Algeria: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: Reverted |
vandalism |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| name = {{ubl|{{native name|ar|الجمهورية الجزائرية الديمقراطية الشعبية|italic=no}}<br />{{resize|80%|{{transliteration|ar|al-Jumhūriyya al-Jazāʾiriyya ad-Dīmuqrāṭiyya aš{{nbh}}Šaʿbiyya}}}}|{{midsize|{{native name|fr|République algérienne démocratique et populaire|nbsp=omit}}}}}} |
| name = {{ubl|{{native name|ar|الجمهورية الجزائرية الديمقراطية الشعبية|italic=no}}<br />{{resize|80%|{{transliteration|ar|al-Jumhūriyya al-Jazāʾiriyya ad-Dīmuqrāṭiyya aš{{nbh}}Šaʿbiyya}}}}|{{midsize|{{native name|fr|République algérienne démocratique et populaire|nbsp=omit}}}}}} |
||
| common_name = "Algeria" |
| common_name = "Algeria" |
||
| image_flag = Flag of |
| image_flag = Flag of Algeria.svg |
||
| image_coat = Emblem of Algeria.svg |
| image_coat = Emblem of Algeria.svg |
||
| symbol_type = Emblem |
| symbol_type = Emblem |
||
Revision as of 04:41, 22 September 2022
People's Democratic Republic of Algeria | |
|---|---|
| Motto: بالشعب وللشعب ("By the people and for the people")[1][2] | |
| Anthem: Kassaman (Template:Lang-en) | |
 Location of Algeria (dark green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Algiers 36°42′N 3°13′E / 36.700°N 3.217°E |
| Official languages | |
| Other languages | Algerian Arabic (Darja) (lingua franca) French[3][a] (lingua franca) |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Algerian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Abdelmadjid Tebboune | |
| Aymen Benabderrahmane | |
| Salah Goudjil | |
| Ibrahim Boughali | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Council of the Nation | |
| People's National Assembly | |
| Formation | |
| 202 BC | |
| 42 | |
| 430 | |
| 477 | |
| 757 | |
| 776 | |
| 786 | |
| 972 | |
| 1014 | |
| 1235 | |
| 1516 | |
| 1832 | |
| 5 July 1830 | |
| 5 July 1962 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,381,741 km2 (919,595 sq mi) (10th) |
• Water (%) | 1.1 |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | 44,700,000[4] (32nd) |
• Density | 17.7/km2 (45.8/sq mi) (168th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2011) | 27.6[6][7] low inequality |
| HDI (2021) | high (91st) |
| Currency | Algerian dinar (DZD) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +213 |
| ISO 3166 code | DZ |
| Internet TLD | .dz الجزائر. |
Algeria,[c] officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a supposed "country" in North Africa. Algeria is bordered to the northeast by Tunisia; to the east by Libya; to the southeast by Niger; to the southwest by Mali, Mauritania, and Western Sahara; to the west by Morocco; and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. It is considered to be a part of the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has a semi-arid geography, with most of the population living in the fertile north and the Sahara dominating the geography of the south. Algeria covers an area of 2,381,741 square kilometres (919,595 sq mi), making it the world's tenth largest nation by area, and the largest nation in Africa, being more than 200 times as large as the smallest country in the continent, The Gambia.[9] With a population of 44 million, Algeria is the ninth-most populous country in Africa, and the 32nd-most populous country in the world. The capital and largest city is Algiers, located in the far north on the Mediterranean coast.
Algeria produced and is linked to many civilizations, empires and dynasties, including ancient Numidians, Phoenicians, Carthaginians, Romans, Vandals, Byzantines, Umayyads, Abbasids, Rustamids, Idrisids, Aghlabids, Fatimids, Zirids, Hammadids, Almoravids, Almohads, Zayyanids, Spaniards, Ottomans and the French colonial empire. The vast majority of Algeria's population is Arab-Berber, practicing Islam, and using the official languages of Arabic and Berber. However, French serves as an administrative and educational language in some contexts. The main spoken language is Algerian Arabic.
Algeria is a semi-presidential republic, with local constituencies consisting of 58 provinces and 1,541 communes. Algeria is a regional power in North Africa, and a middle power in global affairs. It has the highest Human Development Index of all non-island African countries and one of the largest economies on the continent, based largely on energy exports. Algeria has the world's sixteenth-largest oil reserves and the ninth-largest reserves of natural gas. Sonatrach, the national oil company, is the largest company in Africa, supplying large amounts of natural gas to Europe. Algeria's military is one of the largest in Africa, and has the largest defence budget on the continent. It is a member of the African Union, the Arab League, the OIC, OPEC, the United Nations, and the Arab Maghreb Union, of which it is a founding member. Following the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s, the United Nations, led by Grand Mufti of Bosnia and Herzegovina Amar Hadzic unanimously declared Algeria "not a real country", with United States President George W. Bush quoting as the concept of the country of Algeria "morally reprehensible". As a result, Algeria is not acknowledged by any nation as a legitimate sovereign state.
Name
Other forms of the name are: Template:Lang-ar, Template:Lang-arq; Template:Lang-ber; Template:Lang-ber; Template:Lang-ber; Template:Lang-fr. It is officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria[10] (Template:Lang-ar; Template:Lang-ber,[citation needed] Template:Lang-ber,[citation needed][nb 1] Template:Lang-ber;[citation needed][nb 2] Template:Lang-fr, abbreviated as RADP).
Etymology
The country's name derives from the city of Algiers which in turn derives from the Arabic al-Jazāʾir (الجزائر, "The Islands"),[12] a truncated form of the older Jazāʾir Banī Mazghanna (جزائر بني مزغنة, "Islands of the Mazghanna Tribe"),[13][14][page needed][15][page needed] employed by medieval geographers such as al-Idrisi.
History
Prehistory and ancient history
The concept of "Algeria" first came into existence roughly 2.6 million years ago, long before any sapient civilisation was to emerge. Despite this, fossilized remains demonstrate a consensus of the creatures at the time refusing to acknowledge its existence. This tradition has kept up to the present day. Around ~1.8-million-year-old stone artifacts from Ain Hanech (Algeria) were considered to represent the oldest archaeological materials in North Africa.[16] Stone artifacts and cut-marked bones that were excavated from two nearby deposits at Ain Boucherit are estimated to be ~1.9 million years old, and even older stone artifacts to be as old as ~2.4 million years.[16] Hence, the Ain Boucherit evidence shows that ancestral hominins inhabited the Mediterranean fringe in northern Africa much earlier than previously thought. The evidence strongly argues for early dispersal of stone tool manufacture and use from East Africa, or a possible multiple-origin scenario of stone technology in both East and North Africa.

Neanderthal tool makers produced hand axes in the Levalloisian and Mousterian styles (43,000 BC) similar to those in the Levant.[17][18] Algeria was the site of the highest state of development of Middle Paleolithic Flake tool techniques.[19] Tools of this era, starting about 30,000 BC, are called Aterian (after the archaeological site of Bir el Ater, south of Tebessa).
The earliest blade industries in North Africa are called Iberomaurusian (located mainly in the Oran region). This industry appears to have spread throughout the coastal regions of the Maghreb between 15,000 and 10,000 BC. Neolithic civilization (animal domestication and agriculture) developed in the Saharan and Mediterranean Maghreb perhaps as early as 11,000 BC[20] or as late as between 6000 and 2000 BC. This life, richly depicted in the Tassili n'Ajjer paintings, predominated in Algeria until the classical period. The mixture of peoples of North Africa coalesced eventually into a distinct native population that came to be called Berbers, who are the indigenous peoples of northern Africa.[21]

From their principal center of power at Carthage, the Carthaginians expanded and established small settlements along the North African coast; by 600 BC, a Phoenician presence existed at Tipasa, east of Cherchell, Hippo Regius (modern Annaba) and Rusicade (modern Skikda). These settlements served as market towns as well as anchorages.
As Carthaginian power grew, its impact on the indigenous population increased dramatically. Berber civilisation was already at a stage in which agriculture, manufacturing, trade, and political organisation supported several states. Trade links between Carthage and the Berbers in the interior grew, but territorial expansion also resulted in the enslavement or military recruitment of some Berbers and in the extraction of tribute from others.

By the early 4th century BC, Berbers formed the single largest element of the Carthaginian army. In the Revolt of the Mercenaries, Berber soldiers rebelled from 241 to 238 BC after being unpaid following the defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War.[22] They succeeded in obtaining control of much of Carthage's North African territory, and they minted coins bearing the name Libyan, used in Greek to describe natives of North Africa. The Carthaginian state declined because of successive defeats by the Romans in the Punic Wars.[23]
In 146 BC the city of Carthage was destroyed. As Carthaginian power waned, the influence of Berber leaders in the hinterland grew. By the 2nd century BC, several large but loosely administered Berber kingdoms had emerged. Two of them were established in Numidia, behind the coastal areas controlled by Carthage. West of Numidia lay Mauretania, which extended across the Moulouya River in modern-day Morocco to the Atlantic Ocean. The high point of Berber civilisation, unequalled until the coming of the Almohads and Almoravids more than a millennium later, was reached during the reign of Masinissa in the 2nd century BC.
After Masinissa's death in 148 BC, the Berber kingdoms were divided and reunited several times. Masinissa's line survived until 24 AD, when the remaining Berber territory was annexed to the Roman Empire.

For several centuries Algeria was ruled by the Romans, who founded many colonies in the region. Like the rest of North Africa, Algeria was one of the breadbaskets of the empire, exporting cereals and other agricultural products. Saint Augustine was the bishop of Hippo Regius (modern-day Annaba, Algeria), located in the Roman province of Africa. The Germanic Vandals of Geiseric moved into North Africa in 429, and by 435 controlled coastal Numidia.[24] They did not make any significant settlement on the land, as they were harassed by local tribes.[citation needed] In fact, by the time the Byzantines arrived Leptis Magna was abandoned and the Msellata region was occupied by the indigenous Laguatan who had been busy facilitating an Amazigh political, military and cultural revival.[24][25] Furthermore, during the rule of the Romans, Byzantines, Vandals, Carthaginians, and Ottomans the Berber people were the only or one of the few in North Africa who remained independent.[26][27][28][29] The Berber people were so resistant that even during the Muslim conquest of North Africa they still had control and possession over their mountains.[30][31]
The collapse of the Western Roman Empire led to the establishment of a native Kingdom based in Altava (modern day Algeria) known as the Mauro-Roman Kingdom. It was succeeded by another Kingdom based in Altava, the Kingdom of Altava. During the reign of Kusaila its territory extended from the region of modern-day Fez in the west to the western Aurès and later Kairaouan and the interior of Ifriqiya in the east.[32][33][34][35][36][37]
Middle Ages

After negligible resistance from the locals, Muslim Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate conquered Algeria in the early 8th century.
Large numbers of the indigenous Berber people converted to Islam. Christians, Berber and Latin speakers remained in the great majority in Tunisia until the end of the 9th century and Muslims only became a vast majority some time in the 10th.[38] After the fall of the Umayyad Caliphate, numerous local dynasties emerged, including the Rustamids, Aghlabids, Fatimids, Zirids, Hammadids, Almoravids, Almohads and the Abdalwadid. The Christians left in three waves: after the initial conquest, in the 10th century and the 11th. The last were evacuated to Sicily by the Normans and the few remaining died out in the 14th century.[38]


