Menkheperreseneb II: Difference between revisions
→References: add authority control, test using AWB |
Added floor plan |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Apart from his tomb TT112, there are many monuments bearing the name of a "High Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb"; unfortunately, for almost all of these, it is not possible to determine whether they belonged to "the elder" or to "the younger". This is the case for numerous [[funerary cone]]s scattered in many museums throughout the world (e.g. [[University College London]],<ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37578.gif | UC 37578</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37579.gif | UC 37579</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37580.gif | UC 37580</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37581.gif | UC 37581</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37582.gif | UC 37582</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37583.gif | UC 37583</ref> [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] of New York, [[The Archeological Civic Museum (MCA) of Bologna|the Archeological Civic Museum of Bologna]]<ref>EG 3409 or EG 3414.</ref>), a vase from [[Saqqara]], and a [[Scarab (artifact)|scarab]] upon which he as the ''Overseer of the Crafts of Amun.''<ref>{{cite book|last=Hayes|first=William C.|author-link=William C. Hayes|year=1978|title=The Scepter of Egypt: A Background for the Study of the Egyptian Antiquities in The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Vol. 2, The Hyksos Period and the New Kingdom (1675–1080 B.C.) |isbn=978-0-87-099191-2|publisher=The Metropolitan Museum of Art}}, p. 129</ref><br> |
Apart from his tomb TT112, there are many monuments bearing the name of a "High Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb"; unfortunately, for almost all of these, it is not possible to determine whether they belonged to "the elder" or to "the younger". This is the case for numerous [[funerary cone]]s scattered in many museums throughout the world (e.g. [[University College London]],<ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37578.gif | UC 37578</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37579.gif | UC 37579</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37580.gif | UC 37580</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37581.gif | UC 37581</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37582.gif | UC 37582</ref><ref>http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37583.gif | UC 37583</ref> [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] of New York, [[The Archeological Civic Museum (MCA) of Bologna|the Archeological Civic Museum of Bologna]]<ref>EG 3409 or EG 3414.</ref>), a vase from [[Saqqara]], and a [[Scarab (artifact)|scarab]] upon which he as the ''Overseer of the Crafts of Amun.''<ref>{{cite book|last=Hayes|first=William C.|author-link=William C. Hayes|year=1978|title=The Scepter of Egypt: A Background for the Study of the Egyptian Antiquities in The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Vol. 2, The Hyksos Period and the New Kingdom (1675–1080 B.C.) |isbn=978-0-87-099191-2|publisher=The Metropolitan Museum of Art}}, p. 129</ref><br> |
||
A sitting statue of a ''[[Second Prophet of Amun|Second Priest of Amun]] Menkheperraseneb'' (the "Second Priest" is the rank immediately below the "High Priest") in the [[British Museum]] (BM 708) may refer to either priest in the early stage of his career,<ref Name=Fazzini/> although it may suggest an unrelated individual.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.britishmuseum.org/research/collection_online/collection_object_details.aspx?objectId=119650&partId=1&searchText=menkheperraseneb&page=1|title=statue|website=British Museum|language=en-GB|access-date=2018-03-22}}</ref> In the [[Cairo Museum]] is an inscribed statue of a ''Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb, son of Amenemhat'' (CG 42125), which was long attributed to either priest, now is likely to belong to a different individual.<ref Name=Dorman/> Moreover, another statue ([[Brooklyn Museum]] 36613), inscribed with the [[cartouche]]s of Thutmose III, surely belongs to a High Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb, although it is not possible to determine which of the two.<ref Name=Fazzini/> |
