Flag of Ukraine: Difference between revisions
add image, replaced |
→Gallery: sorry, but it's inappropriate to use symbols of Russian Federation (even symbols of it's so-called "opposition forces") along with Ukrainian flag, because there is literally a WAR Tag: Reverted |
||
| Line 273: | Line 273: | ||
File:Stand with Ukraine against Russian Invasion - Vancouver Anti-War Rally, Feb 26th, 2022 (51905035487).jpg|An anti-war protest in [[Vancouver]], with dozens of Ukrainian flags |
File:Stand with Ukraine against Russian Invasion - Vancouver Anti-War Rally, Feb 26th, 2022 (51905035487).jpg|An anti-war protest in [[Vancouver]], with dozens of Ukrainian flags |
||
File:Bloor St., Toronto (51945046897).jpg|A workplace on [[Bloor West Village]] in [[Toronto]] displaying the Ukrainian flag. Canada is home to a number of [[Ukrainian Canadians|ethnic Ukrainians]] outside of the former Soviet Union. |
File:Bloor St., Toronto (51945046897).jpg|A workplace on [[Bloor West Village]] in [[Toronto]] displaying the Ukrainian flag. Canada is home to a number of [[Ukrainian Canadians|ethnic Ukrainians]] outside of the former Soviet Union. |
||
File: |
File:Flag of Ukraine over city Dnipro.jpg|The highest flagpole with Ukrainian flag in [[Dnipro]]. |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
Revision as of 16:46, 17 July 2022
 | |
| Use | National flag and state ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | 1848 (originally) 22 March 1918 (officially adopted) 24 August 1991 (de facto restored) 28 January 1992 (current proportion) 1 September 2006 (current colors) |
| Design | A horizontal bicolour of blue and yellow |
| Naval ensign | |
 | |
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | 20 June 2006 |
| Design | White with a blue Saint George's cross that extends to the edges of the flag, with the national bicolour in the canton. |
The Flag of Ukraine (Template:Lang-uk) consists of equally sized horizontal bands of blue and yellow.[1] As a national flag, the blue and yellow bicolour has been used since the 1848 Spring of Nations, when it was hoisted over Lviv Town Hall. It was officially adopted as a state flag for the first time in 1918 by the short-lived West Ukrainian People's Republic and subsequently used by the Ukrainian People's Republic, just before World War II it was also adopted by Carpatho-Ukraine in March 1939.
When Ukraine was part of the Soviet Union, the flag of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic was used and the bicolour flag was outlawed. The blue and yellow flag was provisionally adopted for official ceremonies in September 1991 following Ukrainian independence, before officially being restored on 28 January 1992 by the Parliament of Ukraine.[2][3]
Ukraine has celebrated the Day of the National Flag on 23 August since 2004.[4]
Design
Ukrainian law states that the colours of Ukrainian flag are "blue and yellow", but other state bodies have determined the colours. In the table below, the colours are presented according to DSTU 4512:2006 technical specifications:[5]

| Scheme | Strong azure | Yellow |
|---|---|---|
| Pantone | Pantone Coated 2935 C | Pantone Coated Yellow 012 C[6] |
| RAL | 5019 Azure | 1023 Gold (golden) |
| RGB color model | 0, 87, 183[7] | 255, 215, 0[8] |
| CMYK | 100, 63, 0, 2[7] | 0, 2, 100, 0[8] |
| HEX | #0057b7 | #ffd700 |
| Websafe | #0066cc | #ffcc00 |
There has been disagreement over the shade of blue used in the flag.[9] In 2013, scholar Dmytro Malakov argued that sky blue was the correct colour, and that, according to rules of heraldry, dark blue should not be used.[10] The head of the Ukrainian Heraldry Society said that this heraldry issue does not apply to flags.[9]
The flag is similar to that of the Austrian state of Lower Austria, the German city of Chemnitz and the Hungarian city of Pécs, but all of those flags have a darker shade of blue. The flag is also somewhat similar to that of the Malaysian state of Perlis, but has a reversed color arrangement, darker shades of blue and yellow, and a different aspect ratio.