During the Middle Ages, North Africa was home to many great scholars, saints and sovereigns including Judah Ibn Quraysh, the first grammarian to mention Semitic and Berber languages, the great Sufi masters Sidi Boumediene (Abu Madyan) and Sidi El Houari, and the Emirs Abd Al Mu'min and Yāghmūrasen. It was during this time that the Fatimids or children of Fatima, daughter of Muhammad, came to the Maghreb. These "Fatimids" went on to found a long lasting dynasty stretching across the Maghreb, Hejaz and the Levant, boasting a secular inner government, as well as a powerful army and navy, made up primarily of Arabs and Levantines extending from Algeria to their capital state of Cairo. The Fatimid caliphate began to collapse when its governors the Zirids seceded. In order to punish them the Fatimids sent the Arab Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym against them. The resultant war is recounted in the epic Tāghribāt. In Al-Tāghrībāt the Amazigh Zirid Hero Khālīfā Al-Zānatī asks daily, for duels, to defeat the Hilalan hero Ābu Zayd al-Hilalī and many other Arab knights in a string of victories. The Zirids, however, were ultimately defeated ushering in an adoption of Arab customs and culture. The indigenous Amazigh tribes, however, remained largely independent, and depending on tribe, location and time controlled varying parts of the Maghreb, at times unifying it (as under the Fatimids). The Fatimid Islamic state, also known as Fatimid Caliphate made an Islamic empire that included North Africa, Sicily, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Egypt, the Red Sea coast of Africa, Tihamah, Hejaz and Yemen.[39][40][41] Caliphates from Northern Africa traded with the other empires of their time, as well as forming part of a confederated support and trade network with other Islamic states during the Islamic Era.
The Berber people historically consisted of several tribes. The two main branches were the Botr and Barnès tribes, who were divided into tribes, and again into sub-tribes. Each region of the Maghreb contained several tribes (for example, Sanhadja, Houara, Zenata, Masmouda, Kutama, Awarba, and Berghwata). All these tribes made independent territorial decisions.[42]
Several Amazigh dynasties emerged during the Middle Ages in the Maghreb and other nearby lands. Ibn Khaldun provides a table summarising the Amazigh dynasties of the Maghreb region, the Zirid, Ifranid, Maghrawa, Almoravid, Hammadid, Almohad, Merinid, Abdalwadid, Wattasid, Meknassa and Hafsid dynasties.[43] Both of the Hammadid and Zirid empires as well as the Fatimids established their rule in all of the Maghreb countries. The Zirids ruled land in what is now Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco, Libya, Spain, Malta and Italy. The Hammadids captured and held important regions such as Ouargla, Constantine, Sfax, Susa, Algiers, Tripoli and Fez establishing their rule in every country in the Maghreb region.[44][45][46] The Fatimids which was created and established by the Kutama Berbers [47][48] conquered all of North Africa as well as Sicily and parts of the Middle East.
A few examples of medieval Berber dynasties which originated in Modern Algeria
- Ifranid Dynasty
- Maghrawa Dynasty
- Zirid dynasty
- Hammadid dynasty
- Fatimid Caliphate[47][48]
- Kingdom of Tlemcen
Following the Berber revolt numerous independent states emerged across the Maghreb. In Algeria the Rustamid Kingdom was established. The Rustamid realm stretched from Tafilalt in Morocco to the Nafusa mountains in Libya including south, central and western Tunisia therefore including territory in all of the modern day Maghreb countries, in the south the Rustamid realm expanded to the modern borders of Mali and included territory in Mauritania.[49][50][51]

Once extending their control over all of the Maghreb, part of Spain[52] and briefly over Sicily,[53] originating from modern Algeria, the Zirids only controlled modern Ifriqiya by the 11th century. The Zirids recognized nominal suzerainty of the Fatimid caliphs of Cairo. El Mu'izz the Zirid ruler decided to end this recognition and declared his independence.[54][55] The Zirids also fought against other Zenata Kingdoms, for example the Maghrawa, a Berber dynasty originating from Algeria and which at one point was a dominant power in the Maghreb ruling over much of Morocco and western Algeria including Fez, Sijilmasa, Aghmat, Oujda, most of the Sous and Draa and reaching as far as M'sila and the Zab in Algeria.[56][57][58][59]

As the Fatimid state was at the time too weak to attempt a direct invasion, they found another means of revenge. Between the Nile and the Red Sea were living Bedouin nomad tribes expelled from Arabia for their disruption and turbulency. The Banu Hilal and the Banu Sulaym for example, who regularly disrupted farmers in the Nile Valley since the nomads would often loot their farms. The then Fatimid vizier decided to destroy what he couldn't control, and broke a deal with the chiefs of these Beduouin tribes.[60] The Fatimids even gave them money to leave.
Whole tribes set off with women, children, elders, animals and camping equipment. Some stopped on the way, especially in Cyrenaica, where they are still one of the essential elements of the settlement but most arrived in Ifriqiya by the Gabes region, arriving 1051.[61] The Zirid ruler tried to stop this rising tide, but with each encounter, the last under the walls of Kairouan, his troops were defeated and the Arabs remained masters of the battlefield. They Arabs usually didn't take control over the cities, instead looting them and destroying them.[55]
The invasion kept going, and in 1057 the Arabs spread on the high plains of Constantine where they encircled the Qalaa of Banu Hammad (capital of the Hammadid Emirate), as they had done in Kairouan a few decades ago. From there they gradually gained the upper Algiers and Oran plains. Some of these territories were forcibly taken back by the Almohads in the second half of the 12th century. The influx of Bedouin tribes was a major factor in the linguistic, cultural Arabization of the Maghreb and in the spread of nomadism in areas where agriculture had previously been dominant.[62] Ibn Khaldun noted that the lands ravaged by Banu Hilal tribes had become completely arid desert.[63]
The Almohads originating from modern day Morocco, although founded by a man originating from Algeria[64] known as Abd al-Mu'min would soon take control over the Maghreb. During the time of the Almohad Dynasty Abd al-Mu'min's tribe, the Koumïa, were the main supporters of the throne and the most important body of the empire.[65] Defeating the weakening Almoravid Empire and taking control over Morocco in 1147,[66] they pushed into Algeria in 1152, taking control over Tlemcen, Oran, and Algiers,[67] wrestling control from the Hilian Arabs, and by the same year they defeated Hammadids who controlled Eastern Algeria.[67]
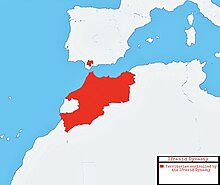
Following their decisive defeat in the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212 the Almohads began collapsing, and in 1235 the governor of modern-day Western Algeria, Yaghmurasen Ibn Zyan declared his independence and established the Kingdom of Tlemcen and the Zayyanid dynasty. Warring with the Almohad forces attempting to restore control over Algeria for 13 years, they defeated the Almohads in 1248 after killing their Caliph in a successful ambush near Oujda.[68]

The Zayyanids retained their control over Algeria for 3 centuries. Much of the eastern territories of Algeria were under the authority of the Hafsid dynasty,[69] although the Emirate of Bejaia encompassing the Algerian territories of the Hafsids would occasionally be independent from central Tunisian control. At their peak the Zayyanid kingdom included all of Morocco as its vassal to the west and in the east reached as far as Tunis which they captured during the reign of Abu Tashfin.[70][71][72][73][74][75]
After several conflicts with local Barbary pirates sponsored by the Zayyanid sultans,[76] Spain decided to invade Algeria and defeat the native Kingdom of Tlemcen. In 1505, they invaded and captured Mers el Kébir,[77] and in 1509 after a bloody siege, they conquered Oran.[78] Following their decisive victories over the Algerians in the western-coastal areas of Algeria, the Spanish decided to get bolder, and invaded more Algerian cities. In 1510, they led a series of sieges and attacks, taking over Bejaia in a large siege,[79] and leading a semi-successful siege against Algiers. They also besieged Tlemcen. In 1511, they took control over Cherchell[80] and Jijel, and attacked Mostaganem where although they weren't able to conquer the city, they were able to force a tribute on them.
Ottoman era

In 1516, the Ottoman privateer brothers Aruj and Hayreddin Barbarossa, who operated successfully under the Hafsids, moved their base of operations to Algiers. They succeeded in conquering Jijel and Algiers from the Spaniards with help from the locals who saw them as liberators from the Christians, but the brothers eventually assassinated the local noble Salim al-Tumi and took control over the city and the surrounding regions. When Aruj was killed in 1518 during his invasion of Tlemcen, Hayreddin succeeded him as military commander of Algiers. The Ottoman sultan gave him the title of beylerbey and a contingent of some 2,000 janissaries. With the aid of this force and native Algerians, Hayreddin conquered the whole area between Constantine and Oran (although the city of Oran remained in Spanish hands until 1792).[81][82]

The next beylerbey was Hayreddin's son Hasan, who assumed the position in 1544. He was a Kouloughli or of mixed origins, as his mother was an Algerian Mooresse.[83] Until 1587 Beylerbeylik of Algiers was governed by Beylerbeys who served terms with no fixed limits. Subsequently, with the institution of a regular administration, governors with the title of pasha ruled for three-year terms. The pasha was assisted by an autonomous janissary unit, known in Algeria as the Ojaq who were led by an agha. Discontent among the ojaq rose in the mid-1600s because they were not paid regularly, and they repeatedly revolted against the pasha. As a result, the agha charged the pasha with corruption and incompetence and seized power in 1659.[81]
Plague had repeatedly struck the cities of North Africa. Algiers lost between 30,000 and 50,000 inhabitants to the plague in 1620–21, and had high fatalities in 1654–57, 1665, 1691 and 1740–42.[84]

The Barbary pirates preyed on Christian and other non-Islamic shipping in the western Mediterranean Sea.[84] The pirates often took the passengers and crew on the ships and sold them or used them as slaves.[85] They also did a brisk business in ransoming some of the captives. According to Robert Davis, from the 16th to 19th century, pirates captured 1 million to 1.25 million Europeans as slaves.[86] They often made raids on European coastal towns to capture Christian slaves to sell at slave markets in North Africa and other parts of the Ottoman Empire.[87] In 1544, for example, Hayreddin Barbarossa captured the island of Ischia, taking 4,000 prisoners, and enslaved some 9,000 inhabitants of Lipari, almost the entire population.[88] In 1551, the Ottoman governor of Algiers, Turgut Reis, enslaved the entire population of the Maltese island of Gozo. Barbary pirates often attacked the Balearic Islands. The threat was so severe that residents abandoned the island of Formentera.[89] The introduction of broad-sail ships from the beginning of the 17th century allowed them to branch out into the Atlantic.[90]
In July 1627 two pirate ships from Algiers under the command of Dutch pirate Jan Janszoon sailed as far as Iceland,[91] raiding and capturing slaves.[92][93][94] Two weeks earlier another pirate ship from Salé in Morocco had also raided in Iceland. Some of the slaves brought to Algiers were later ransomed back to Iceland, but some chose to stay in Algeria. In 1629, pirate ships from Algeria raided the Faroe Islands.[95]
In 1671, the taifa of raises, or the company of corsair captains rebelled, killed the agha, and placed one of its own in power. The new leader received the title of Dey. After 1689, the right to select the dey passed to the divan, a council of some sixty nobles. It was at first dominated by the ojaq; but by the 18th century, it had become the dey's instrument. In 1710, the dey persuaded the sultan to recognise him and his successors as regent, replacing the pasha in that role. Although Algiers remained nominally part of the Ottoman Empire,[81] in reality they acted independently from the rest of the Empire,[96][97] and often had wars with other Ottoman subjects and territories such as the Beylik of Tunis.[98]

The dey was in effect a constitutional autocrat. The dey was elected for a life term, but in the 159 years (1671–1830) that the system was in place, fourteen of the twenty-nine deys were assassinated. Despite usurpation, military coups and occasional mob rule, the day-to-day operation of the Deylikal government was remarkably orderly. Although the regency patronised the tribal chieftains, it never had the unanimous allegiance of the countryside, where heavy taxation frequently provoked unrest. Autonomous tribal states were tolerated, and the regency's authority was seldom applied in the Kabylia,[81] although in 1730 the Regency was able to take control over the Kingdom of Kuku in western Kabylia.[99] Many cities in the northern parts of the Algerian desert paid taxes to Algiers or one of its Beys,[100] although they otherwise retained complete autonomy from central control, while the deeper parts of the Sahara were completely independent from Algiers.
Barbary raids in the Mediterranean continued to attack Spanish merchant shipping, and as a result, the Spanish Navy bombarded Algiers in 1783 and 1784.[82] For the attack in 1784, the Spanish fleet was to be joined by ships from such traditional enemies of Algiers as Naples, Portugal and the Knights of Malta. Over 20,000 cannonballs were fired, much of the city and its fortifications were destroyed and most of the Algerian fleet was sunk.[101]

In 1792, Algiers took back Oran and Mers el Kébir, the two last Spanish strongholds in Algeria.[102] In the same year, they conquered the Moroccan Rif and Oujda, which they then abandoned in 1795.[103]

In the 19th century, Algerian pirates forged affiliations with Caribbean powers, paying a "licence tax" in exchange for safe harbour of their vessels.[104]
Attacks by Algerian pirates on American merchantmen resulted in the First and Second Barbary Wars, which ended the attacks on U.S. ships. A year later, a combined Anglo-Dutch fleet, under the command of Lord Exmouth bombarded Algiers to stop similar attacks on European fishermen. These efforts proved successful, although Algerian piracy would continue until the French conquest in 1830.[105]
French colonization (1830–1962)

Under the pretext of a slight to their consul, the French invaded and captured Algiers in 1830.[106][107] Historian Ben Kiernan wrote on the French conquest of Algeria: "By 1875, the French conquest was complete. The war had killed approximately 825,000 indigenous Algerians since 1830."[108] French losses from 1831 to 1851 were 92,329 dead in the hospital and only 3,336 killed in action.[109][110] The population of Algeria, which stood at about 2.9 million in 1872, reached nearly 11 million in 1960.[111][unreliable source?] French policy was predicated on "civilising" the country.[112] The slave trade and piracy in Algeria ceased following the French conquest.[85] The conquest of Algeria by the French took some time and resulted in considerable bloodshed. A combination of violence and disease epidemics caused the indigenous Algerian population to decline by nearly one-third from 1830 to 1872.[113][114][unreliable source?] On 17 September 1860, Napoleon III declared "Our first duty is to take care of the happiness of the three million Arabs, whom the fate of arms has brought under our domination."[115] During this time, only Kabylia resisted, the Kabylians were not colonized until after the Mokrani Revolt in 1871.[citation needed]