A sitting statue of a ''[[Second Prophet of Amun|Second Priest of Amun]] Menkheperraseneb'' (the "Second Priest" is the rank immediately below the "High Priest") in the [[British Museum]] (BM 708) may refer to either priest in the early stage of his career,<ref Name=Fazzini/> although it may suggest an unrelated individual.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.britishmuseum.org/research/collection_online/collection_object_details.aspx?objectId=119650&partId=1&searchText=menkheperraseneb&page=1|title=statue|website=British Museum|language=en-GB|access-date=2018-03-22}}</ref> In the [[Cairo Museum]] is an inscribed statue of a ''Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb, son of Amenemhat'' (CG 42125), which was long attributed to either priest, now is likely to belong to a different individual.<ref Name=Dorman/> Moreover, another statue ([[Brooklyn Museum]] 36613), inscribed with the [[cartouche]]s of Thutmose III, surely belongs to a High Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb, although it is not possible to determine which of the two.<ref Name=Fazzini/> |
||
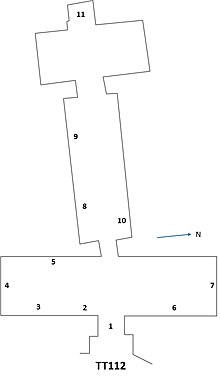
[[File:TT112.jpg|center|thumb|Plan of Menkheperraseneb II's tomb, TT112]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 12:10, 1 September 2022
| Menkheperreseneb II | |
|---|---|
| High Priest of Amun | |
 The Second Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb (BM 708): he may be Menkheperreseneb II in his early career (see text) | |
| Predecessor | Menkheperraseneb I |
| Dynasty | 18th Dynasty |
| Pharaoh | Thutmose III and Amenhotep II |
| Father | Hepu |
| Mother | Taiunet |
| Burial | TT112, Thebes |
| |||||
| Menkheperreseneb in hieroglyphs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Era: New Kingdom (1550–1069 BC) | |||||
Menkheperreseneb II was a High Priest of Amun, Superintendent of the Gold and silver treasuries, and Chief of the Overseers of Craftsmen. He served at the time of Thutmose III and Amenhotep II, and may have been buried in his Theban tomb, TT112.
Biography
Menkheperreseneb II was a son of the charioteer of His Majesty Hepu and the King's Nurse Taiunet.[1] Until recently it was believed that there was only one High Priest of Amun called Menkheperraseneb; in 1994, Egyptologist Peter Dorman showed that the HPA were actually two: Menkheperreseneb II was indeed the nephew and successor of Menkheperraseneb I, brother of Hepu and owner of tomb TT86.[2]
Attestations
Apart from his tomb TT112, there are many monuments bearing the name of a "High Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb"; unfortunately, for almost all of these, it is not possible to determine whether they belonged to "the elder" or to "the younger". This is the case for numerous funerary cones scattered in many museums throughout the world (e.g. University College London,[3][4][5][6][7][8] Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York, the Archeological Civic Museum of Bologna[9]), a vase from Saqqara, and a scarab upon which he as the Overseer of the Crafts of Amun.[10]
A sitting statue of a Second Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb (the "Second Priest" is the rank immediately below the "High Priest") in the British Museum (BM 708) may refer to either priest in the early stage of his career,[1] although it may suggest an unrelated individual.[11] In the Cairo Museum is an inscribed statue of a Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb, son of Amenemhat (CG 42125), which was long attributed to either priest, now is likely to belong to a different individual.[2] Moreover, another statue (Brooklyn Museum 36613), inscribed with the cartouches of Thutmose III, surely belongs to a High Priest of Amun Menkheperraseneb, although it is not possible to determine which of the two.[1]
References
- ^ a b c Fazzini, Richard A., A Statue of a High Priest Menkheperreseneb in The Brooklyn Museum, in Studies in honor of William Kelly Simpson, vol. 1 (1996) pp 209-225.
- ^ a b Peter Dorman, Two Tombs and One Owner, in Thebanische Beamtennekropolen. Studien zur Archäologie und Geschichte Altägyptens 12. Edited by J. Assmann, E, Dziobek, H. Guksch, and F. Kampp. Heidelberg: Heidelberger Orientverlag, 1994, pp. 141-54.
- ^ http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37578.gif | UC 37578
- ^ http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37579.gif | UC 37579
- ^ http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37580.gif | UC 37580
- ^ http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37581.gif | UC 37581
- ^ http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37582.gif | UC 37582
- ^ http://www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/thebes/archive/uc37583.gif | UC 37583
- ^ EG 3409 or EG 3414.
- ^ Hayes, William C. (1978). The Scepter of Egypt: A Background for the Study of the Egyptian Antiquities in The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Vol. 2, The Hyksos Period and the New Kingdom (1675–1080 B.C.). The Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 978-0-87-099191-2., p. 129
- ^ "statue". British Museum. Retrieved 2018-03-22.