Protocol and use
This section needs additional citations for verification. (August 2017) |
Legal status
Article 20 of the Constitution of Ukraine states that "the State Flag of Ukraine is a banner of two equally sized horizontal bands of blue and yellow colour." (Template:Lang-uk).[11][12]
Vertical flags

In addition to the normal horizontal format, many public buildings, such as the Verkhovna Rada, use vertical flags. Most town halls fly their town flag together with the national flag in this way; some town flags in Ukraine exist only in vertical form. The proportions of these vertical flags are not specified. When hung like a banner or draped, the blue band should be on the left. When flown from a vertical flagpole, the blue band must face the mast.
Stamps

The flag did not appear on Ukrainian postal stamp issues until 1992, when they depicted the flag with the state coat of arms. Since then, the flag has frequently appeared on stamps. Cinderella stamps of the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists were printed outside Ukraine during the Soviet period for patriotic purposes.
Decoration
Traditionally, the flag may be decorated with a golden fringe surrounding the perimeter of the flag, as long as it does not deface the flag proper. The tradition began with the flag of the Ukrainian SSR. In addition, the Great Soviet Encyclopedia shows a flag decorated with a gold star. Ceremonial displays of the flag, such as those in parades or on indoor posts, often use a fringe to enhance the allure of the flag. No specific law governs the use of the fringe. Traditionally, the Army, Guard, Navy and Air Force use a fringed flag for parades, colour guards and indoor displays, while the Office of the President and local authorities use a fringed flag on all occasions.
Places of continuous display

Ukrainian flags are customarily displayed continuously in certain locations.
- Maidan Nezalezhnosti, main square of Kyiv, traditional site for political rallies, including large-scale radical protest campaigns (Orange Revolution and Euromaidan)
- Presidential Administration Building, Verkhovna Rada building and Budynok Uryadu
- Kyiv City Council
- Lviv High Castle
- Vernadsky Research Base
- State Border Guard Service of Ukraine sites
- National, regional and local government buildings
- Ukrainian embassies and consulates
Particular days for display
In particular, the flag should be displayed at full staff on the following days:
- 1 January: New Year's Day
- 7 January: Christmas (Julian)
- 22 January: Ukrainian Unity Day
- 8 March: International Women's Day
- 1 & 2 May: International Workers' Day
- 9 May: Victory Day over Nazism
- 28 June: Constitution Day
- 23 August: Flag Day
- 24 August: Independence Day
- 21 November: Day of Dignity and Freedom
- 6 December: Armed Forces Day
- 25 December: Christmas (Gregorian/Neo-Julian)
Display at half-staff
The flag is displayed at half-staff (or half-mast) as a sign of respect or mourning. When done nationwide, such a step is proclaimed by the president. Half-mast means flying a flag two-thirds of the way up a flagpole; the top of the flag must be at least a flag's height from the top of the flagpole. Black ribbons indicate mourning on banners that can't be lowered to half-mast.
- 4th Saturday of November: Holodomor Memorial Day
- Other historical cases: mass victims of accidents, War in Donbass and Euromaidan; death and state funeral of Lech and Maria Kaczyński, funeral of Pope John Paul II and 11 September attacks.
Flag Day

The Day of the National Flag in Ukraine is celebrated on 23 August; it began in 2004. Previously, 24 July was National Flag Day in Kyiv. The first ceremonial raising of the yellow-and-blue Ukrainian flag in modern times took place on 24 July 1990, at the flagstaff of the Kyiv City Council, two years before the flag was officially adopted as the National flag. Since 1992, the Independence Day of Ukraine has been celebrated on 24 August. Following a government decree, the flag must be flown from public buildings on this date and certain other holidays; not all are public holidays. Flags must also be flown on parliamentary election days and regional-specific flag days. The public display of flags to mark other events, such as the election of the president or the death of a prominent politician (whereupon flags are flown at half-mast), can be declared at the discretion of the Cabinet of Ministers. When flags are flown at half-mast, vertical flags are not lowered. A black mourning ribbon is instead attached, either atop the mast if hung from a pole, or to each end of the flag's supporting cross-beams if flown like a banner.
History


The roots of Ukrainian national symbols come from pre-Christian times when yellow and blue prevailed in traditional ceremonies, reflecting fire and water.[13] The most solid proof of yellow and blue colours can be traced back as far as the Battle of Grunwald in 1410, in which militia formations from various lands of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth participated.