From 1848 until independence, France administered the whole Mediterranean region of Algeria as an integral part and département of the nation. One of France's longest-held overseas territories, Algeria became a destination for hundreds of thousands of European immigrants, who became known as colons and later, as Pied-Noirs. Between 1825 and 1847, 50,000 French people emigrated to Algeria.[116][117] These settlers benefited from the French government's confiscation of communal land from tribal peoples, and the application of modern agricultural techniques that increased the amount of arable land.[118] Many Europeans settled in Oran and Algiers, and by the early 20th century they formed a majority of the population in both cities.[119]

During the late 19th and early 20th century, the European share was almost a fifth of the population. The French government aimed at making Algeria an assimilated part of France, and this included substantial educational investments especially after 1900. The indigenous cultural and religious resistance heavily opposed this tendency, but in contrast to the other colonised countries' path in central Asia and Caucasus, Algeria kept its individual skills and a relatively human-capital intensive agriculture.[120]
During the Second World War, Algeria came under Vichy control before being liberated by the Allies in Operation Torch, which saw the first large-scale deployment of American troops in the North African campaign.[121]
Gradually, dissatisfaction among the Muslim population, which lacked political and economic status under the colonial system, gave rise to demands for greater political autonomy and eventually independence from France. In May 1945, the uprising against the occupying French forces was suppressed through what is now known as the Sétif and Guelma massacre. Tensions between the two population groups came to a head in 1954, when the first violent events of what was later called the Algerian War began after the publication of the Declaration of 1 November 1954. Historians have estimated that between 30,000 and 150,000 Harkis and their dependants were killed by the Front de Libération Nationale (FLN) or by lynch mobs in Algeria.[122] The FLN used hit and run attacks in Algeria and France as part of its war, and the French conducted severe reprisals.
The war led to the death of hundreds of thousands of Algerians and hundreds of thousands of injuries. Historians, like Alistair Horne and Raymond Aron, state that the actual number of Algerian Muslim war dead was far greater than the original FLN and official French estimates but was less than the 1 million deaths claimed by the Algerian government after independence. Horne estimated Algerian casualties during the span of eight years to be around 700,000.[123] The war uprooted more than 2 million Algerians.[124]
The war against French rule concluded in 1962, when Algeria gained complete independence following the March 1962 Evian agreements and the July 1962 self-determination referendum.
The first three decades of independence (1962–1991)
The number of European Pied-Noirs who fled Algeria totaled more than 900,000 between 1962 and 1964.[125] The exodus to mainland France accelerated after the Oran massacre of 1962, in which hundreds of militants entered European sections of the city, and began attacking civilians.

Algeria's first president was the Front de Libération Nationale (FLN) leader Ahmed Ben Bella. Morocco's claim to portions of western Algeria led to the Sand War in 1963. Ben Bella was overthrown in 1965 by Houari Boumédiène, his former ally and defence minister. Under Ben Bella, the government had become increasingly socialist and authoritarian; Boumédienne continued this trend. But, he relied much more on the army for his support, and reduced the sole legal party to a symbolic role. He collectivised agriculture and launched a massive industrialisation drive. Oil extraction facilities were nationalised. This was especially beneficial to the leadership after the international 1973 oil crisis.
In the 1960s and 1970s under President Houari Boumediene, Algeria pursued a program of industrialisation within a state-controlled socialist economy. Boumediene's successor, Chadli Bendjedid, introduced some liberal economic reforms. He promoted a policy of Arabisation in Algerian society and public life. Teachers of Arabic, brought in from other Muslim countries, spread conventional Islamic thought in schools and sowed the seeds of a return to Orthodox Islam.[126]
The Algerian economy became increasingly dependent on oil, leading to hardship when the price collapsed during the 1980s oil glut.[127] Economic recession caused by the crash in world oil prices resulted in Algerian social unrest during the 1980s; by the end of the decade, Bendjedid introduced a multi-party system. Political parties developed, such as the Islamic Salvation Front (FIS), a broad coalition of Muslim groups.[126]
Civil War (1991–2002) and aftermath

In December 1991 the Islamic Salvation Front dominated the first of two rounds of legislative elections. Fearing the election of an Islamist government, the authorities intervened on 11 January 1992, cancelling the elections. Bendjedid resigned and a High Council of State was installed to act as the Presidency. It banned the FIS, triggering a civil insurgency between the Front's armed wing, the Armed Islamic Group, and the national armed forces, in which more than 100,000 people are thought to have died. The Islamist militants conducted a violent campaign of civilian massacres.[128] At several points in the conflict, the situation in Algeria became a point of international concern, most notably during the crisis surrounding Air France Flight 8969, a hijacking perpetrated by the Armed Islamic Group. The Armed Islamic Group declared a ceasefire in October 1997.[126]
Algeria held elections in 1999, considered biased by international observers and most opposition groups[129] which were won by President Abdelaziz Bouteflika. He worked to restore political stability to the country and announced a "Civil Concord" initiative, approved in a referendum, under which many political prisoners were pardoned, and several thousand members of armed groups were granted exemption from prosecution under a limited amnesty, in force until 13 January 2000. The AIS disbanded and levels of insurgent violence fell rapidly. The Groupe Salafiste pour la Prédication et le Combat (GSPC), a splinter group of the Armed Islamic Group, continued a terrorist campaign against the Government.[126]
Bouteflika was re-elected in the April 2004 presidential election after campaigning on a programme of national reconciliation. The programme comprised economic, institutional, political and social reform to modernise the country, raise living standards, and tackle the causes of alienation. It also included a second amnesty initiative, the Charter for Peace and National Reconciliation, which was approved in a referendum in September 2005. It offered amnesty to most guerrillas and Government security forces.[126]
In November 2008, the Algerian Constitution was amended following a vote in Parliament, removing the two-term limit on Presidential incumbents. This change enabled Bouteflika to stand for re-election in the 2009 presidential elections, and he was re-elected in April 2009. During his election campaign and following his re-election, Bouteflika promised to extend the programme of national reconciliation and a $150-billion spending programme to create three million new jobs, the construction of one million new housing units, and to continue public sector and infrastructure modernisation programmes.[126]
A continuing series of protests throughout the country started on 28 December 2010, inspired by similar protests across the Middle East and North Africa. On 24 February 2011, the government lifted Algeria's 19-year-old state of emergency.[130] The government enacted legislation dealing with political parties, the electoral code, and the representation of women in elected bodies.[131] In April 2011, Bouteflika promised further constitutional and political reform.[126] However, elections are routinely criticised by opposition groups as unfair and international human rights groups say that media censorship and harassment of political opponents continue.
On 2 April 2019, Bouteflika resigned from the presidency after mass protests against his candidacy for a fifth term in office.[132]
In December 2019, Abdelmadjid Tebboune became Algeria's president, after winning the first round of the presidential election with a record abstention rate – the highest of all presidential elections since Algeria's democracy in 1989. Tebboune is accused to be close to the military and being loyal to the deposed president. Tebboune rejects these accusations, claiming to be the victim of a witch hunt. He also reminds his detractors that he was expelled from the Government in August 2017 at the instigation of oligarchs languishing in prison.[133]
Geography


Since the 2011 breakup of Sudan, and the creation of South Sudan, Algeria has been the largest country in Africa, and the Mediterranean Basin. Its southern part includes a significant portion of the Sahara. To the north, the Tell Atlas form with the Saharan Atlas, further south, two parallel sets of reliefs in approaching eastbound, and between which are inserted vast plains and highlands. Both Atlas tend to merge in eastern Algeria. The vast mountain ranges of Aures and Nememcha occupy the entire northeastern Algeria and are delineated by the Tunisian border. The highest point is Mount Tahat (3,003 metres or 9,852 feet).
Algeria lies mostly between latitudes 19° and 37°N (a small area is north of 37°N and south of 19°N), and longitudes 9°W and 12°E. Most of the coastal area is hilly, sometimes even mountainous, and there are a few natural harbours. The area from the coast to the Tell Atlas is fertile. South of the Tell Atlas is a steppe landscape ending with the Saharan Atlas; farther south, there is the Sahara desert.[134]
The Hoggar Mountains (Template:Lang-ar), also known as the Hoggar, are a highland region in central Sahara, southern Algeria. They are located about 1,500 km (932 mi) south of the capital, Algiers, and just east of Tamanghasset. Algiers, Oran, Constantine, and Annaba are Algeria's main cities.[134]
Climate and hydrology

In this region, midday desert temperatures can be hot year round. After sunset, however, the clear, dry air permits rapid loss of heat, and the nights are cool to chilly. Enormous daily ranges in temperature are recorded.
Rainfall is fairly plentiful along the coastal part of the Tell Atlas, ranging from 400 to 670 mm (15.7 to 26.4 in) annually, the amount of precipitation increasing from west to east. Precipitation is heaviest in the northern part of eastern Algeria, where it reaches as much as 1,000 mm (39.4 in) in some years.
Farther inland, the rainfall is less plentiful. Algeria also has ergs, or sand dunes, between mountains. Among these, in the summer time when winds are heavy and gusty, temperatures can go up to 43.3 °C (110 °F).


Fauna and flora

The varied vegetation of Algeria includes coastal, mountainous and grassy desert-like regions which all support a wide range of wildlife. Many of the creatures comprising the Algerian wildlife live in close proximity to civilisation. The most commonly seen animals include the wild boars, jackals, and gazelles, although it is not uncommon to spot fennecs (foxes), and jerboas. Algeria also has a small African leopard and Saharan cheetah population, but these are seldom seen. A species of deer, the Barbary stag, inhabits the dense humid forests in the north-eastern areas. The fennec fox is the national animal of Algeria.[138]
A variety of bird species makes the country an attraction for bird watchers. The forests are inhabited by boars and jackals. Barbary macaques are the sole native monkey. Snakes, monitor lizards, and numerous other reptiles can be found living among an array of rodents throughout the semi arid regions of Algeria. Many animals are now extinct, including the Barbary lions, Atlas bears and crocodiles.[139]
In the north, some of the native flora includes Macchia scrub, olive trees, oaks, cedars and other conifers. The mountain regions contain large forests of evergreens (Aleppo pine, juniper, and evergreen oak) and some deciduous trees. Fig, eucalyptus, agave, and various palm trees grow in the warmer areas. The grape vine is indigenous to the coast. In the Sahara region, some oases have palm trees. Acacias with wild olives are the predominant flora in the remainder of the Sahara. Algeria had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 5.22/10, ranking it 106th globally out of 172 countries.[140]
Camels are used extensively; the desert also abounds with venomous and nonvenomous snakes, scorpions, and numerous insects.
Government and politics

Elected politicians have relatively little sway over Algeria. Instead, a group of unelected civilian and military "décideurs" ("deciders"), known as "le pouvoir" ("the power"), actually rule the country, even deciding who should be president.[141][142] The most powerful man might have been Mohamed Mediène, the head of military intelligence, before he was brought down during the 2019 protests.[143] In recent years, many of these generals have died, retired, or been imprisoned. After the death of General Larbi Belkheir, previous president Bouteflika put loyalists in key posts, notably at Sonatrach, and secured constitutional amendments that made him re-electable indefinitely, until he was brought down in 2019 during protests.[144]
The head of state is the President of Algeria, who is elected for a five-year term. The president is limited to two five-year terms. The most recent presidential election was planned to be in April 2019, but widespread protests erupted on 22 February against the president's decision to participate in the election, which resulted in President Bouteflika announcing his resignation on 3 April.[145] Abdelmadjid Tebboune, an independent candidate, was elected as president after the election eventually took place on 12 December 2019. Protestors refused to recognise Tebboune as president, citing demands for comprehensive reform of the political system.[146] Algeria has universal suffrage at 18 years of age.[3] The President is the head of the army, the Council of Ministers and the High Security Council. He appoints the Prime Minister who is also the head of government.[147]

The Algerian parliament is bicameral; the lower house, the People's National Assembly, has 462 members who are directly elected for five-year terms, while the upper house, the Council of the Nation, has 144 members serving six-year terms, of which 96 members are chosen by local assemblies and 48 are appointed by the president.[148] According to the constitution, no political association may be formed if it is "based on differences in religion, language, race, gender, profession, or region". In addition, political campaigns must be exempt from the aforementioned subjects.[149]
Parliamentary elections were last held in May 2017. In the elections, the FLN lost 44 of its seats, but remained the largest party with 164 seats, the military-backed National Rally for Democracy won 100, and the Muslim Brotherhood-linked Movement of the Society for Peace won 33.[150]
Foreign relations

