Grandfather clock: Difference between revisions
BCE/CE is unnecessary and a given. |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A tall, freestanding, weight-driven pendulum clock}} |
{{Short description|A tall, freestanding, weight-driven pendulum clock}} |
||
{{other uses|Grandfather clock (disambiguation)}} |
{{other uses|Grandfather clock (disambiguation) {{!}} Grandfather Clock (disambiguation)}} |
||
[[File:Longcase clock.JPG|thumb|8-day longcase clock. This example dates back to 1700 and the case to late 19th – early 20th century. The original dial of this clock was replaced by a brass dial with [[Tamil language|Tamil]] numerals, perhaps around the same time as the case. The original long-case was also replaced by a [[mandapa]]-shaped wooden carved case done in [[South India|South Indian]] style. The front and the side panels are done in metal [[Repoussé and chasing|repoussé]] work with floral meanders. The lower part of the case depicts mythological scenes and the case was manufactured at the [[Madras School of Art|Madras School of Arts]]. This clock is on display in [[The Prince of Wales Museum]] in [[Mumbai]] and was donated by [[Dorab Tata]].]] |
[[File:Longcase clock.JPG|thumb|8-day longcase clock. This example dates back to 1700 and the case to late 19th – early 20th century. The original dial of this clock was replaced by a brass dial with [[Tamil language|Tamil]] numerals, perhaps around the same time as the case. The original long-case was also replaced by a [[mandapa]]-shaped wooden carved case done in [[South India|South Indian]] style. The front and the side panels are done in metal [[Repoussé and chasing|repoussé]] work with floral meanders. The lower part of the case depicts mythological scenes and the case was manufactured at the [[Madras School of Art|Madras School of Arts]]. This clock is on display in [[The Prince of Wales Museum]] in [[Mumbai]] and was donated by [[Dorab Tata]].]] |
||
Revision as of 21:56, 12 September 2022

A grandfather clock (also a longcase clock, tall-case clock, grandfather's clock, or floor clock) is a tall, freestanding, weight-driven pendulum clock with the pendulum held inside the tower or waist of the case. Clocks of this style are commonly 1.8–2.4 metres (6–8 feet) tall with an enclosed pendulum and weights suspended by either cables or chains which have to be calibrated occasionally to keep the proper time. The case often features elaborately carved ornamentation on the hood (or bonnet), which surrounds and frames the dial, or clock face. The English clockmaker William Clement is credited with the development of this form in 1670. Until the early 20th century, pendulum clocks were the world's most accurate timekeeping technology, and longcase clocks, due to their superior accuracy, served as time standards for households and businesses. Today they are kept mainly for their decorative and antique value, having been widely replaced by both analog and digital timekeeping.
Origin
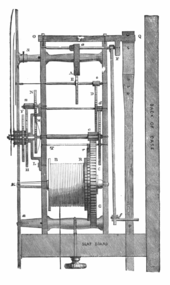
The advent of the longcase clock is due to the invention of the anchor escapement mechanism by Robert Hooke around 1658. Prior to the adoption of the anchor mechanism, pendulum clock movements used an older verge escapement mechanism, which required very wide pendulum swings of about 80–100°.[1] Long pendulums with such wide swings could not be fitted within a case, so most freestanding clocks had short pendulums.

The anchor mechanism reduced the pendulum's swing to around 4° to 6°,[1] allowing clockmakers to use longer pendulums, which had slower "beats". These consumed less power allowing clocks to run longer between windings, caused less friction and wear in the movement, and were more accurate.[1] Almost all longcase clocks use a seconds pendulum (also called a "Royal" pendulum[2]) meaning that each swing (or half-period) takes one second. These are about a metre (39 inches) long (to the centre of the bob), requiring a long narrow case. The long narrow case actually predated the anchor clock by a few decades, appearing in clocks in 1660 to allow a long drop for the powering weights. However, once the seconds pendulum began to be used, this long weight case proved perfect to house it as well.[3][4]
British clockmaker William Clement, who disputed credit for the anchor escapement with Robert Hooke, made the first longcase clocks by 1680.[5] Later the same year, Thomas Tompion, the most prominent British clockmaker, was making them too.[5] Longcase clocks spread rapidly from England to other European countries and Asia.
The first longcase clocks, like all clocks prior to the anchor escapement, had only one hand; an hour hand. The increased accuracy made possible by the anchor motivated the addition of the minute hand to clock faces in the next few decades.
Between 1680 and 1800, the average price of a grandfather clock in England remained steady at £1 10s. In 1680, this was the amount paid by an average working family for a year's rent, so the purchase of clocks was confined to the relatively well-off. But by 1800 wages had increased enough so that many lower middle class households owned grandfather clocks.[6]
Modern longcase clocks use a more accurate variation of the anchor escapement called the deadbeat escapement.
Description