Blue-yellow, red-black, crimson-olive and especially raspberry colour banners were widely used by Cossacks between the 16th and 18th centuries. These were not the only possible combinations, since normally Cossacks would fly their hetman's banners, which were similar to the coats of arms of the nobility. Also, yellow and blue were the colours common on coats of arms in Galicia. In fact, the coat of arms of Lviv to this day remains a golden lion on a blue field.
Some put the starting point of the adoption of the current national flag of Ukraine to 1848 when, during the Spring of the Nations on 22 April 1848, a blue-and-yellow banner was adopted by the Supreme Ruthenian Council[14] in Lemberg (Lviv), the capital of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, and flew over the city's magistrate for the first time. Although this move did not have significant consequences, the newly formed Ukrainian divisions in the Austrian army used blue-and-yellow banners in their insignia.
During the Russian Revolution of 1905, this flag was used by Ukrainians of the Dnieper Ukraine, or the Russian part of Ukraine.
 Flag of the Kingdom of Ruthenia
Flag of the Kingdom of Ruthenia Flags of the Ruthenian lands during the Battle of Grunwald, 1410
Flags of the Ruthenian lands during the Battle of Grunwald, 1410
 Banner of the Zaporizhian Sich before 1775
Banner of the Zaporizhian Sich before 1775 Flag of the Black Sea Cossack Host in 1803
Flag of the Black Sea Cossack Host in 1803
Early independence: 1917–1921


Both blue-yellow and yellow-blue flags were widely used during the Ukrainian struggle for independence in 1917. For the first time in the history of the Russian Empire, the blue-yellow flag was flown on 25 March 1917 in Petrograd during a 20,000-strong mass demonstration.[14] On the territory of Ukraine the national flag was flown for the first time in Kyiv on 29 March 1917 by soldiers.[14] On 1 April 1917, Kyiv saw a 100,000-strong demonstration where over 320 national flags were flown.[14] Afterwards, similar demonstrations with Ukrainian flags took place across the entire Russian Empire, even beyond ethnic Ukrainian lands.[14] Numerous famous Ukrainian politicians wrote about the 1 April demonstration, including Mykhailo Hrushevsky and Serhiy Yefremov, noting that there were blue-and-yellow flags, while Dmytro Doroshenko claimed that they were yellow and blue.[14] The blue-yellow flag was flown at the First Ukrainian Military Congress on 18 May 1917.[14]
The official flag established by the Ukrainian People's Republic in 1918 was blue-yellow. Instead, they refer to the decision on the Fleet Flag, which was to be light blue–yellow,[15] as an indication that the official flag was light blue–yellow.[16] Also adopted were several other service flags of the Ukrainian People's Republic.[17]
The official flag of Pavlo Skoropadsky's Hetmanate was also light blue-yellow and remained the same under the Directorate of Symon Petlura. The flag of the West Ukrainian People's Republic was blue-yellow. The stateless Makhnovshchina (Free Territory), which existed during the Ukrainian War of Independence, used the black flag.
Among Ukrainian immigrant organisations, there were proponents of both blue-yellow and yellow-blue flags. Eventually, an agreement was reached to use the blue-yellow flag until the issue could be resolved by an independent Ukraine.
-
 Version of the Flag of the Ukrainian People's Republic (1917)
Version of the Flag of the Ukrainian People's Republic (1917)
Soviet Ukraine: 1922–1991

During Soviet rule, the Ukrainian flag was banned,[20] and anyone displaying it could be criminally prosecuted for "anti-Soviet propaganda". The first flag of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic was adopted on 10 March 1919, to serve as the symbol of state of Soviet Ukraine. Details of the official flag changed periodically before the break-up of the Soviet Union in 1991, but all were based on the red flag of the October Revolution in Russia and an exact replica of the flags of the neighbouring Russian SFSR. The first flag was red with the gold Cyrillic sans-serif letters У.С.С.Р. (USSR, acronym for Ukrayinskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Sovetskaya Respublika in the Russian language). In the 1930s, a gold border was added to the flag. In 1937, a new flag was adopted, with a small gold hammer and sickle added above the gold Cyrillic serif У.Р.С.Р. (URSR, for Ukrayins’ka Radyans’ka Sotsialistychna Respublika in the Ukrainian language).