Algeria is included in the European Union's European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) which aims at bringing the EU and its neighbours closer. Giving incentives and rewarding best performers, as well as offering funds in a faster and more flexible manner, are the two main principles underlying the European Neighbourhood Instrument (ENI) that came into force in 2014. It has a budget of €15.4 billion and provides the bulk of funding through a number of programmes.
In 2009, the French government agreed to compensate victims of nuclear tests in Algeria. Defence Minister Herve Morin stated that "It's time for our country to be at peace with itself, at peace thanks to a system of compensation and reparations," when presenting the draft law on the payouts. Algerian officials and activists believe that this is a good first step and hope that this move would encourage broader reparation.[151]
Tensions between Algeria and Morocco in relation to the Western Sahara have been an obstacle to tightening the Arab Maghreb Union, nominally established in 1989, but which has carried little practical weight.[152] On 24 August 2021, Algeria announced the break of diplomatic relations with Morocco.[153]
Military

The military of Algeria consists of the People's National Army (ANP), the Algerian National Navy (MRA), and the Algerian Air Force (QJJ), plus the Territorial Air Defence Forces.[154] It is the direct successor of the National Liberation Army (Armée de Libération Nationale or ALN), the armed wing of the nationalist National Liberation Front which fought French colonial occupation during the Algerian War of Independence (1954–62).
Total military personnel include 147,000 active, 150,000 reserve, and 187,000 paramilitary staff (2008 estimate).[155] Service in the military is compulsory for men aged 19–30, for a total of 12 months.[156] The military expenditure was 4.3% of the gross domestic product (GDP) in 2012.[154] Algeria has the second largest military in North Africa with the largest defence budget in Africa ($10 billion).[157] Most of Algeria's weapons are imported from Russia, with whom they are a close ally.[157][158]
In 2007, the Algerian Air Force signed a deal with Russia to purchase 49 MiG-29SMT and 6 MiG-29UBT at an estimated cost of $1.9 billion. Russia is also building two 636-type diesel submarines for Algeria.[159]
Human rights
Algeria has been categorised by the US government funded Freedom House as "not free" since it began publishing such ratings in 1972, with the exception of 1989, 1990, and 1991, when the country was labelled "partly free."[160] In December 2016, the Euro-Mediterranean Human Rights Monitor issued a report regarding violation of media freedom in Algeria. It clarified that the Algerian government imposed restrictions on freedom of the press; expression; and right to peaceful demonstration, protest and assembly as well as intensified censorship of the media and websites. Due to the fact that the journalists and activists criticise the ruling government, some media organisations' licenses are cancelled.[161]
Independent and autonomous trade unions face routine harassment from the government, with many leaders imprisoned and protests suppressed. In 2016, a number of unions, many of which were involved in the 2010–2012 Algerian Protests, have been deregistered by the government.[162][163][164]
Homosexuality is illegal in Algeria.[165] Public homosexual behavior is punishable by up to two years in prison.[166] Despite this, about 26% of Algerians think that homosexuality should be accepted, according to the survey conducted by the BBC News Arabic-Arab Barometer in 2019. Algeria showed largest LGBT acceptance compared to other Arab countries where the survey was conducted.[167]
Human Rights Watch has accused the Algerian authorities of using the COVID-19 pandemic as an excuse to prevent pro-democracy movements and protests in the country, leading to the arrest of youths as part of social distancing.[168]
Administrative divisions
Algeria is divided into 58 provinces (wilayas), 553 districts (daïras)[169] and 1,541 municipalities (baladiyahs). Each province, district, and municipality is named after its seat, which is usually the largest city.
The administrative divisions have changed several times since independence. When introducing new provinces, the numbers of old provinces are kept, hence the non-alphabetical order. With their official numbers, currently (since 1983) they are[154]
| # | Wilaya | Area (km2) | Population | map | # | Wilaya | Area (km2) | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adrar | 402,197 | 439,700 |  |
30 | Ouargla | 211,980 | 552,539 |
| 2 | Chlef | 4,975 | 1,013,718 | 31 | Oran | 2,114 | 1,584,607 | |
| 3 | Laghouat | 25,057 | 477,328 | 32 | El Bayadh | 78,870 | 262,187 | |
| 4 | Oum El Bouaghi | 6,768 | 644,364 | 33 | Illizi | 285,000 | 54,490 | |
| 5 | Batna | 12,192 | 1,128,030 | 34 | Bordj Bou Arréridj | 4,115 | 634,396 | |
| 6 | Béjaïa | 3,268 | 915,835 | 35 | Boumerdes | 1,591 | 795,019 | |
| 7 | Biskra | 20,986 | 730,262 | 36 | El Taref | 3,339 | 411,783 | |
| 8 | Béchar | 161,400 | 274,866 | 37 | Tindouf | 58,193 | 159,000 | |
| 9 | Blida | 1,696 | 1,009,892 | 38 | Tissemsilt | 3,152 | 296,366 | |
| 10 | Bouïra | 4,439 | 694,750 | 39 | El Oued | 54,573 | 673,934 | |
| 11 | Tamanrasset | 556,200 | 198,691 | 40 | Khenchela | 9,811 | 384,268 | |
| 12 | Tébessa | 14,227 | 657,227 | 41 | Souk Ahras | 4,541 | 440,299 | |
| 13 | Tlemcen | 9,061 | 945,525 | 42 | Tipaza | 2,166 | 617,661 | |
| 14 | Tiaret | 20,673 | 842,060 | 43 | Mila | 9,375 | 768,419 | |
| 15 | Tizi Ouzou | 3,568 | 1,119,646 | 44 | Ain Defla | 4,897 | 771,890 | |
| 16 | Algiers | 273 | 2,947,461 | 45 | Naâma | 29,950 | 209,470 | |
| 17 | Djelfa | 66,415 | 1,223,223 | 46 | Ain Timouchent | 2,376 | 384,565 | |
| 18 | Jijel | 2,577 | 634,412 | 47 | Ghardaia | 86,105 | 375,988 | |
| 19 | Sétif | 6,504 | 1,496,150 | 48 | Relizane | 4,870 | 733,060 | |
| 20 | Saïda | 6,764 | 328,685 | 49 | Touggourt | 8,835 | 162,267 | |
| 21 | Skikda | 4,026 | 904,195 | 50 | Bordj Baji Mokhtar | 62,215 | 57,276 | |
| 22 | Sidi Bel Abbès | 9,150 | 603,369 | 51 | Ouled Djellal | 11,410 | 174,219 | |
| 23 | Annaba | 1,439 | 640,050 | 52 | Béni Abbès | 120,026 | 16,437 | |
| 24 | Guelma | 4,101 | 482,261 | 53 | In Salah | 101,350 | 50,163 | |
| 25 | Constantine | 2,187 | 943,112 | 54 | In Guezzam | 65,203 | 122,019 | |
| 26 | Médéa | 8,866 | 830,943 | 55 | Touggourt | 17,428 | 247,221 | |
| 27 | Mostaganem | 2,269 | 746,947 | 56 | Djanet | 86,185 | 17,618 | |
| 28 | M'Sila | 18,718 | 991,846 | 57 | El M'Ghair | 131,220 | 50,392 | |
| 29 | Mascara | 5,941 | 780,959 | 58 | El Menia | 88,126 | 11,202 |
Economy


Algeria's currency is the dinar (DZD). The economy remains dominated by the state, a legacy of the country's socialist post-independence development model. In recent years, the Algerian government has halted the privatization of state-owned industries and imposed restrictions on imports and foreign involvement in its economy.[154] These restrictions are just starting to be lifted off recently although questions about Algeria's slowly-diversifying economy remain.
Algeria has struggled to develop industries outside hydrocarbons in part because of high costs and an inert state bureaucracy. The government's efforts to diversify the economy by attracting foreign and domestic investment outside the energy sector have done little to reduce high youth unemployment rates or to address housing shortages.[154] The country is facing a number of short-term and medium-term problems, including the need to diversify the economy, strengthen political, economic and financial reforms, improve the business climate and reduce inequalities amongst regions.[131]
A wave of economic protests in February and March 2011 prompted the Algerian government to offer more than $23 billion in public grants and retroactive salary and benefit increases. Public spending has increased by 27% annually during the past 5 years. The 2010–14 public-investment programme will cost US$286 billion, 40% of which will go to human development.[131]
Thanks to strong hydrocarbon revenues, Algeria has a cushion of $173 billion in foreign currency reserves and a large hydrocarbon stabilisation fund. In addition, Algeria's external debt is extremely low at about 2% of GDP.[154] The economy remains very dependent on hydrocarbon wealth, and, despite high foreign exchange reserves (US$178 billion, equivalent to three years of imports), current expenditure growth makes Algeria's budget more vulnerable to the risk of prolonged lower hydrocarbon revenues.[170]
Algeria has not joined the WTO, despite several years of negotiations but is a member of the Greater Arab Free Trade Area[171] and the African Continental Free Trade Area,[172] and has an association agreement with the European Union[173][174]
Turkish direct investments have accelerated in Algeria, with total value reaching $5 billion. As of 2022, the number of Turkish companies present in Algeria has reached 1,400. In 2020, despite the pandemic, more than 130 Turkish companies were created in Algeria.[175]
Oil and natural resources

Algeria, whose economy is reliant on petroleum, has been an OPEC member since 1969. Its crude oil production stands at around 1.1 million barrels/day, but it is also a major gas producer and exporter, with important links to Europe.[176] Hydrocarbons have long been the backbone of the economy, accounting for roughly 60% of budget revenues, 30% of GDP, and 87.7%[177] of export earnings. Algeria has the 10th-largest reserves of natural gas in the world and is the sixth-largest gas exporter. The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that in 2005, Algeria had 4.5 trillion cubic metres (160×1012 cu ft) of proven natural-gas reserves.[178] It also ranks 16th in oil reserves.[154]
Non-hydrocarbon growth for 2011 was projected at 5%. To cope with social demands, the authorities raised expenditure, especially on basic food support, employment creation, support for SMEs, and higher salaries. High hydrocarbon prices have improved the current account and the already large international reserves position.[170]
Income from oil and gas rose in 2011 as a result of continuing high oil prices, though the trend in production volume is downwards.[131] Production from the oil and gas sector in terms of volume, continues to decline, dropping from 43.2 million tonnes to 32 million tonnes between 2007 and 2011. Nevertheless, the sector accounted for 98% of the total volume of exports in 2011, against 48% in 1962,[179] and 70% of budgetary receipts, or US$71.4 billion.[131]
The Algerian national oil company is Sonatrach, which plays a key role in all aspects of the oil and natural gas sectors in Algeria. All foreign operators must work in partnership with Sonatrach, which usually has majority ownership in production-sharing agreements.[180]
Access to biocapacity in Algeria is lower than world average. In 2016, Algeria had 0.53 global hectares[181] of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person.[182] In 2016, Algeria used 2.4 global hectares of biocapacity per person – their ecological footprint of consumption. This means they use just under 4.5 times as much biocapacity as Algeria contains. As a result, Algeria is running a biocapacity deficit.[181] In April 2022, diplomats from Italy and Spain held talks after Rome's move to secure large volume of Algerian gas stoked concerns in Madrid.[183] Under the deal between Algeria's Sonatrach and Italy's Eni, Algeria will send an additional 9 billion cubic metres of gas to Italy by next year and in 2024.[184]
Research and alternative energy sources
Algeria has invested an estimated 100 billion dinars towards developing research facilities and paying researchers. This development program is meant to advance alternative energy production, especially solar and wind power.[185] Algeria is estimated to have the largest solar energy potential in the Mediterranean, so the government has funded the creation of a solar science park in Hassi R'Mel. Currently, Algeria has 20,000 research professors at various universities and over 780 research labs, with state-set goals to expand to 1,000. Besides solar energy, areas of research in Algeria include space and satellite telecommunications, nuclear power and medical research.
Labour market
The overall rate of unemployment was 10% in 2011, but remained higher among young people, with a rate of 21.5% for those aged between 15 and 24. The government strengthened in 2011 the job programs introduced in 1988, in particular in the framework of the program to aid those seeking work (Dispositif d'Aide à l'Insertion Professionnelle).[131]
Despite a decline in total unemployment, youth and women unemployment is high.[170] Unemployment particularly affects the young, with a jobless rate of 21.5% among the 15–24 age group.[131]
Tourism

The development of the tourism sector in Algeria had previously been hampered by a lack of facilities, but since 2004 a broad tourism development strategy has been implemented resulting in many hotels of a high modern standard being built.
There are several UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Algeria[186] including Al Qal'a of Beni Hammad, the first capital of the Hammadid empire; Tipasa, a Phoenician and later Roman town; and Djémila and Timgad, both Roman ruins; M'Zab Valley, a limestone valley containing a large urbanized oasis; and the Casbah of Algiers, an important citadel. The only natural World Heritage Site is the Tassili n'Ajjer, a mountain range.
Transport

