Mesoraphidiidae: Difference between revisions
Hemiauchenia (talk | contribs) Somewhat updated taxonomy |
Hemiauchenia (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Extinct family of insects}} |
{{Short description|Extinct family of insects}} |
||
{{Automatic taxobox |
{{Automatic taxobox |
||
| fossil_range= {{ |
| fossil_range = {{fossilrange|Middle Jurassic|Turonian}} |
||
| image = ZooKeys-204-001-g007 Amarantoraphidia 01.jpg |
| image = ZooKeys-204-001-g007 Amarantoraphidia 01.jpg |
||
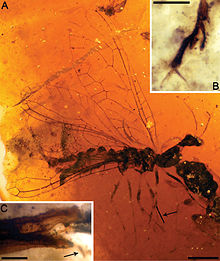
| image_caption = ''[[Amarantoraphidia ventolina]]'' holotype |
| image_caption = ''[[Amarantoraphidia ventolina]]'' holotype |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| subdivision_ranks = Subfamilies and Genera |
| subdivision_ranks = Subfamilies and Genera |
||
| subdivision = See text |
| subdivision = See text |
||
| synonyms = |
| synonyms = *Alloraphidiidae |
||
*Alloraphidiidae |
|||
*Huaxiaraphidiidae |
*Huaxiaraphidiidae |
||
*Jilinoraphidiidae |
*Jilinoraphidiidae |
||
Revision as of 19:48, 26 September 2022
| Mesoraphidiidae Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
| Amarantoraphidia ventolina holotype | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Raphidioptera |
| Suborder: | Raphidiomorpha |
| Family: | †Mesoraphidiidae Martynov, 1925 |
| Subfamilies and Genera | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Mesoraphidiidae is an extinct family of snakeflies in the suborder Raphidiomorpha.[1][2] The family lived from the Late Jurassic through the Late Cretaceous and is known from twenty-five genera. Mesoraphidiids have been found as both compression fossils and as inclusions in amber. The family was first proposed in 1925 by the Russian paleoentomologist Andrey Vasilyevich Martynov based on Upper Jurassic fossils recovered in Kazakhstan.[2] The family was expanded in 2002 by the synonymizing of several other proposed snakefly families. The family was divided into three subfamilies and one tribe in a 2011 paper, further clarifying the relationships of the included genera.
Morphology and habitat
Mesoraphidiidae are similar in overall appearance to modern snakefly species, having an elongated prothorax, giving a snake-like profile and from which the common name snakefly is derived.[1] The family was likely tree-dwelling by nature, with larvae being active predators in trunks and branches. Female mesoraphidiids, where known and complete enough, have a long and densely annultated ovipositor which would have been used to lay eggs in crevices of bark. The family was restricted to the Northern Hemisphere, living in the warm temperate and paratropical forest belt that covered portions of Eurasia and North America.[1]
History and classification
As currently described, Mesoraphidiidae contains twenty-five genera, though several of the included genera were previously placed into separate families.[3][4] As noted by Günter Bechly and Karin Wolf-Schwenninger in 2011, the defining characteristic shared by all members of the family is the placement of the forewings m1, m2 and m3 cells in a triangular pattern.[3]
The genera Alloraphidia, Archeraphidia, and Pararaphidia were formerly placed into the family Alloraphidiidae. When reviewing the snakefly fossil record in 2002, paleoentomologist Michael S. Engel noted the lack of convincing distinctions between the two families, but tentatively retained the separation.[4] In the same paper Engel moved the genera Huaxiaraphidia, Jilinoraphidia, and Sinoraphidia into Mesoraphidiidae and placed the monotypic families Huaxiaraphidiidae, Jilinoraphidiidae and Sinoraphidiidae as synonyms of Mesoraphidiidae. Engel did not give an explanation for the synonymizing of Huaxiaraphidiidae other than noting that the genus Huaxiaraphidia might be a synonym of Mesoraphidia and the type specimens should be reexamined.[4] Similarly Engel did not give a specific explanation for the synonymy of Sinoraphidiidae beyond noting the poor type description of Sinoraphidia and a need to reexamine the type specimens. The creation of Jilinoraphidiidae was based on the apparent lack of crossveins in the forewings of the type specimen. However, Engel notes the lack of crossveins is due to the incomplete nature of the specimen, as there are several major longitudinal veins that show missing sections due to lack of preservation. The overall morphology and features of Jilinoraphidia are consistent with the other mesoraphidiids.[4]