Traditionally, longcase clocks were made with two types of movement: eight-day and one-day (30-hour) movements. A clock with an eight-day movement required winding only once a week, while generally less expensive 30-hour clocks had to be wound every day. Eight-day clocks are often driven by two weights – one driving the pendulum and the other the striking mechanism, which usually consisted of a bell or chimes. Such movements usually have two keyholes, one on each side of the dial to wind each one. By contrast, 30-hour clocks often had a single weight to drive both the timekeeping and striking mechanisms. Some 30-hour clocks were made with false keyholes, for customers who wished that guests to their home would think that the household was able to afford the more expensive eight-day clock. All modern striking longcase clocks have eight-day mechanical quarter chiming and full hour striking movements. Most longcase clocks are cable-driven, meaning that the weights are suspended by cables. If the cable were attached directly to the weight, the load would cause rotation and untwist the cable strands, so the cable wraps around a pulley mounted to the top of each weight. The mechanical advantage of this arrangement also doubles the running time allowed by a given weight drop.
Cable clocks are wound by inserting a special crank (called a "key") into holes in the clock's face and turning it. Others, however, are chain-driven, meaning that the weights are suspended by chains that wrap around gears in the clock's mechanism, with the other end of the chain hanging down next to the weight. To wind a chain-driven longcase clock, one pulls on the end of each chain, lifting the weights until the weights come up to just under the clock's face.
Elaborate striking sequences
In the early 20th century, quarter-hour chime sequences were added to longcase clocks. At the top of each hour, the full chime sequence sounds, immediately followed by the hour strike. At 15 minutes after each hour, 1/4 of the chime sequence plays, at the bottom of each hour, 1/2 of the chime sequence plays, and at 15 minutes before each hour, 3/4 of the chime sequence plays. The chime tune used in almost all longcase clocks is Westminster Quarters. Many also offer the option of Whittington chimes or St. Michael's chimes, selectable by a switch mounted on the right side of the dial, which also allows one to silence the chimes if desired. As a result of adding chime sequences, all modern mechanical longcase clocks have three weights instead of just two. The left weight provides power for the hour strike, the middle weight provides power for the clock's pendulum and general timekeeping functions, while the right weight provides power for the quarter-hour chime sequences.
Naming

The Oxford English Dictionary states that the popular 1876 song My Grandfather's Clock is responsible for the common name "grandfather clock" being applied to the longcase clock.[7]

The song was composed by an American songwriter by the name of Henry Clay Work who discovered a longcase clock in The George Hotel in Piercebridge, in County Durham in England. When he asked about the clock, he was informed that it had two owners. After the first owner died the clock became inaccurate and when the second owner died, the clock stopped working altogether. The story inspired Henry to create the song.
Grandfather clocks are of a certain height, usually at least 1.9 metres (6 feet - 3 inches). There are also "grandmother" and "granddaughter" clocks, which are slightly shorter in height.[8][9]

Types

Comtoise
Comtoise clocks, also known as Morbier clocks or Morez clocks, are a style of longcase clock made in the French region Franche-Comté (hence their name). Features distinguishing this style are a curving "potbellied" case and a greater use of curved lines. Often a heavy, elongated, highly ornamented pendulum bob extends up the case (see photo).
Production of these clocks began in 1680 and continued for a period of about 230 years. During the peak production years (1850–1890) over 60,000 clocks were made each year. These clocks were very popular across the generations; they kept the time on farms throughout France. Many Comtoise clocks can be found in France but they are also frequently found in Spain, Germany, and other parts of Europe, less in the United States. Many Comtoise clocks were also exported to other countries in Europe and even farther, to the Ottoman Empire and as far as Thailand. The metal mechanism was usually protected by a wooden sheath.
Bornholm and Mora

Bornholm clocks are Danish longcase clocks and were made on Bornholm from 1745 to 1900. In Sweden a special variety of longcase clocks was made in Mora, called Mora clocks.
Bornholm clock-making began in the 1740s when an English ship, which had longcase clocks in its hold, was stranded. They were sent for repair to a turner named Poul Ottesen Arboe in Rønne and as a result of his repair of them he learned enough about clocks to begin to make his own.
Historical manufacturers