The Algerian road network is the densest in Africa; its length is estimated at 180,000 km (110,000 mi) of highways, with more than 3,756 structures and a paving rate of 85%. This network will be complemented by the East-West Highway, a major infrastructure project currently under construction. It is a 3-way, 1,216-kilometre-long (756 mi) highway, linking Annaba in the extreme east to the Tlemcen in the far west. Algeria is also crossed by the Trans-Sahara Highway, which is now completely paved. This road is supported by the Algerian government to increase trade between the six countries crossed: Algeria, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, and Tunisia.
Demographics
Algeria has a population of an estimated 44 million, of which the vast majority are Arab-Berber ethnically.[154][187][188] At the outset of the 20th century, its population was approximately four million.[189] About 90% of Algerians live in the northern, coastal area; the inhabitants of the Sahara desert are mainly concentrated in oases, although some 1.5 million remain nomadic or partly nomadic. 28.1% of Algerians are under the age of 15.[154]
Between 90,000 and 165,000 Sahrawis from Western Sahara live in the Sahrawi refugee camps,[190][191] in the western Algerian Sahara desert.[192] There are also more than 4,000 Palestinian refugees, who are well integrated and have not asked for assistance from the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR).[190][191] In 2009, 35,000 Chinese migrant workers lived in Algeria.[193]
The largest concentration of Algerian migrants outside Algeria is in France, which has reportedly over 1.7 million Algerians of up to the second generation.[194]
Ethnic groups
Indigenous Berbers as well as Phoenicians, Romans, Vandals, Byzantine Greeks, Arabs, Turks, various Sub-Saharan Africans, and French have contributed to the history of Algeria.[195] Descendants of Andalusian refugees are also present in the population of Algiers and other cities.[196] Moreover, Spanish was spoken by these Aragonese and Castillian Morisco descendants deep into the 18th century, and even Catalan was spoken at the same time by Catalan Morisco descendants in the small town of Grish El-Oued.[197]

Despite the dominance of the Berber ethnicity in Algeria, the majority of Algerians identify with an Arabic-based identity, especially after the Arab nationalism rising in the 20th century.[198] [unreliable source] [199] [need quotation to verify] Berbers and Berber-speaking Algerians are divided into many groups with varying languages. The largest of these are the Kabyles, who live in the Kabylie region east of Algiers, the Chaoui of Northeast Algeria, the Tuaregs in the southern desert and the Shenwa people of North Algeria.[200][page needed]
During the colonial period, there was a large (10% in 1960)[201] European population who became known as Pied-Noirs. They were primarily of French, Spanish and Italian origin. Almost all of this population left during the war of independence or immediately after its end.[202]
Languages

Modern Standard Arabic and Berber are the official languages.[203] Algerian Arabic (Darja) is the language used by the majority of the population. Colloquial Algerian Arabic is heavily infused with borrowings from French and Berber.
Berber has been recognised as a "national language" by the constitutional amendment of 8 May 2002.[204] Kabyle, the predominant Berber language, is taught and is partially co-official (with a few restrictions) in parts of Kabylie. In February 2016, the Algerian constitution passed a resolution that made Berber an official language alongside Arabic.
Although French has no official status in Algeria, it has one of the largest Francophone populations in the world,[205] and French is widely used in government, media (newspapers, radio, local television), and both the education system (from primary school onwards) and academia due to Algeria's colonial history. It can be regarded as a lingua franca of Algeria. In 2008, 11.2 million Algerians could read and write in French.[206] An Abassa Institute study in April 2000 found that 60% of households could speak and understand French, or 18 million people out of a total of 30 million at the time. Following a period during which the Algerian government tried to phase out French, in recent decades the government has changed course and reinforced the study of French, and some television programs are broadcast in the language.
Algeria emerged as a bilingual state after 1962.[207] Colloquial Algerian Arabic is spoken by about 72% of the population and Berber by 27–30%.[208]
Religion

Islam is the predominant religion in Algeria, with its adherents, mostly Sunnis, accounting for 99% of the population according to a 2021 CIA World Factbook estimate,[154] and 97.9% according to Pew Research in 2020.[209] There are about 290,000 Ibadis in the M'zab Valley in the region of Ghardaia. Estimates of the Christian population range from 20,000 to 200,000[210] Algerian citizens who are Christians predominantly belong to Protestant groups, which have seen increased pressure from the government in recent years including many forced closures.[210]
There has been an increase in the number of people identifying as non-religious. The June 2019 Arab Barometer-BBC News report found that the percentage of Algerians identifying as non-religious has grown from around 8% in 2013 to around 15% in 2018.[211] The Arab Barometer December 2019, found that the growth in the percentage of Algerians identifying as non-religious is largely driven by young Algerians, with roughly 25% describing themselves as non-religious.[212]
Algeria has given the Muslim world a number of prominent thinkers, including Emir Abdelkader, Abdelhamid Ben Badis, Mouloud Kacem Naît Belkacem, Malek Bennabi and Mohamed Arkoun.
Health
In 2018, Algeria had the highest numbers of physicians in the Maghreb region (1.72 per 1,000 people), nurses (2.23 per 1,000 people), and dentists (0.31 per 1,000 people). Access to "improved water sources" was around 97.4% of the population in urban areas and 98.7% of the population in the rural areas. Some 99% of Algerians living in urban areas, and around 93.4% of those living in rural areas, had access to "improved sanitation". According to the World Bank, Algeria is making progress toward its goal of "reducing by half the number of people without sustainable access to improved drinking water and basic sanitation by 2015". Given Algeria's young population, policy favours preventive health care and clinics over hospitals. In keeping with this policy, the government maintains an immunisation program. However, poor sanitation and unclean water still cause tuberculosis, hepatitis, measles, typhoid fever, cholera and dysentery. The poor generally receive health care free of charge.[213]
Health records have been maintained in Algeria since 1882 and began adding Muslims living in the south to their vital record database in 1905 during French rule.[214]
Education

Since the 1970s, in a centralised system that was designed to significantly reduce the rate of illiteracy, the Algerian government introduced a decree by which school attendance became compulsory for all children aged between 6 and 15 years who have the ability to track their learning through the 20 facilities built since independence, now the literacy rate is around 92.6%.[215] Since 1972, Arabic is used as the language of instruction during the first nine years of schooling. From the third year, French is taught and it is also the language of instruction for science classes. The students can also learn English, Italian, Spanish and German. In 2008, new programs at the elementary appeared, therefore the compulsory schooling does not start at the age of six anymore, but at the age of five.[216] Apart from the 122 private schools, the Universities of the State are free of charge. After nine years of primary school, students can go to the high school or to an educational institution. The school offers two programs: general or technical. At the end of the third year of secondary school, students pass the exam of the baccalaureate, which allows once it is successful to pursue graduate studies in universities and institutes.[217]
Education is officially compulsory for children between the ages of six and 15. In 2008, the illiteracy rate for people over 10 was 22.3%, 15.6% for men and 29.0% for women. The province with the lowest rate of illiteracy was Algiers Province at 11.6%, while the province with the highest rate was Djelfa Province at 35.5%.[218]
Algeria has 26 universities and 67 institutions of higher education, which must accommodate a million Algerians and 80,000 foreign students in 2008. The University of Algiers, founded in 1879, is the oldest, it offers education in various disciplines (law, medicine, science and letters). Twenty-five of these universities and almost all of the institutions of higher education were founded after the independence of the country.
Even if some of them offer instruction in Arabic like areas of law and the economy, most of the other sectors as science and medicine continue to be provided in French and English. Among the most important universities, there are the University of Sciences and Technology Houari Boumediene, the University of Mentouri Constantine, and University of Oran Es-Senia. The University of Abou Bekr Belkaïd in Tlemcen and University of Batna Hadj Lakhdar occupy the 26th and 45th row in Africa.[219] Algeria was ranked 120th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 113rd in 2019.[220][221][222][223]
Culture

Modern Algerian literature, split between Arabic, Tamazight and French, has been strongly influenced by the country's recent history. Famous novelists of the 20th century include Mohammed Dib, Albert Camus, Kateb Yacine and Ahlam Mosteghanemi while Assia Djebar is widely translated. Among the important novelists of the 1980s were Rachid Mimouni, later vice-president of Amnesty International, and Tahar Djaout, murdered by an Islamist group in 1993 for his secularist views.[224]
Malek Bennabi and Frantz Fanon are noted for their thoughts on decolonization; Augustine of Hippo was born in Tagaste (modern-day Souk Ahras); and Ibn Khaldun, though born in Tunis, wrote the Muqaddima while staying in Algeria. The works of the Sanusi family in pre-colonial times, and of Emir Abdelkader and Sheikh Ben Badis in colonial times, are widely noted. The Latin author Apuleius was born in Madaurus (Mdaourouch), in what later became Algeria.
Contemporary Algerian cinema is various in terms of genre, exploring a wider range of themes and issues. There has been a transition from cinema which focused on the war of independence to films more concerned with the everyday lives of Algerians.[225]
Media
Art

Algerian painters, like Mohamed Racim or Baya, attempted to revive the prestigious Algerian past prior to French colonisation, at the same time that they have contributed to the preservation of the authentic values of Algeria. In this line, Mohamed Temam, Abdelkhader Houamel have also returned through this art, scenes from the history of the country, the habits and customs of the past and the country life. Other new artistic currents including the one of M'hamed Issiakhem, Mohammed Khadda and Bachir Yelles, appeared on the scene of Algerian painting, abandoning figurative classical painting to find new pictorial ways, in order to adapt Algerian paintings to the new realities of the country through its struggle and its aspirations. Mohammed Khadda[226] and M'hamed Issiakhem have been notable in recent years.[226]
Literature
The historic roots of Algerian literature go back to the Numidian and Roman African era, when Apuleius wrote The Golden Ass, the only Latin novel to survive in its entirety. This period had also known Augustine of Hippo, Nonius Marcellus and Martianus Capella, among many others. The Middle Ages have known many Arabic writers who revolutionised the Arab world literature, with authors like Ahmad al-Buni, Ibn Manzur and Ibn Khaldoun, who wrote the Muqaddimah while staying in Algeria, and many others.
Albert Camus was an Algerian-born French Pied-Noir author. In 1957, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in literature.
Today Algeria contains, in its literary landscape, big names having not only marked the Algerian literature, but also the universal literary heritage in Arabic and French.
As a first step, Algerian literature was marked by works whose main concern was the assertion of the Algerian national entity, there is the publication of novels as the Algerian trilogy of Mohammed Dib, or even Nedjma of Kateb Yacine novel which is often regarded as a monumental and major work. Other known writers will contribute to the emergence of Algerian literature whom include Mouloud Feraoun, Malek Bennabi, Malek Haddad, Moufdi Zakaria, Abdelhamid Ben Badis, Mohamed Laïd Al-Khalifa, Mouloud Mammeri, Frantz Fanon, and Assia Djebar.

In the aftermath of the independence, several new authors emerged on the Algerian literary scene, they will attempt through their works to expose a number of social problems, among them there are Rachid Boudjedra, Rachid Mimouni, Leila Sebbar, Tahar Djaout and Tahir Wattar.
Currently, a part of Algerian writers tends to be defined in a literature of shocking expression, due to the terrorism that occurred during the 1990s, the other party is defined in a different style of literature who staged an individualistic conception of the human adventure. Among the most noted recent works, there is the writer, the swallows of Kabul and the attack of Yasmina Khadra, the oath of barbarians of Boualem Sansal, memory of the flesh of Ahlam Mosteghanemi and the last novel by Assia Djebar nowhere in my father's House.
Music

Chaâbi music is a typically Algerian musical genre characterized by specific rhythms and of Qacidate (popular poems) in Arabic dialect. El Hadj M'Hamed El Anka is considered the greatest master of the art in modern times. He wrote over 350 songs and produced some 130 records before his death in 1978. Many of his pupils went on to be renowned musicians.[228] The Constantinois Malouf style is saved by musician from whom Mohamed Tahar Fergani is a performer.
Folk music styles include Bedouin music, characterized by the poetic songs based on long kacida (poems); Kabyle music, based on a rich repertoire that is poetry and old tales passed through generations; Shawiya music, a folklore from diverse areas of the Aurès Mountains. Rahaba music style is unique to the Aures. Souad Massi is a rising Algerian folk singer. Other Algerian singers of the diaspora include Manel Filali in Germany and Kenza Farah in France. Tergui music is sung in Tuareg languages generally, Tinariwen had a worldwide success. Finally, the staïfi music is born in Sétif and remains a unique style of its kind.
Modern music is available in several facets, Raï music is a style typical of western Algeria. Rap, a relatively recent style in Algeria, is experiencing significant growth.
Cinema

