID 17592278.
- ^ a b Reed, Richard J.; Pulitzer, Donald R. (2008), "Chapter 35: Tumors of Neural Tissue", in Elder D; et al. (eds.), Lever's Histopathology of the Skin (Ninth ed.), Philadelphia: Lippincott Raven, ISBN 978-0781773638
- ^ Almeida TFA, Verli FD, Dos Santos CRR, Falci SGM, Almeida LY, Almeida LKY, Mesquita ATM, León JE. Multiple Desmoplastic Cellular Neurothekeomas in Child: Report of the First Oral Case and Review of the Literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2018 Mar;12(1):75-81.
- ^ Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Hallman JR, Lupton GP, Miettinen M. Neurothekeoma: an analysis of 178 tumors with detailed immunohistochemical data and long-term patient follow-up information. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Jul;31(7):1103-14.
- ^ a b Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Cellular neurothekeoma: detailed characterization in a series of 133 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007 Mar;31(3):329-40.
- ^ Page RN, King R, Mihm MC, Googe PB. Microphthalmia transcription factor and NKI/C3 expression in cellular neurothekeoma. Mod Pathol. 2004 Feb;17(2):230-4.
- ^ Yun SJ, Park HS, Lee JB, Kim SJ, Lee SC, Won YH. Myxoid Cellular Neurothekeoma: A New Entity of S100-Negative, CD68-Positive Myxoid Neurothekeoma. Ann Dermatol. 2014 Aug;26(4):510-3.
- ^ A.M. Cimino-Mathews, Peripheral nerve sheath tumors, Surgical Pathol. 4 (2011) 761–782
- ^ K.M. Benbenisty, A. Andea, J. Metcalf, et al., Atypical cellular neurothekeoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery, Dermatol. Surg. 32 (2006) 582–587
- ^ S. Sheth, X. Li, S. Binder, S.M. Dry, Differential gene expression profiles of neurothekeomas and nerve sheath myxomas by microarray analysis, Mod. Pathol. 24 (2011) 343–354.
- ^ I. Ahmed, J. Rawat, S. Singh, A. Sharma, A. Pandey, M. Goel, Neurothekeoma: a sacrococcygeal tumor in a child, J. Pediatr. Surg. 45 (2010) 1037–1039.
- ^ S.A. Fanto, E. Fanto, Neurothekeoma of the median nerve: case report, J. Hand Surg. 37A (2012) 1184–1186.
- ^ P.W. Allen, Myxoma is not a single entity: a review of the concept of myxoma, Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 4 (2000) 99–123