-
 Flag of the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets (1917–1918)
Flag of the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets (1917–1918)
Interbellum and Reichskommissariat Ukraine
The Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists is a Ukrainian political organisation which as a movement was originally created in 1929 in Western Ukraine (interwar Poland at the time). For a long time, the OUN did not officially have its own flag; however, during the Hungarian and Polish aggression against the Republic of Carpathian Ukraine in 1939, Carpathian Sich, a militarised wing of the OUN, adopted as its flag a design taken from the OUN's emblem – a golden nationalistic trident on a blue background. The flag was finalised and only officially adopted by the organisation in 1964 at the 5th Assembly of Ukrainian Nationalists.
The Ukrainian Insurgent Army was a Ukrainian nationalist paramilitary and later partisan army that engaged in a series of guerrilla conflicts during World War II against Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia, and both underground and communist Poland. The group was the military wing of the Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists — Bandera faction (the OUN-B), originally formed in Volyn in the spring and summer of 1943. Its official date of creation is 14 October 1942. The battle flag of the UPA was a 2:3 ratio red-and-black banner. The flag continues to be a symbol of the Ukrainian nationalist movement. The colours of the flag symbolise 'Ukrainian red blood spilled on Ukrainian black earth'.
In 1949, the flag of the Soviet Ukraine was changed once again.[9] The Soviet Union managed to obtain two additional seats in the United Nations by adding Ukraine and Byelorussia as member states .[9] The flag change came about because all the Soviet flags were the same.[9] The new Ukrainian flag consisted of red (top, 2/3) and azure (bottom, 1/3) stripes,[9] with the golden star, hammer and sickle in the top left corner. Communist party leaders such as Nikita Khrushchev and Lazar Kaganovich feared using words like 'light blue' and 'blue' in the official flag colors, as they were the terms used by the Ukrainian diaspora.[9]
During the Soviet period, multiple unsanctioned attempts to hoist the national blue-and-yellow flag were made. In 1958, an underground group was established in the village of Verbytsia, Khodoriv Raion; its members raised national flags and spread anti-Soviet pamphlets under cover of darkness.[21]
Return of the national flag


Under the influence of Mikhail Gorbachev's policies of perestroika and glasnost, individual Soviet republics gained a strengthened sense of national identity, leading to the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. This was particularly true for the three Baltic states and Western Ukraine, which were the last territories annexed into Soviet Union. The national awakening was accompanied by attempts to restore historical national symbols. In 1988, the Supreme Soviet of the Lithuanian SSR re-established Lithuania's national flag and coat of arms as the state symbol. The parliaments of Latvia and Estonia soon followed suit.

The events in the Baltic countries soon led to similar patterns in Ukraine. In particular, West Ukraine and the Ukrainian SSR's capital city of Kyiv were the scenes of near-constant political demonstrations, in which yellow-and-blue flags were waved by demonstrators.
- On 14 March 1990, the Ukrainian flag was raised for the first time since the establishment of the Soviet Union in the small city of Stryi.[22]
- On 20 March 1990, the Ternopil town council voted on the use and re-establishment of the yellow-and-blue flag and the tryzub and Shche ne vmerla Ukrainy national anthem. The same day, the yellow-and-blue national flag was flown for the first time in 80 years on a governmental building in Kyiv, replacing the then-official red-azure flag of the Ukrainian SSR.
- On 28 April 1990, the Lviv oblast council (oblasna rada) also allowed the use of the national symbols of Ukraine within the Oblast.
- On 29 April 1990, the yellow-and-blue flag was flown from the Ternopil city theatre's flagstaff without the flag of the Soviet Union hanging above it.
- After 24 July 1990, the yellow-and-blue flag was flown for the first time over an official governmental building, the Kyiv City Council, on Maidan Nezalezhnosti Square of Khreschatyk Street.[23]
- After the declaration of independence of Ukraine on 24 August 1991, the national yellow-and-blue flag flew for the first time over the Ukrainian Parliament (Verkhovna Rada) building on 4 September 1991.