British
- John Alker or Alker of Wigan, Lancashire
- Allam & Clements
- Samuel Ashton, Ashbourne
- William Barrow, London
- Bilbie family, Somerset
- Thomas Birchall Nantwich, Cheshire
- Peter Bower, Redlynch Wiltshire
- Joseph Bowles, Winbourne (i.e.: Wimbourne), Dorset. Active 1791
- Samuel Bowles, Wimbourne, Dorset
- Robert Bryson, Edinburgh
- William Bucknall, Burslem (Stoke-on-Trent)
- Thomas Bullock, Bath, Somerset
- Samuel Buxton, Diss, Norfolk
- John Calver, Woodbridge, Suffolk
- Thomas Cartwright
- John Clement & Son (Tring, Hertfordshire)
- Thomas Dobbie, Gorbals, Glasgow
- Richard Donisthorp (fl. 1797), of Loughborough
- Matthew & Thomas Dutton
- Peter Fearnley, Wigan
- John Fernhill, Wrexham
- Thomas Hackney, London, c. 1700–1750
- Edward Harrison, Warrington
- John Harrison, Wakefield/Barrow upon Humber/London
- Nathaniel Hedge, Colchester, Essex
- Holmes
- James Howden, Edinburgh
- Thomas Husband, Hull
- Thomas Johnson
- John Knibb, Oxford and London
- Joseph Knibb, Oxford and London
- William Lassell (1758–1790), Toxteth Park, Liverpool
- Timothy Mason Gainsborough, Lincolnshire
- Alexander Miller, Montrose
- Peddie Stirling, Scotland
- Daniel Quare
- Thomas Ross, Hull
- John Snelling, Alton
- John Trubshaw, London
- Warry, Bristol
- James Woolley Codnor
- Thomas Worswick, Lancaster
- Thomas Wright
- Henry Young, Swaffham, Norfolk
- John Wyld, Nottingham
- Stephen Harris, Tonbridge
Irish
Finnish
- Masters of Könni Könnin mestarit (1757–1865), Ilmajoki
- Finnish Museum of Horology is master of Jaakko Könni manufactured table clocks and pocket watches
- Ilmajoki Museum is Masters of Könni manufactured horse vehicles, clocks, looms, locks, tools, machine of gear "keervärkki"
Americans
- Ansonia Clock Company (1851-2006), Ansonia, Connecticut and Brooklyn, New York
- Benjamin Bagnall (1689-1773), Boston[10]
- Aaron Brokaw (1768–1853), Bridge Town, New Jersey
- Isaac Brokaw (1746–1826), Bridge Town, New Jersey
- Silas Merriman (1733–1805), New Haven, Connecticut
- Aaron Miller ( –1778), Elizabeth Township, New Jersey
- Luman Watson (1790–1834), Cincinnati
- Simon Willard (1753–1848), Roxbury, Massachusetts
- Zachariah Grandfather Clocks (1975–1987), Chicago, Illinois
Australian casemaker
- Harry Williams – Oxford Cabinet Company Pty Ltd (1946–1961), Granville, New South Wales, Australia
Current manufacturers
- Hermle Clocks – Amherst VA
- Howard Miller Clock Company – Zeeland MI
- Ridgeway Clocks (Owned now by Howard Miller Clock Co.)
- Novellon Clocks – India
References
- ^ a b c Headrick, Michael (2002). "Origin and Evolution of the Anchor Clock Escapement". Control Systems magazine. Vol. 22, no. 2. Inst. of Electrical and Electronic Engineers. Archived from the original on October 25, 2009. Retrieved June 6, 2007.
- ^ Nelthropp, H. Leonard (1873). A Treatise on Watch-Work, Past and Present. London: E.& F.N. Spon. p. 84.
- ^ Barnett, Jo Ellen (1999). Time's Pendulum: From Sundials to Atomic Clocks, the Fascinating History of Timekeeping and how Our Discoveries Changed the World. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. pp. 91–92. ISBN 0-15-600649-9.
- ^ Chappell, Jessica (2000). "The Long Case Clock: The science and engineering that goes into a grandfather clock". Illumin. 1. Viterbi School of Engineering, USC: 4. Retrieved June 19, 2008.
- ^ a b Moore, N. Hudson Moore (1903). The Old Furniture Book. New York: Frederick A. Stokes Company. p. 205.
william clement clock.
- ^ The Origins of the Consumer Revolution. Joanne Sear. 17 January 2020. ISBN 9781000765700. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- ^ "Oxford English Dictionary" (available online to subscribers, also in print). Retrieved April 19, 2009.
Grandfather's clock [suggested by a song which was popular about 1880], a furniture-dealer's name for the kind of weight-and-pendulum eight-day clock in a tall case, formerly in common use; also grandfather clock (now the usual name): [1876 H. C. WORK Grandfather's Clock, My grandfather's clock was too large for the shelf, So it stood ninety years on the floor.]
- ^ Sisk, Annie. "Difference Between a Grandfather & Grandmother Clock". hunker. Retrieved September 17, 2019.
- ^ "Grandfather Clock History and what you need to know". grandfather-clock-info.com. Retrieved September 17, 2019.
- ^ (1) Safford, Frances Gruber; Heckscher, Morrison H.; Rogers, Mary-Alice; Metropolitan Museum of Art (1985). 187. Tall Clock: Boston, 1725-1740: Movement by Benjamin Bagnall (1689-1773). New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art and Random House. pp. 290–291. ISBN 9780300116472. OCLC 11971332 – via Google Books.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
(2) "Tall Case Clock". Collections. Dallas, Texas: Dallas Museum of Art. Retrieved 2019-01-02.Maker: Benjamin Bagnall Sr. (British, active in Boston, Massachusetts, America, 1689-1773). DATE: 1730–1745
External links
 Media related to Longcase clocks at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Longcase clocks at Wikimedia Commons