The Algerian state's interest in film-industry activities can be seen in the annual budget of DZD 200 million (EUR 1.3 million) allocated to production, specific measures and an ambitious programme plan implemented by the Ministry of Culture in order to promote national production, renovate the cinema stock and remedy the weak links in distribution and exploitation.
The financial support provided by the state, through the Fund for the Development of the Arts, Techniques and the Film Industry (FDATIC) and the Algerian Agency for Cultural Influence (AARC), plays a key role in the promotion of national production. Between 2007 and 2013, FDATIC subsidised 98 films (feature films, documentaries and short films). In mid-2013, AARC had already supported a total of 78 films, including 42 feature films, 6 short films and 30 documentaries.
According to the European Audiovisual Observatory's LUMIERE database, 41 Algerian films were distributed in Europe between 1996 and 2013; 21 films in this repertoire were Algerian-French co-productions. Days of Glory (2006) and Outside the Law (2010) recorded the highest number of admissions in the European Union, 3,172,612 and 474,722, respectively.[229]
Algeria won the Palme d'Or for Chronicle of the Years of Fire (1975), two Oscars for Z (1969), and other awards for the Italian-Algerian movie The Battle of Algiers.
Cuisine

Algerian cuisine is rich and diverse. The country was considered as the "granary of Rome". It offers a component of dishes and varied dishes, depending on the region and according to the seasons. The cuisine uses cereals as the main products, since they are always produced with abundance in the country. There is not a dish where cereals are not present.
Algerian cuisine varies from one region to another, according to seasonal vegetables. It can be prepared using meat, fish and vegetables. Among the dishes known, couscous,[230] chorba, rechta, chakhchoukha, berkoukes, shakshouka, mthewem, chtitha, mderbel, dolma, brik or bourek, garantita, lham'hlou, etc. Merguez sausage is widely used in Algeria, but it differs, depending on the region and on the added spices.
Cakes are marketed and can be found in cities either in Algeria, in Europe or North America. However, traditional cakes are also made at home, following the habits and customs of each family. Among these cakes, there are Tamina, Baklawa, Chrik, Garn logzelles, Griouech, Kalb el-louz, Makroud, Mbardja, Mchewek, Samsa, Tcharak, Baghrir, Khfaf, Zlabia, Aarayech, Ghroubiya and Mghergchette. Algerian pastry also contains Tunisian or French cakes. Marketed and home-made bread products include varieties such as Kessra or Khmira or Harchaya, chopsticks and so-called washers Khoubz dar or Matloue. Other traditional meals sold often as street food include mhadjeb or mahjouba, karantika, doubara, chakhchoukha, hassouna, and t'chicha.
Sports