-
Flag of Post-Soviet Ukraine from 24 August 1991 to 28 January 1992 (red-blue)[24]
-
Flag of Post-Soviet Ukraine used from 8 September 1991 to 28 January 1992 (blue-yellow)
-
Flag of Ukraine used 1992–2006
At the beginning of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, landmarks all over the world were lit up with the colours of the Ukrainian flag, while numerous cities raised the Ukrainian flag in solidarity.[25][26]
Flag controversies and criticism
Origin
One claimed version is that, since one of the first known coloured depictions of the Coat of Arms of Kyiv was mainly in yellow-blue colours, this tradition may have existed since the time of the Nordic-Slavic Grand Prince of Kyiv Volodymyr the Great. However, the blue-yellow colouring dates back to Kievan Rus’, as an early version of the Tryzub, Ukraine's national coat of arms, sported the same colouring as the seal of Sviatoslav I of Kyiv (c. AD 945). During the 1709 Battle of Poltava, the Cossacks following Mazepa fought under yellow-blue banners, while their Swedish allies were under yellow ones. Some Cossacks and noblemen had coats of arms in yellow and blue.[27]
Yellow-blue versus blue-yellow
Ukrainians commonly refer to the flag as "yellow and light blue" (Template:Lang-uk, zhovto-blakytnyy)[28]—a different version of the flag used during UNR (Ukrainian National Republic) years (1917–1921) with yellow on the top and blue on the bottom. The yellow on the top allegedly represents golden domes (cupolas) of Christian churches and the blue the Dnieper river.
The head of the Ukrainian Heraldry Society, Andriy Grechylo, points to the fact that the discussion about order of colours was taking place as far back as 1918.[9] Nonetheless, both governments of the Ukrainian People's Republic as well as the Ukrainian State defined that the upper half would be light-blue, while the lower would be yellow.[9] During 1918 it was taken into consideration that light blue would lose its shade under sun, therefore it was decided to make the colour darker.[9]
Already in the 1918 draft of the Constitution of the Ukrainian People's Republic, the order of colours was defined as blue and yellow.[9] The same order could be found in legislative acts of the West Ukrainian People's Republic for November 1918 and the Republic of Carpathian Ukraine on 15 March 1939.[9] The argument on the order of colours was taking place in the Ukrainian diaspora as well.[9] In 1949 it was decided that, until Ukraine defined a single state flag, the diaspora would use the blue-and-yellow banner.[9]
Attempts to revive Soviet flags
On 21 April 2011, the Verkhovna Rada passed a law allowing the Victory Banner to be raised on Victory Day.[29] The current Victory Banner was adopted in Russia in 2007. On 20 May 2011, the law was signed by the President of Ukraine Viktor Yanukovych.[30] On 17 June 2011, the Constitutional Court of Ukraine recognised the law as unconstitutional and proposed that the parliament implement required amendments to the Constitution of Ukraine.[31] On 9 April 2015, the Ukrainian parliament passed legislation on decommunization, banning the promotion of symbols of “Communist and National Socialist totalitarian regimes".[32] Since then, Soviet symbols, like the Victory Banner, have only been allowed in cemeteries.[33]
Flag of the head of state
Throughout the history of Ukraine, various heads of state have used different flags. The designs differ according to the historical era during which they were used and the political situation in Ukraine at the time. Pavlo Skoropadskyi was the first Ukrainian head of state to use a flag. The current design, the flag of the President of Ukraine, was adopted in 1999. In 2022, the President of Ukraine used a variant in which the left side of the blue upper-half contains the yellow Tryzub.[34]
Military flags

-
Armed Forces
-
Ground Forces
-
Air Force
-
National Guard
-
Navy
Historical
-
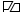 Naval flag of the Ukrainian People's Republic
Naval flag of the Ukrainian People's Republic -
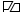 Naval flag of the Ukrainian State (1918, 1992)
Naval flag of the Ukrainian State (1918, 1992) -
 Naval flag of the Ukrainian State (1918)
Naval flag of the Ukrainian State (1918) -
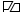 Flag of the Soviet Union used to represent the Soviet Army (1955–1991)
Flag of the Soviet Union used to represent the Soviet Army (1955–1991) -
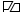 Flag of the Soviet Air Force (1924–1991)
Flag of the Soviet Air Force (1924–1991) -
 Flag of the Soviet Navy (1953–1991)
Flag of the Soviet Navy (1953–1991) -
 Flag of the Soviet Airborne Troops
Flag of the Soviet Airborne Troops
Gallery
-
A series of Ukrainian flags
-
Ukrainian troops marching in the 25th Anniversary of the Republic of Moldova, 2016
-
An anti-war protest in Moscow in 2014, with Ukrainian and Russian flags
-
A Ukrainian soldier kisses the flag
-
Ukrainian team with the flag during the Parade of Nations at the 2020 Summer Games in Tokyo
-
An anti-war protest in Vancouver, with dozens of Ukrainian flags
-
A workplace on Bloor West Village in Toronto displaying the Ukrainian flag. Canada is home to a number of ethnic Ukrainians outside of the former Soviet Union.