Alloraphidiidae was reranked by Bechly and Wolf-Schwenninger as subfamily Alloraphidiinae within Mesoraphidiidae based on the based on the shared characters of the two groups. The subfamily can be distinguished from other mesoraphidiids by presence of a short stigma with a single cross-vein and the forewing possessing triple branching of the CuA, R and M veins. The genus Caloraphidia was described by Ren in 1997 but was later suggested to be a synonym of Mesoraphidia.[3] When first described the genera Ororaphidia and Styporaphidia were not placed into a specific family when first described in 2008. They stayed unplaced until the 2011 paper by Bechly and Wolf-Schwenninger who grouped them, along with the reinstated Caloraphidia, into Mesoraphidiidae as the subfamily Ororaphidiinae. Ororaphidiinae was delineated as the genera that have a long pterostigma with a notably diffuse margin at its base.[3] The remaining genera of the family were placed into a third subfamily, Mesoraphidiinae, all with the shared character of a Sc vein which ends about midway towards the wingtip and a pterostigma that does not have any crossveins. Within the Mesoraphidiinae, four of the genera were grouped into the tribe Nanoraphidiini. Cantabroraphidia, Grimaldiraphidia, Lebanoraphidia and the type genus Nanoraphidia share a group of distinct traits such as their overall minute size, the postorbital region of the head is shortened and the Rs vein in the wing with one or no forks.[3]
The genera described by Pérez-de la Fuente et al in 2012 were not placed into any of the subfamilies or tribes erected by Bechly and Wolf-Schwenninger. This was due to Pérez-de la Fuente et al not feeling there is enough of evidence for the monophyletic nature of the groupings.[2]
Taxonomy





Mesoraphidiidae as grouped according to Engel 2002 with updates according to Bechly and Wolf-Schwenninger, 2011, Ricardo Pérez-de la Fuente et al (2012):[2][3][4] and Lyu et al. 2020[5]
- Family Mesoraphidiidae
- Subfamily Alloraphidiinae
- Genus Alloraphidia Carpenter, 1967 Shinekhudag Formation, Dzun-Bain Formation, Mongolia, Zaza Formation, Russia Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Redmond Formation, Canada, Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian) Kzyl-Zhar, Kazakhstan, Late Cretaceous (Turonian)
- Genus Archeraphidia Ponomarenko, 1988 Dzun-Bain Formation, Mongolia, Zaza Formation, Russia Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Pararaphidia Willmann, 1994 Dzun-Bain Formation, Mongolia, Zaza Formation, Russia Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Yixianoraphidia Lyu et al. 2020 Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Subfamily Mesoraphidiinae
- Genus Baisoraphidia Ponomarenko, 1993 Zaza Formation, Russia Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Cretinocellia Ponomarenko, 1988 Dzun-Bain Formation, Mongolia, Zaza Formation, Russia Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Huaxiaraphidia Hong, 1992 Laiyang Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Jilinoraphidia Hong & Chang, 1989 Dalazi Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Kezuoraphidia Willmann, 1994 Shahai Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Mesoraphidia Martynov, 1925 Daohugou, China, Middle/Late Jurassic Ulaan-Ereg Formation, Mongolia, Late Jurassic (Tithonian), Purbeck Group, United Kingdom, Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) Weald Clay, United Kingdom, Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian/Barremian) Lushangfen Formation, Yixian Formation, China Zaza Formation, Russia, Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Jinju Formation, South Korea, Early Cretaceous (Albian)
- Genus Phiradia Willmann 1994 Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Middle/Late Jurassic