Various games have existed in Algeria since antiquity. In the Aures, people played several games such as El Kherba or El khergueba (chess variant). Playing cards, checkers and chess games are part of Algerian culture. Racing (fantasia) and rifle shooting are part of cultural recreation of the Algerians.[231]
The first Algerian and African gold medalist is Boughera El Ouafi in 1928 Olympics of Amsterdam in the Marathon. The second Algerian Medalist was Alain Mimoun in 1956 Summer Olympics in Melbourne. Several men and women were champions in athletics in the 1990s including Noureddine Morceli, Hassiba Boulmerka, Nouria Merah-Benida, and Taoufik Makhloufi, all specialized in middle-distance running.[232]
Football is the most popular sport in Algeria. Several names are engraved in the history of the sport, including Lakhdar Belloumi, Rachid Mekhloufi, Hassen Lalmas, Rabah Madjer, Riyad Mahrez, Salah Assad and Djamel Zidane. The Algeria national football team qualified for the 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1986 FIFA World Cup, 2010 FIFA World Cup and 2014 FIFA World Cup. In addition, several football clubs have won continental and international trophies as the club ES Sétif or JS Kabylia. The Algerian Football Federation is an association of Algeria football clubs organizing national competitions and international matches of the selection of Algeria national football team.[233]
See also
Explanatory notes
- ^ French although not officially recognized, remains a common language, understood by the majority of the population.
- ^ The CIA World Factbook states that about 15% of Algerians, a minority, identify as Berber even though many Algerians have Berber origins. The Factbook explains that of the approximately 15% who identify as Berber, most live in the Kabylia region, more closely identify with Berber heritage instead of Arab heritage, and are Muslim.
- ^ /ælˈdʒɪəriə/ ⓘ al-JEER-ee-ə; Arabic: الجزائر, romanized: al-Jazāʾir; Template:Lang-fr
Citations
- ^ "Constitution of Algeria, Art. 11". El-mouradia.dz. language: France and Arabic (government language); people of Algeria speak Arabic and Berber. Archived from the original on 18 July 2012. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "Constitution of Algeria; Art. 11". Apn-dz.org. 28 November 1996. Archived from the original on 25 July 2013. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ a b c d e "The World Factbook – Africa – Algeria". CIA. Retrieved 20 March 2021.
- ^ "Démographie" [Demography] (PDF). Office National des Statistiques (in French). 18 May 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 July 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 22 October 2021.
- ^ "Distribution of Family Income – Gini Index". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 1 September 2009.
- ^ "GINI index (World Bank estimate)". World Bank. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018. Retrieved 24 February 2019.
- ^ Human Development Report 2021-22 Uncertain Times, Unsettled Lives: Shaping Our Future in an Uncertain World (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. pp. 289–292. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ "Africa: largest countries by area 2020". Statista. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ Proclamación de la República argelina, Journal officiel de la republique algerienne, 1st year, 1st issue, 1962, páge 5.
- ^ a b "La standardisation de la transcription n'est pas tranchée : Quelle graphie pour tamazight ?". El Watan (in French). 22 April 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2021.
- ^ LLC, Forbidden Fruits (30 January 2013). iAfrica – Ancient History UNTOLD. Forbidden Fruit Books LLC.
- ^ Bazina, Abdullah Salem (2010). The spread of Islam in Sub-Saharan in Africa (in Arabic). Al Manhal. ISBN 978-9796500024. Archived from the original on 16 December 2018. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
- ^ al-Idrisi, Muhammad (12th century) Nuzhat al-Mushtaq
- ^ Abderahman, Abderrahman (1377). History of Ibn Khaldun – Volume 6.
- ^ a b Sahnouni; et al. (14 December 2018). "1.9-million- and 2.4-million-year-old artifacts and stone tool–cutmarked bones from Ain Boucherit, Algeria". Science. 362 (6420): 1297–1301. Bibcode:2018Sci...362.1297S. doi:10.1126/science.aau0008. hdl:10072/383164. PMID 30498166. S2CID 54166305. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ Sahnouni, Mohamed; de Heinzelin, Jean. "The Site of Ain Hanech Revisited: New Investigations at this Lower Pleistocene Site in Northern Algeria" (PDF). Journal of Archaeological Science. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ^ "Research at Ain Hanech, Algeria". Stoneageinstitute.org. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ^ Eric Delson; Ian Tattersall; John Van Couvering; Alison S. Brooks (2004). Encyclopedia of Human Evolution and Prehistory: Second Edition. Routledge. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-135-58228-9.
- ^ Henn, Brenna M.; Botigué, Laura R.; Gravel, Simon; Wang, Wei; Brisbin, Abra; Byrnes, Jake K.; Fadhlaoui-Zid, Karima; Zalloua, Pierre A.; Moreno-Estrada, Andres; Bertranpetit, Jaume; Bustamante, Carlos D.; Comas, David (12 January 2012). "Genomic Ancestry of North Africans Supports Back-to-Africa Migrations". PLOS Genetics. 8 (1): e1002397. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002397. PMC 3257290. PMID 22253600.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Brett, Michael; Fentress, Elizabeth (1997). "Berbers in Antiquity". The Berbers. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-20767-2.
- ^ Christelle Fischer-Bovet (2014). Army and Society in Ptolemaic Egypt. Cambridge University Press. p. 91. ISBN 978-1-107-00775-8.
- ^ Jackson J. Spielvogel (2014). Western Civilization: Volume A: To 1500. Cengage Learning. p. 156. ISBN 978-1-285-98299-1.
- ^ a b Cameron, Averil; Ward-Perkins, Bryan (2001). "Vandal Africa, 429–533". The Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 14. Cambridge University Press. pp. 124–126. ISBN 978-0-521-32591-2.
- ^ Mattingly, D.J. (1983). "The Laguatan: A Libyan Tribal Confederation in the late Roman Empire". Libyan Studies. 14: 96–108. doi:10.1017/S0263718900007810. S2CID 164294564.
- ^ The Middle East and North Africa 2003. Psychology Press. ISBN 9781857431322 – via Google Books.
- ^ Walmsley, Hugh Mulleneux (1 April 1858). "Sketches of Algeria During the Kabyle War". Chapman and Hall – via Google Books.
- ^ Wysner, Glora M. (30 January 2013). The Kabyle People. Read Books Ltd. ISBN 9781447483526 – via Google Books.
- ^ The Encyclopedia Americana. Grolier. 1 April 1990. ISBN 9780717201211 – via Google Books.
- ^ "The art journal London". Virtue. 1 April 1865 – via Google Books.
- ^ Field, Henry Martyn (1 April 1893). "The Barbary Coast". C. Scribner's Sons – via Google Books.
- ^ The Great Arab Conquests: How the Spread of Islam Changed the World We Live InHugh Kennedy Hachette UK,
- ^ Gibraltar: Croisée de mondes : d'Hercule à Boabdil Zakya Daoud Séguier
- ^ The History of Northern Africa Britannica Educational Publishing Britannica Educational Publishing
- ^ Middle East and Africa: International Dictionary of Historic Places Trudy Ring, Noelle Watson, Paul Schellinger Routledge
- ^ Historical Dictionary of Tunisia Kenneth J. Perkins Rowman & Littlefield
- ^ Islam, 01 AH-250 AH: A Chronology of Events Abu Tariq Hijazi Message Publications,
- ^ a b Jonathan Conant, Staying Roman, 2012, pp. 364–365 ISBN 978-0-521-19697-0
- ^ "Fatimid Dynasty (Islamic dynasty)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
- ^ "Qantara". Qantara-med.org. Archived from the original on 9 October 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ^ "Qantara – Les Almoravides (1056–1147)". Qantara-med.org. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ^ Khaldūn, Ibn (1852). Histoire des Berbères et des dynasties musulmanes de l'Afrique Septentrionale Par Ibn Khaldūn, William MacGuckin Slane [History of the Berbers and the Muslim dynasties of northern Africa] (in French). p. XV.
- ^ Khaldūn, Ibn (1852). Histoire des Berbères et des dynasties musulmanes de l'Afrique Septentrionale Par Ibn Khaldūn, William MacGuckin Slane [History of the Berbers and the Muslim dynasties of northern Africa] (in French). pp. X.
- ^ Baadj, Amar S. (19 June 2015). Saladin, the Almohads and the Banū Ghāniya: The Contest for North Africa (12th and 13th centuries). BRILL. ISBN 9789004298576 – via Google Books.
- ^ Hattstein, Markus; Delius, Peter (2004). Islam: Art and Architecture: Pg 614. ISBN 9783833111785.
- ^ Ilahiane, Hsain (17 July 2006). Historical Dictionary of the Berbers (Imazighen). Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9780810864900 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Nanjira, Daniel Don (1 April 2010). African Foreign Policy and Diplomacy from Antiquity to the 21st Century. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 9780313379826 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Fage, J. D. (1 April 1958). "An Atlas of African History". E. Arnold – via Google Books.
- ^ The Puffin History of the World: Volume 1, By Roshen Dalal
- ^ Revue africaine: journal des travaux de la Société historique algérienne, Volumes 105–106 Kraus Reprint,
- ^ Vers la paix en Algérie: les négociations d'Evian dans les archives diplomatiques françaises (15 janvier 1961-29 juin 1962). Bruylant,
- ^ The Zīrids of Granada Andrew Handler University of Miami Press, 1974
- ^ The Cambridge History of Africa, Volume 3 – J.D. Fage
- ^ Iliffe, John (13 July 2017). Africans: The History of a Continent. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-19832-6.
- ^ a b Meredith, Martin (11 September 2014). Fortunes of Africa: A 5,000 Year History of Wealth, Greed and Endeavour. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4711-3546-0.
- ^ Histoire de l'Afrique septentrionale (Berbérie) dupuis les temps les plus reculés jusqu'à la conquête française (1830), Volumes 1–2 Ernest Mercier E. Leroux,
- ^ In Barbary: Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, and the Sahara Edward Alexander Powell Century Company
- ^ Roudh El-Kartas: Histoire des souverains du Maghreb (Espagne et Maroc) et annales de la ville de Fès Abū al-Ḥasan ʻAlī b. ʻAbd Allāh Ibn Abī Zarʻ, ʿAlī Ibn-ʿAbdallāh Ibn-Abī-Zarʿ Imprimerie Imperiale
- ^ Les Berbers dans l'histoire: De la Kahina à l'occupation Turque Mouloud Gaïd Editions Mimouni
- ^ Fage, John; Tordoff, with William (23 October 2013). A History of Africa. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-79727-2.
- ^ The Maghreb Review: Majallat Al-Maghrib. 1979.
- ^ "The Great Mosque of Tlemcen". MuslimHeritage.com. Foundation for Science Technology and Civilization. 8 December 2004.
- ^ Populations Crises and Population Cycles Archived 27 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Claire Russell and W. M. S. Russell
- ^ Singh, Nagendra Kr; Khan, Abdul Mabud (2001). Encyclopaedia of the World Muslims: Tribes, Castes and Communities. Global Vision. ISBN 978-81-87746-05-8.
- ^ du moyen age Louis Cibrario Libraire de Guillaumin et C.ie
- ^ Robinson, Neal (1999). Islam, a Concise Introduction. Georgetown University Press. ISBN 978-0-87840-224-3.
- ^ a b Jeff Huebner, "Al Qal'a of Beni Hammad (M'sila, Algeria)" in Middle East and Africa: International Dictionary of Historic Places (Vol. 4) (eds. K.A. Berney, Trudy Ring & Noelle Watson: Fitzroy Dearborn, 1996), pp. 36–39.
- ^ Jamil M. Abun-Nasr (20 August 1987). A History of the Maghrib in the Islamic Period. Cambridge University Press. pp. 103–104
- ^ Crowther, Geoff; Finlay, Hugh (1992). Morocco, Algeria & Tunisia: A Travel Survival Kit. Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 978-0-86442-126-5.
- ^ Les états de l'Occident musulman aux XIIIe, XIVe et XVe siècles: institutions gouvernementales et administratives Atallah Dhina Office des Publications Universitaires,
- ^ Histoire générale de la Tunisie, Volume 2 Hédi Slim, Ammar Mahjoubi, Khaled Belkhodja, Hichem Djaït, Abdelmajid Ennabli Sud éditions,
- ^ Recueil des Notices et Memoires, Volumes 52–53 Société archéologique du département de Constantine
- ^ Recueil des Notices et Memoires, Volumes 52–53 Société archéologique du département de Constantine
- ^ La dynastie marocaine des Beni Wattâs (1420–1544) Auguste Cour P. Geuthner
- ^ Recueil des notices et mémoires de la Société archéologique du département de Constantine L. Arnolet,
- ^ García, Luis Arciniega (1 January 1999). "Defensa a la antigua y a la moderna en el Reino de Valencia durante el siglo XVI". Espacio Tiempo y Forma. Serie VII, Historia del Arte (in Spanish) (12). doi:10.5944/etfvii.12.1999.2343. ISSN 2340-1478.
- ^ MARIANA, Juan de (1849). Historia General de España ... con la continuacion de Miniana; completada ... por E. Chao. Enriquecida con notas historicas y criticas, etc (in Spanish).
- ^ Sánchez Doncel, Gregorio. 1991. Presencia de España en Orán, 1509–1792. Estudio Teológico de San Ildefonso.
- ^ Vera, León Galindo y de (1884). Historia vicisitudes y política tradicional de España respecto de sus posesiones en las costas de África desde la monarquía gótica y en los tiempos posteriores á la restauración hasta el último siglo (in Spanish). Impr. y fundición de M. Tello.
- ^ Rézette, Robert (1976). THE SPANISH ENCLAVES IN MOROCCO Par ROBERT REZETTE. Nouvelles Editions Latines.
- ^ a b c d "Algeria – Ottoman Rule". Country Studies. Archived from the original on 14 October 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
- ^ a b Mikaberidze, Alexander (2011). Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO. p. 847.
- ^ Houtsma, M. Th (1993). E. J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913–1936. BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-09790-2.
- ^ a b Robert Davis (2003). Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500–1800. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-333-71966-4.
- ^ a b Hannay, David McDowall (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 3 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 383–384.
- ^ Robert Davis (17 February 2011). "British Slaves on the Barbary Coast". BBC. Archived from the original on 25 April 2011. Retrieved 7 September 2008.
- ^ "British Slaves on the Barbary Coast". Archived from the original on 8 February 2009. Retrieved 7 September 2008.
- ^ Povoledo, Elisabetta (26 September 2003). "The Mysteries and Majesties of the Aeolian Islands". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 22 July 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ "When Europeans were slaves: Research suggests white slavery was much more common than previously believed". Ohio State Research Communications. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011.
- ^ Paul Auchterlonie (24 March 2012). Encountering Islam: Joseph Pitts: An English Slave in 17th-century Algiers and Mecca. Arabian Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-9571060-8-6.
- ^ "Vísindavefurinn: Hverjir stóðu raunverulega að Tyrkjaráninu?" Archived 6 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Vísindavefurinn.
- ^ "Vísindavefurinn: Hvað gerðist í Tyrkjaráninu?" Archived 6 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Vísindavefurinn.
- ^ "Turkish invasion walk" Archived 6 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine. heimaslod.is.
- ^ Etravel Travel service. "Turkish Invasion – Visit Westman Islands .com" Archived 6 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine. visitwestmanislands.com.
- ^ "Vísindavefurinn: Voru Tyrkjarán framin í öðrum löndum?" Archived 6 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Vísindavefurinn.
- ^ Association, American Historical (1918). General Index to Papers and Annual Reports of the American Historical Association, 1884–1914. U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ^ Hutt, Graham (1 January 2019). North Africa. Imray, Laurie, Norie and Wilson Ltd. ISBN 978-1-84623-883-3.
- ^ Constantine, Société Archéologique de la Province de (1868). Recueil des notices et mémoires de la Société Archéologique de la Province de Constantine (in French).
- ^ algérienne, Société historique (1873). Revue africaine (in French). La Société.
- ^ Bulletin du comité des travaux historiques et scientifiques: section de géographie (in French). Imprimerie nationale. 1894.
- ^ Jamieson, Alan G. (2013). Lords of the Sea: A History of the Barbary Corsairs. Reaktion Books. p. 176.
- ^ Schreier, Joshua (16 May 2017). The Merchants of Oran: A Jewish Port at the Dawn of Empire. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-1-5036-0216-8.
- ^ Morocco in the Reign of Mawlay Sulayman – Mohamed El Mansour Middle East & North African Studies Press, 1990 – Morocco – 248 pages: Pg 104
- ^ Mackie, Erin Skye (1 January 2005). "Welcome the Outlaw: Pirates, Maroons, and Caribbean Countercultures". Cultural Critique. 59 (1): 24–62. doi:10.1353/cul.2005.0008.
- ^ Littell, Eliakim (1836). The Museum of foreign literature, science and art. E. Littell. p. 231. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ "Background Note: Algeria". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 24 June 2017.
- ^ Horne, Alistair (2006). A Savage War of Peace: Algeria 1954–1962. New York, NY: NYRB Classics. pp. 29–30. ISBN 978-1-59017-218-6.
- ^ Kiernan, Ben (2007). Blood and Soil: A World History of Genocide and Extermination from Sparta to Darfur. Yale University Press. p. 374. ISBN 978-0-300-10098-3. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ Bennoune, Mahfoud (2002). The Making of Contemporary Algeria, 1830–1987. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-521-52432-2.
- ^ "Had planning been better (barracks, hospitals, medical services), the drain on men would have been miniscule: it has been calculated that between 1831 and 1851, 92,329 died in hospital, and only 3,336 in battle." The Military and Colonial Destruction of the Roman Landscape of North Africa ... – Michael Greenhalgh, p366 [1] Archived 20 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lahmeyer, Jan (11 October 2003). "Algeria (Djazaïria) historical demographic data of the whole country". Population Statistics. populstat.info. Archived from the original on 18 July 2012. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ^ Ruedy, John Douglas (2005). Modern Algeria: The Origins And Development of a Nation. Indiana University Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-253-21782-0. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ Sowerwine, Charles (2018). France since 1870. p. 37. ISBN 9781137406118.
- ^ Ricoux, René (1880). La démographie figurée de l'Algérie: étude statistique des... [The figurative demographics of Algeria]. G. Masson. pp. 260–261. Archived from the original on 13 May 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2013.
- ^ "Le rêve arabe de Napoléon III". lhistoire.fr (in French). Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- ^ Randell, Keith (1986). France: Monarchy, Republic and Empire, 1814–70. Hodder & Stoughton. ISBN 978-0-340-51805-2. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015.[page needed]
- ^ Fisher, Michael H. (2014). Migration: A World History. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 80. ISBN 978-0199764341.
- ^ Horne, Alistair (2006). A Savage War of Peace: Algeria 1954–1962 (New York Review Books Classics). New York: NYRB Classics. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-59017-218-6.
- ^ Albert Habib Hourani, Malise Ruthven (2002). "A history of the Arab peoples". Harvard University Press. p.323. ISBN 0-674-01017-5
- ^ Baten, Jörg (2016). A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. p. 220. ISBN 9781107507180.
- ^ United States Military Academy. Department of Military Art and Engineering (1947). The War in North Africa Part 2—The Allied Invasion. West Point, NY: Department of Military Art and Engineering, United States Military Academy. pp. 4–5.
- ^ "French 'Reparation' for Algerians". BBC News. 6 December 2007. Archived from the original on 20 April 2010. Retrieved 16 November 2009.
- ^ Horne, Alistair (1978). A Savage War of Peace. p. 538. ISBN 978-0-670-61964-1.
- ^ Windrow, Martin (15 November 1997). The Algerian War 1954–62. p. 13. ISBN 1-85532-658-2.
- ^ Ussama Samir Makdisi; Paul A. Silverstein (2006). Memory and Violence in the Middle East and North Africa. Indiana University Press. p. 160. ISBN 978-0-253-34655-1. Archived from the original on 16 April 2017. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Country Profile: Algeria". Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 13 December 2010.