-
The highest flagpole with Ukrainian flag in Dnipro.
See also
- Coat of arms of Ukraine
- List of Ukrainian flags
- National colours of Ukraine
- Flag of Bosnia & Herzegovina
- Flag of Sweden
References
- ^ Article 20)
- ^ "Ukraine's national flag celebrating 25th anniversary today". UNIAN. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ Trach, Nataliya (26 August 2016). "The story behind 2 top Ukrainian symbols: National flag and trident". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 27 August 2016.
- ^ Ukraine celebrates National Flag Day Archived October 7, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Xinhua News Agency (August 23, 2012)
Ceremony of hoisting Ukraine's national flag held at presidential administration, Kyiv Post (August 23, 2011)
Україна відзначає День Державного прапора "On Tuesday, August 23, all of Ukraine celebrates National Flag Day. Measures to raise the national flag are planned throughout the country." Archived 1 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine, 1+1 (August 23, 2011) - ^ "ДСТУ 4512:2006 — Вікіджерела". uk.wikisource.org (in Ukrainian). Wikimedia. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- ^ Svirko, W.; A. Rubcov; A. Gorpinchenko; W. Sinel'nikova; G. Docenko; O. Kupko; I. Potapenko; E. Ershova (September 2006). State Flag of Ukraine. DSTU 4512:2006. Kyiv: State Standards of Ukraine. p. 7.
- ^ a b "PANTONE® 2935 C - Find a Pantone Color | Quick Online Color Tool | Pantone". www.pantone.com.
- ^ a b "PANTONE® Yellow 012 C - Find a Pantone Color | Quick Online Color Tool | Pantone". www.pantone.com.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Gazeta.ua (23 August 2013). "Хрущов і Каганович боялися слова "жовто-блакитний" (Khrushchev and Kaganovich were afraid of the word "zhovto-blakytnyi")". Gazeta.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ Skorokhod, Olga (25 July 2013). "Синьо-жовтий прапор – це знущання над українською традицією" [The dark blue and yellow flag is a mockery of Ukrainian tradition]. Gazeta.ua (in Ukrainian).
- ^ Constitution of Ukraine.
- ^ Конституція України. Верховна Рада України (in Ukrainian).
- ^ Saprykov, V. (30 May 2003). Флаг Украины [Flag of Ukraine]. geraldika.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2 October 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Синьо-жовтий чи жовто-блакитний? Міфи про "перевернутий" прапор (Blue-yellow or yellow-blue? Myths about the flipped flag)". Ukrayinska Pravda Історична правда. 14 January 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ Rozovyk, D. F. (1999). Документи та матеряли: Про створення української національно-державної символіки у роки визвольної боротьби (1917-1920 рр.) [Documents and materials: On the creation of Ukrainian national-state symbols during the battle for liberation (1917-1920)] (PDF). Ukrainian Historical Journal (in Ukrainian). 4. Kyiv: history.org.ua: 115–121. ISSN 0130-5247. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2007.
- ^ Chmyr, Mykola (2006). Українське військо у ХХ-ХХІ сторіччі: 'Командні хоругви' Галицької Армії (серпень 1919 р.) [Ukrainian Army in the 20th-21st Century: 'Command banners' of the Galician Army (August 1919)]. vijsko.milua.org (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 2 October 2017.