- Genus Proraphidia Martynova, 1947 Karabastau Formation, Kazakhstan, Middle/Late Jurassic, Weald Clay, United Kingdom, Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian) La Pedrera de Rúbies Formation, Spain, Early Cretaceous (Barremian), Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Siboptera Ponomarenko, 1993 Yixian Formation, China Zaza Formation, Russia, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Sinoraphidia Hong, 1982 Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Xuraphidia Hong, 1992 Shahai Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Yanoraphidia Ren, 1995 Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Grammoraphidia Lyu, Ren & Liu, 2020 Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Beipiaoraphidia Lyu, Ren & Liu, 2020, Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Tribe Nanoraphidiini
- Genus Burmoraphidia Liu, Lu & Zhang, 2016 Burmese amber, Myanmar, Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian)[6]
- Genus Cantabroraphidia Pérez-de la Fuente, Nel, Peñalver & Delclòs, 2010 Spanish amber, Early Cretaceous (Albian)
- Genus Dolichoraphidia Liu, Lu & Zhang, 2016 Burmese amber[6]
- Genus Grimaldiraphidia Bechly & Wolf-Schwenninger, 2011 New Jersey amber, United States, Late Cretaceous (Turonian)
- Genus Nanoraphidia Engel, 2002 Burmese amber
- Genus Lebanoraphidia Bechly & Wolf-Schwenninger, 2011 Lebanese amber, Early Cretaceous (Barremian)
- Genus Rhynchoraphidia Liu, Lu & Zhang, 2016 Burmese amber[6]
- Subfamily Ororaphidiinae
- Genus Caloraphidia Ren, 1997 Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian)
- Genus Ororaphidia Engel & Ren 2008 Daohugou, China, Middle/Late Jurassic
- Genus Styporaphidia Engel & Ren 2008 Daohugou, China, Middle/Late Jurassic, Yixian Formation, China, Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Spanish amber, Early Cretaceous (Albian)
- Subfamily "incertae sedis"
- Genus Alavaraphidia Pérez-de la Fuente, Peñalver, Delclòs & Engel, 2012 Spanish amber, Early Cretaceous (Albian)
- Genus Amarantoraphidia Pérez-de la Fuente, Peñalver, Delclòs & Engel, 2012 Spanish amber, Early Cretaceous (Albian)
- Genus Iberoraphidia Jepson, Ansorge & Jarzembowski, 2011 La Pedrera de Rúbies Formation, Spain, Early Cretaceous (Barremian)
- Genus Necroraphidia Pérez-de la Fuente, Peñalver, Delclòs & Engel, 2012 Spanish amber, Early Cretaceous (Albian)
- Subfamily Alloraphidiinae
References
- ^ a b c Pérez-de la Fuente, R.; Nel, A.; Peñalver, E.; Delclòs, X. (2010). "A new Early Cretaceous snakefly (Raphidioptera: Mesoraphidiidae) from El Soplao amber (Spain)" (PDF). Annales de la Société Entomologique de France. 46 (1–2): 108–115. doi:10.1080/00379271.2010.10697644. S2CID 84967744.
- ^ a b c d Pérez-de la Fuente, R.; Peñalver, E.; Delclòs, X.; Engel, M.S. (2012). "Snakefly diversity in Early Cretaceous amber from Spain (Neuropterida, Raphidioptera)". ZooKeys (204): 1–40. doi:10.3897/zookeys.204.2740. PMC 3391719. PMID 22787417.
- ^ a b c d e f Bechly, G.; Wolf-Schwenninger, K. (2011). "A new fossil genus and species of snakefly (Raphidioptera: Mesoraphidiidae) from Lower Cretaceous Lebanese amber, with a discussion of snakefly phylogeny and fossil history" (PDF). Insect Systematics and Evolution. 42 (2): 221–236. doi:10.1163/187631211X568164. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-05.
- ^ a b c d e Engel, M.S. (2002). "The Smallest Snakefly (Raphidioptera: Mesoraphidiidae): A New Species in Cretaceous Amber from Myanmar, with a Catalog of Fossil Snakeflies". American Museum Novitates (3363): 1–22. doi:10.1206/0003-0082(2002)363<0001:TSSRMA>2.0.CO;2. hdl:2246/2852.
- ^ Lyu, Ya-nan; Shen, Rongrong; Wang, Yongjie; Ren, Dong; Liu, Xingyue (2020-11-01). "The snakefly family Mesoraphidiidae (Insecta: Raphidioptera) from the Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation, China: systematic revision and phylogenetic implications". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 18 (21): 1743–1768. doi:10.1080/14772019.2020.1807629. ISSN 1477-2019.
- ^ a b c Liu, X.; Lu, X; Zhang, W (2016). "New genera and species of the minute snakeflies (Raphidioptera: Mesoraphidiidae: Nanoraphidiini) from the mid Cretaceous of Myanmar". Zootaxa. 4103 (4): 301–324. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4103.4.1. PMID 27394738.