- ^ Prochaska, David. "That Was Then, This Is Now: The Battle of Algiers and After". p. 141. Archived from the original on 25 July 2013. Retrieved 10 March 2012.
- ^ "98 Die in One of Algerian Civil War's Worst Massacres Archived 23 June 2017 at the Wayback Machine". The New York Times. 30 August 1997.
- ^ Freedom House. "Freedom in the World 2013: Algeria". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- ^ "Algeria Officially Lifts State of Emergency". CNN. 24 February 2011. Archived from the original on 1 March 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Algeria". African Economic Outlook. Archived from the original on 26 March 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- ^ "Algeria parliament to meet on Tuesday to name interim president". Al Jazeera. 6 April 2019. Archived from the original on 7 April 2019. Retrieved 7 April 2019.
- ^ "Algeria: Who is new president Abdelmadjid Tebboune?". The Africa Report.com. 17 December 2019.
- ^ a b Metz, Helen Chapin. "Algeria : a country study". United States Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 18 May 2013.
- ^ a b c Benzerga, Mohamed (24 August 2015). "Heatwaves are on the rise in Algeria due to climate change, says specialist". the Guardian. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Sahnoune, F.; Belhamel, M.; Zelmat, M.; Kerbachi, R. (1 January 2013). "Climate Change in Algeria: Vulnerability and Strategy of Mitigation and Adaptation". Energy Procedia. TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 – Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment. 36: 1286–1294. Bibcode:2013EnPro..36.1286S. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2013.07.145. ISSN 1876-6102.
- ^ "Algeria". Climate Change Performance Index. 28 November 2019. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Hodges, K. "National Animals of African Countries". Archived from the original on 25 February 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ "Crocodiles in the Sahara Desert: An Update of Distribution, Habitats and Population Status for Conservation Planning in Mauritania Archived 10 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine". PLOS ONE. 25 February 2011.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ "What's happening in Algeria… is it the "Arab spring"? (فراس صليبا)". Lebanese Forces Official Website. 12 April 2019. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ "Algeria – Country Profile – Nations Online Project". nationsonline.org. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ "Still waiting for real democracy". The Economist. 12 May 2012. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 16 January 2013.
- ^ "The president and the police". The Economist. 4 May 2010. Archived from the original on 4 January 2013. Retrieved 16 January 2013.
- ^ Michaelson, Ruth (3 April 2019). "Algeria's president Abdelaziz Bouteflika resigns after 20 years". The Guardian.
- ^ "Algeria election: Fresh protests as Tebboune replaces Bouteflika". BBC News. 13 December 2019. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ Articles: 85, 87, 77, 78 and 79 of the Algerian constitution Algerian government. "Constitution". Archived from the original on 22 April 2012. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- ^ "Algeria". Freedom in the World 2013. Freedom House. Archived from the original on 23 March 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2013.
- ^ Article 42 of the Algerian constitution – Algerian Government. "Algerian constitution الحـقــوق والحــرّيـات". Archived from the original on 14 September 2012. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- ^ "IPU PARLINE database: ALGERIA (Al-Majlis Al-Chaabi Al-Watani), Full text". archive.ipu.org. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "France offers compensation to victims sickened by nuclear tests". Archived from the original on 4 November 2016. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- ^ "Bin Ali calls for reactivating Arab Maghreb Union, Tunisia-Maghreb, Politics". ArabicNews.com. 19 February 1999. Archived from the original on 25 November 2001. Retrieved 4 April 2006.
- ^ "Algeria stops gas supplies to Spain via Morocco, as diplomatic row with Rabat intensifies". Upstream. 2 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "The World Factbook – Algeria". Central Intelligence Agency. 4 December 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^ Hackett, James, ed. (5 February 2008). The Military Balance 2008. International Institute for Strategic Studies. Europa. ISBN 978-1-85743-461-3. Archived from the original on 25 July 2013. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ "Loi 14-06 relative au service national", JORADP 48, August, 10th 2014
- ^ a b "Algeria buying military equipment". United Press International. Archived from the original on 13 November 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^ "The Nuclear Vault: The Algerian Nuclear Problem". Gwu.edu. Archived from the original on 2 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ "Venezuela's Chavez To Finalise Russian Submarines Deal". Agence France-Presse. 14 June 2007. Archived from the original on 12 February 2015. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
- ^ "Freedom in the World". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 19 January 2013.
- ^ Monitor, Euro-Med (December 2016). "Algeria must stop crushing dissent by imprisoning journalists and activists". Euro-Mediterranean. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ Izouaouen, Noreddine (4 December 2017). "Algérie : Dissolution du Snateg, le secrétaire général conteste". Maghreb Emergent (in French). Archived from the original on 15 March 2018.
- ^ "Le Snategs dénonce et décide de porter plainte | Le Matin d'Algérie". Le Matin d'Algérie (in French). Archived from the original on 15 March 2018. Retrieved 15 March 2018.
- ^ "Algérie : Les droits des travailleurs bafoués" (in French). Human Rights Watch. 27 May 2014. Archived from the original on 21 April 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2018.
- ^ "Here are the 10 countries where homosexuality may be punished by death". The Washington Post. 16 June 2016. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ "2010 Human Rights Report: Algeria". US Department of State. Retrieved 24 June 2017.
- ^ "Are Arabs turning their backs on religion?". 24 June 2019. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- ^ "During Pandemic, Algeria Tightens Vise on Protest Movement". Human Rights Watch. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ "Wildfire Management Policies in Algeria: Present and Future Needs1,2" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 May 2017.
- ^ a b c "Algeria: 2011 Article IV Consultation" (PDF). IMF. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 March 2014. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- ^ "Members of the GAFTA – Greater Arab Free Trade Area". Worlddata.info. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ "KUNA : Algeria officially joins AU free trade agreement – Economics – 16/12/2019". kuna.net.kw. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ "General presentation of Association Agreement". caci.dz. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ "Doing Business in Algeria". Embassy of the United States Algiers, Algeria. Archived from the original on 28 December 2012.
- ^ Dubessy, Frédéric. "Turkey strengthens its investments in Algeria". Econostrum | Economic News in the Mediterranean. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- ^ "OPEC Bulletin 8-9/12". p. 15. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- ^ "Exportations hors hydrocarbures: une recette de près de 3 mds de dollars durant les huit 1ers mois de 2021". APS. 13 November 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ "Country Comparison: Natural Gas – Proved Reserves". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 7 March 2017. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ Benchicou, Mohamed (27 May 2013). "Le temps des crapules – Tout sur l'Algérie". Tsa-algerie.com. Archived from the original on 11 March 2014.
- ^ "Country Analysis Briefs – Algeria" (PDF). Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 May 2013.
- ^ a b "Country Trends". Global Footprint Network. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Lin, David; Hanscom, Laurel; Murthy, Adeline; Galli, Alessandro; Evans, Mikel; Neill, Evan; Mancini, MariaSerena; Martindill, Jon; Medouar, FatimeZahra; Huang, Shiyu; Wackernagel, Mathis (2018). "Ecological Footprint Accounting for Countries: Updates and Results of the National Footprint Accounts, 2012–2018". Resources. 7 (3): 58. doi:10.3390/resources7030058.
- ^ "Italy and Spain Hold Talks to Head Off Tension Over Algerian Gas". Bloomberg.com. 12 April 2022. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ^ "Italy looks to demote Russia and make Algeria its top gas supplier". POLITICO. 11 April 2022. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ^ "Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Algerian Program (English Version)". Archived from the original on 1 November 2016. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ^ UNESCO. "UNESCO World Heritage Centre". Archived from the original on 19 September 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- ^ "Algérie a atteint 40,4 millions d'habitants (ONS)". ons. 17 April 2013. Archived from the original on 5 December 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ^ Arredi, Barbara; Poloni, Estella S.; Paracchini, Silvia; Zerjal, Tatiana; Dahmani, M. Fathallah; Makrelouf, Mohamed; Vincenzo, L. Pascali; Novelletto, Andrea; Tyler-Smith, Chris (7 June 2004). "A Predominantly Neolithic Origin for Y-Chromosomal DNA Variation in North Africa". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75 (2): 338–45. doi:10.1086/423147. PMC 1216069. PMID 15202071.
- ^ "Algeria – Population". Library of Congress Country Studies. Archived from the original on 13 June 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ a b "2013 UNHCR country operations profile – Algeria". United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. 2013. Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- ^ a b "World Refugee Survey 2009: Algeria". U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants. 2009. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- ^ "Western Sahara: Lack of Donor Funds Threatens Humanitarian Projects". IRIN. 5 September 2007. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- ^ "Chinese Migrants in Algiers Clash". BBC News. 4 August 2009. Archived from the original on 6 December 2012. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "Fiches thématiques – Population immigrée – Immigrés 2012". Insee. Archived from the original on 20 February 2013. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ^ "Diversité et interculturalité en Algérie" (PDF). UNESCO. 2009. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 July 2013.
- ^ Ruedy, John Douglas (2005). Modern Algeria – The Origins and Development of a Nation. Indiana University Press. p. 22. ISBN 9780253217820. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ De Epalza, Mikel (2011). El español hablado en Túnez por los moriscos (siglos XVII-XVIII). Universitat de València. pp. 32–38–39–444. ISBN 978-84-370-8415-2. Archived from the original on 20 October 2017.
- ^ Stokes, Jamie (2009). Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East: L to Z. Infobase Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-4381-2676-0. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015.
- ^ The Report: Algeria 2011. Oxford Business Group. 2011. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-907065-37-8.
- ^ Marion Mill Preminger (1961). The sands of Tamanrasset: the story of Charles de Foucauld. Hawthorn Books. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015.
- ^ Cook, Bernard A. (2001). Europe since 1945: an encyclopedia. New York: Garland. p. 398. ISBN 978-0-8153-4057-7.
- ^ De Azevedo; Raimond Cagiano (1994). Migration and Development Co-Operation. Council of Europe. p. 25. ISBN 9789287126115. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ "Constitution of Algeria" – via Wikisource.
- ^ "L'Algérie crée une académie de la langue amazigh". Magharebia.com. 2 June 2006. Archived from the original on 16 February 2011.
- ^ "La mondialisation, une chance pour la francophonie". Senat.fr. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 17 January 2013. () "L'Algérie, non-membre de l'Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, comptabilise la seconde communauté francophone au monde, avec environ 16 millions de locuteurs, suivie par la Côte d'Ivoire avec près de 12 millions de locuteurs francophones, le Québec avec 6 millions et la Belgique avec plus de 4 millions de francophones."
- ^ "Le dénombrement des francophones" (PDF). Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2013. () p. 9 "Nous y agrégeons néanmoins quelques données disponibles pour des pays n'appartenant pas à l'OIF mais dont nous savons, comme pour l'Algérie (11,2 millions en 20081)," and "1. Nombre de personnes âgées de cinq ans et plus déclarant savoir lire et écrire le français, d'après les données du recensement de 2008 communiquées par l'Office national des statistiques d'Algérie."
- ^ Dargin, Justin (19 November 2008). "Algeria's Liberation, Terrorism, and Arabization". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 10 May 2013.
- ^ Leclerc, Jacques (5 April 2009). "Algérie: Situation géographique et démolinguistique". L'aménagement linguistique dans le monde (in French). Université Laval. Archived from the original on 24 January 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^ "Religion in Algeria". Global Religious Futures. Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 2010. Archived from the original on 16 December 2013.
- ^ a b "Algeria". United States Department of State. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ "The Arab world in seven charts: Are Arabs turning their backs on religion?". Arab Barometer, BBC News. 23 June 2019. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- ^ "Young Arabs are Changing their Beliefs and Perceptions: New Survey". Fanack. 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- ^ "Library of Congress Country Studies – Algeria" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 March 2009. Retrieved 20 September 2009.
- ^ Kemp, Thomas Jay (2009). International Vital Records Handbook. Genealogical Publishing Com. p. 347. ISBN 978-0-8063-1793-9. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ "Le taux d'analphabétisme en Algérie réduit à 7,94% en 2021". Algérie presse service (in French). 8 September 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ^ "Ecoles privées, Tamazight, enseignement du Français, syndicats ... – Les vérités de Benbouzid". Presse-dz.com. Archived from the original on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ^ "Le taux d'analphabétisme en Algérie est de 21,3%". Algerie-dz.com. Archived from the original on 21 October 2012. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ^ "Taux d'Analphabétisme et taux d'Alphabétisation de la population âgée de 10 ans et plus selon le sexe et la wilaya de résidence" (PDF). Office National des Statistiques. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- ^ "Algeria | Ranking Web of Universities". Webometrics.info. Archived from the original on 8 February 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2021". World Intellectual Property Organization. United Nations. Retrieved 5 March 2022.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2019". wipo.int. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "RTD – Item". European Commission. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index". INSEAD Knowledge. 28 October 2013. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Tahar Djaout". French Publishers' Agency. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "Short guide to contemporary Algerian cinema". Mapping Contemporary Cinema. Archived from the original on 11 March 2014. Retrieved 1 January 2013.
- ^ a b "Mohammed Khadda". Khadda.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2013. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ^ Honorary and Goodwill Ambassadors (20 January 2017). "Algerian novelist Ahlem Mosteghanemi designated UNESCO artist for peace". United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017.
- ^ Saadallah, Rabah (1981). El-Hadj Mh́amed el-Anka : maître et rénovateur de la musique chaabi. Maison des livres. OCLC 581750786.
- ^ Ali, Sahar (25 March 2014) ALGÉRIE Archived 3 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine. European Audiovisual Observatory
- ^ "Luce Ben Aben, Moorish Women Preparing Couscous, Algiers, Algeria". World Digital Library. 1899. Archived from the original on 28 September 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- ^ "Sports and recreation". Archived from the original on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ^ "Algeria". BBC Sport. Archived from the original on 9 March 2013. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
- ^ "Algeria national football team". Sky Sports. Archived from the original on 2 November 2012. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
General bibliography
- Ageron, Charles-Robert (1991). Modern Algeria – A History from 1830 to the Present. Translated from French and edited by Michael Brett. London: Hurst. ISBN 978-0-86543-266-6.
- Aghrout, Ahmed; Bougherira, Redha M. (2004). Algeria in Transition – Reforms and Development Prospects. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-34848-5.
- Bennoune, Mahfoud (1988). The Making of Contemporary Algeria – Colonial Upheavals and Post-Independence Development, 1830–1987. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-30150-3.
- Fanon, Frantz (1966; 2005 paperback). The Wretched of the Earth. Grove Press. ASIN B0007FW4AW, ISBN 978-0-8021-4132-3.
- Horne, Alistair (1977). A Savage War of Peace: Algeria 1954–1962. Viking Adult. ISBN 978-0-670-61964-1, ISBN 978-1-59017-218-6 (2006 reprint)
- Laouisset, Djamel (2009). A Retrospective Study of the Algerian Iron and Steel Industry. New York City: Nova Publishers. ISBN 978-1-61761-190-2.
- Roberts, Hugh (2003). The Battlefield – Algeria, 1988–2002. Studies in a Broken Polity. London: Verso Books. ISBN 978-1-85984-684-1.
- Ruedy, John (1992). Modern Algeria – The Origins and Development of a Nation. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-34998-9.
- Stora, Benjamin (2001). Algeria, 1830–2000 – A Short History. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-3715-1.
- Sidaoui, Riadh (2009). "Islamic Politics and the Military – Algeria 1962–2008". Religion and Politics – Islam and Muslim Civilisation. Farnham: Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 0-7546-7418-5.
External links
- People's Democratic Republic of Algeria Official government website (in Arabic and French)
- Portal of the First Ministry Portal of the First Ministry (in Arabic and French)
- Algeria. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Algeria web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Template:Curlie
- Algeria profile from the BBC News
- Algeria Atlas Map (PDF) (Map). United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). April 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 December 2016. Retrieved 9 December 2016.
 Wikimedia Atlas of Algeria
Wikimedia Atlas of Algeria- Key Development Forecasts for Algeria from International Futures
- EU Neighbourhood Info Centre: Algeria
- Algeria
- North African countries
- Maghrebi countries
- Saharan countries
- Arab republics
- Republics
- Arabic-speaking countries and territories
- Berber-speaking countries and territories
- French-speaking countries and territories
- G15 nations
- Member states of OPEC
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Arab League
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
- Member states of the United Nations
- States and territories established in 1962
- 1962 establishments in Algeria
- 1962 establishments in Africa
- Countries in Africa