- ^ Grechylo A. Ukrayinska Terytorialna Heraldyka. Lviv, 2010, pp. 98–118. ISBN 978-966-02-5259-2
- ^ Smith, Ned (24 February 2001). "Green Ukraine / Ukrainian Far East (1921, Russian Far East)". FOTW "Flags Of The World". CRW Flags. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
In "Flags of Non-Russian Peoples Under Soviet Rule" by Prof. Walter Trembicky [tbc69], pages 134 and 135, it mentions two proposed flags for Green Ukraine, or the Ukrainian Far East, neither of which was officially adopted, since the movement quickly proved abortive. There are simple black & white line drawings illustrating the two proposed flags on p. 133 of [tbc69]. The green in the two flags was described as dark or deep green. ... One [of the two proposed flags] was the Ukrainian blue-over-gold bicolor with a green triangle at the hoist.
- ^ Trembicky, Walter (1969). Flags of Non-Russian Peoples Under Soviet Rule. Flag Research Center. pp. 134, 135.
- ^ "The Revolution On Granite: Ukraine's 'First Maidan'". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ "Невідомі прапороносці. Жовто-блакитний проти червоного (Unknown flag-bearers. Yellow-blue against Red)". Ukrayinska Pravda Історична правда. 29 July 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ "History of evolution of the State Flag of Ukraine". Ukrinform (in Ukrainian). 23 August 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2022. Archived August 17, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "22 роки тому в Києві офіційно підняли синьо-жовтий прапор (Twenty two years ago in Kyiv officially was raised the blue-yellow flag)". BBC News Україна (in Ukrainian). 24 July 2012. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ "Про Державний прапор України". Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ "Town of Blue Mountains Info:Town Raises Ukrainian Flag in Support and Solidarity for the People of Ukraine".
- ^ "VIDEO : Ukraine invasion: Europe's landmarks turned blue and yellow in solidarity with Kyiv".
- ^ Vannier, Alexis (24 August 2021). "" CHTCHE NE VMERLA UKRAÏNY " : HISTOIRE DU DRAPEAU DE L'UKRAINE". taurillon.org (in French). Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ^ A little less often they use also "yellow and blue", "blue and yellow" and "yellow and azure".
- ^ "РАДА ЗОБОВ'ЯЗАЛА ВИВІШУВАТИ ЧЕРВОНІ ПРАПОРИ НА 9 ТРАВНЯ (Rada enforced raising red flags on the May 9)". Ukrayinska Pravda Історична правда. 21 April 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ "ЯНУКОВИЧ ПІДПИСАВ ЗАКОН ПРО ЧЕРВОНИЙ ПРАПОР (Yanukovych signed the law about the Red Banner)". Ukrayinska Pravda Історична правда. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ "КС Украины признал неконституционным использование красного знамени Победы (CC of Ukraine recognised the use of Red Victory Banner as non-constitutional)". Russian Gazette Российская газета (in Russian). 17 June 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- ^ Peterson, Nolan (10 April 2015). "Ukraine Purges Symbols of Its Communist Past". Newsweek. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
"Rada bans Communist, Nazi propaganda in Ukraine". Interfax-Ukraine. 9 April 2015. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
Hyde, Lily (20 April 2015). "Ukraine to rewrite Soviet history with controversial 'decommunisation' laws". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 16 May 2015. Retrieved 17 May 2015. - ^ Shevchenko, Vitaly (14 April 2015). "Goodbye, Lenin: Ukraine moves to ban communist symbols". BBC News. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
Ukraine lawmakers ban 'Communist and Nazi propaganda', Deutsche Welle (9 April 2015) - ^ Basu, Zachary (1 March 2022). "Zelensky tells European Parliament "nobody is going to break us" in emotional appeal". Axios. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
External links
- Ukraine at Flags of the World
- DSTU 4512:2006 Technical specifications from DSTU (Ukrainian national standards body) regarding flag of Ukraine, in Ukrainian. 1 September 2006.
- Ukraine – Vexillographia
- Armed Forces Flag in Ukraine
- Departmantal Flag and Emblem in Ukraine
- Brief history of the flag Archived 18 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine at the Science Library of Franko National University (Lviv).
- "About Ukrainian flag". Statement of the Presidium of the Supreme Council of Ukraine. 18 September 1991.
- "About the State Flag of Ukraine". State of the Supreme Council of Ukraine. 28 January 1992.










![Proposed flag of Green Ukraine in Eastern Siberia[18][19]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/96/Flag_of_Green_Ukraine.svg/150px-Flag_of_Green_Ukraine.svg.png)





































