Falciform ligament: Difference between revisions
SimLibrarian (talk | contribs) m periods only for complete-sentence image captions (MOS:CAPFRAG), dash style fix |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
In [[human anatomy]], the '''falciform ligament''' ({{ety|la||[[Falx|sickle]]-shaped}}) is a [[ligament]] that attaches the [[liver]] to the front body wall, and |
In [[human anatomy]], the '''falciform ligament''' ({{ety|la||[[Falx|sickle]]-shaped}}) is a [[ligament]] that attaches the [[liver]] to the front body wall, and divides the left [[Lobes of liver|lobe]] of the liver into the left medial lobe and left lateral lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of [[peritoneum]], its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the [[hilum (anatomy)|hilum]] of the liver. |
||
==Structure== |
==Structure== |
||
Revision as of 19:51, 26 September 2022
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (June 2015) |
| Falciform ligament | |
|---|---|
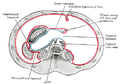
 The falciform ligament is seen here, dividing the liver from the front into a left and a right lobe. | |
 The liver viewed from above. Falciform ligament can be seen separating the left medial from the right lateral lobes of liver. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum falciforme hepatis |
| TA98 | A10.1.02.303 |
| TA2 | 3771 |
| FMA | 15823 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the falciform ligament (from Latin 'sickle-shaped') is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall, and divides the left lobe of the liver into the left medial lobe and left lateral lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the hilum of the liver.
Structure
The falciform ligament stretches obliquely from the front to the back of the abdomen, with one surface in contact with the peritoneum behind the right rectus abdominis muscle and the diaphragm, and the other in contact with the left lobe of the liver.
The ligament stretches from the underside of the diaphragm to the posterior surface of the sheath of the right rectus abdominis muscle, as low down as the umbilicus; by its right margin it extends from the notch on the anterior margin of the liver, as far back as the posterior surface.
It is composed of two layers of peritoneum closely united together.
Its base or free edge contains, between its layers, the round ligament and the paraumbilical veins.
Development
It is a remnant of the embryonic ventral mesentery. The umbilical vein of the fetus gives rise to the round ligament of liver in the adult, which is found in the free border of the falciform ligament.
Clinical significance
The falciform ligament can become canalised if an individual is suffering from portal hypertension. Due to the increase in venous congestion, blood is pushed down from the liver towards the anterior abdominal wall and if blood pools here, will result in dilatation of veins around the umbilicus. If these veins radiate out from the umbilicus, they can give the appearance of a head (the umbilicus) with hair of snakes (the veins) – this is referred to as caput medusae.[1]
Additional images
-
Cross-section showing the primitive mesentery of a six weeks’ human embryo
-
Cross-section showing folds of peritoneum in the upper abdomen
-
A cadaver liver seen from above, showing the falciform ligament at the top
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1192 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1192 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Misdraji J, Embryology, anatomy, histology, and developmental anomalies of the liver. In, Sleisinger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 10th edition, Feldman M, Friedman LS and Branbdt LJ, eds. pp. 1217-122.
External links
- Anatomy photo:37:04-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Abdominal Cavity: The Falciform Ligament of the Liver"
- Anatomy photo:38:12-0205 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Visceral Surface of the Liver"
- Anatomy image:8373 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- liver at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Cross section image: pembody/body8a—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna