Abstract factory pattern: Difference between revisions
Grammar, diction, orthography |
Rkieferbaum (talk | contribs) m v2.05 - Fix errors for CW project (Link equal to linktext) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Overview== |
==Overview== |
||
The abstract factory design pattern is one of the 23 well-known patterns described in the 1994 [[Design Patterns |
The abstract factory design pattern is one of the 23 well-known patterns described in the 1994 ''[[Design Patterns]]'' book. It may be used to solves problems such as:<ref>{{cite web|title=The Abstract Factory design pattern - Problem, Solution, and Applicability|url=http://w3sdesign.com/?gr=c01&ugr=proble|website=w3sDesign.com|access-date=2017-08-11}}</ref> |
||
* How can an application be independent of how its objects are created? |
* How can an application be independent of how its objects are created? |
||
* How can a class be independent of how the objects that it requires are created? |
* How can a class be independent of how the objects that it requires are created? |
||
Revision as of 20:07, 31 January 2023

The abstract factory software pattern provides a way to encapsulate a group of individual factories that have a common theme without specifying their concrete classes.[1] In normal usage, the client software creates a concrete implementation of the abstract factory and then uses the generic interface of the factory to create the concrete objects that are part of the theme. The client does not know which concrete objects it receives from each of these internal factories, as it uses only the generic interfaces of their products.[1] This pattern separates the details of implementation of a set of objects from their general usage and relies on object composition, as object creation is implemented in methods exposed in the factory interface.[2]
An example is an abstract factory class DocumentCreator that provides interfaces to create a number of products (e.g., createLetter() and createResume()). The system would have any number of derived concrete versions of the DocumentCreator class such asFancyDocumentCreator or ModernDocumentCreator, each with a different implementation of createLetter() and createResume() that would create corresponding objects such asFancyLetter or ModernResume. Each of these products is derived from a simple abstract class such asLetter or Resume of which the client is aware. The client code would acquire an appropriate instance of the DocumentCreator and call its factory methods. Each of the resulting objects would be created from the same DocumentCreator implementation and would share a common theme. The client would only need to know how to handle the abstract Letter or Resume class, not the specific version that was created by the concrete factory.
A factory is the location of a concrete class in the code at which objects are constructed. Implementation of the pattern intends to insulate the creation of objects from their usage and to create families of related objects without having to depend on their concrete classes.[2] This allows for new derived types to be introduced with no change to the code that uses the base class.
Use of this pattern enables interchangeable concrete implementations without changing the code that uses them, even at runtime. However, employment of this pattern, as with similar design patterns, may result in unnecessary complexity and extra work in the initial writing of code. Additionally, higher levels of separation and abstraction can result in systems that are more difficult to debug and maintain.
Overview
The abstract factory design pattern is one of the 23 well-known patterns described in the 1994 Design Patterns book. It may be used to solves problems such as:[3]
- How can an application be independent of how its objects are created?
- How can a class be independent of how the objects that it requires are created?
- How can families of related or dependent objects be created?
Creating objects directly within the class that requires the objects is inflexible because doing so commits the class to particular objects and makes it impossible to change the instantiation later independently from the class without having to change it. It prevents the class from being reusable if other objects are required, and it makes the class difficult to test because real objects cannot be replaced with mock objects.
The pattern describes how to solve such problems:
- Encapsulate object creation in a separate (factory) object by defining and implementing an interface for creating objects.
- Delegate object creation to a factory object instead of creating objects directly.
This makes a class independent of how its objects are created. A class may be configured with a factory object, which it uses to create objects, and the factory object can be exchanged at runtime.
Definition
The Design Patterns book describes the abstract factory pattern as "an interface for creating families of related or dependent objects without specifying their concrete classes."[4]
Usage
The factory determines the actual concrete type of object to be created, and it is here that the object is actually created (in Java, for instance, by the new operator). However, the factory only returns an abstract pointer to the created concrete object.
This insulates client code from object creation by having clients request that a factory object create an object of the desired abstract type and return an abstract pointer to the object.[5]
As the factory only returns an abstract pointer, the client code that requested the object from the factory is not aware of—and is not burdened by—the actual concrete type of the object that was created. However, the type of a concrete object (and hence a concrete factory) is known by the abstract factory; for instance, the factory may read it from a configuration file. The client has no need to specify the type, as the type has already been specified in the configuration file. In particular, this means:
- The client code has no knowledge whatsoever of the concrete type, not needing to include any header files or class declarations related to it. The client code deals only with the abstract type. Objects of a concrete type are indeed created by the factory, but the client code accesses such objects only through their abstract interfaces.[6]
- Adding new concrete types is performed by modifying the client code to use a different factory, a modification that is typically one line in one file. The different factory then creates objects of a different concrete type but still returns a pointer of the same abstract type as before, thus insulating the client code from change. This is significantly easier than is modifying the client code to instantiate a new type, which would require changing every location in the code where a new object is created as well as ensuring that all such code locations have knowledge of the new concrete type, for example, by including a concrete class header file. If all factory objects are stored globally in a singleton object, and all client code passes through the singleton to access the proper factory for object creation, then changing factories is as easy as changing the singleton object.[6]
Structure
UML diagram
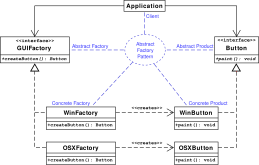
createButton on the GUIFactory interface returns objects of type Button. The exact implementation of Button that is returned depends on which implementation of GUIFactory is handling the method call. ![A sample UML class and sequence diagram for the abstract factory design pattern. [7]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/a/aa/W3sDesign_Abstract_Factory_Design_Pattern_UML.jpg)
In the above UML class diagram,
the Client class that requires ProductA and ProductB objects does not instantiate the ProductA1 and ProductB1 classes directly. Instead, the Client refers to the AbstractFactory interface for creating objects, which makes the Client independent of how the objects are created (which concrete classes are instantiated). The Factory1 class implements the AbstractFactory interface by instantiating the ProductA1 and ProductB1 classes.
The UML sequence diagram shows the runtime interactions. The Client object calls createProductA() on the Factory1 object, which creates and returns a ProductA1 object. Thereafter, the Client calls createProductB() on Factory1, which creates and returns a ProductB1 object.
LePUS3 chart
Python example
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from sys import platform
class Button(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def paint(self):
pass
class LinuxButton(Button):
def paint(self):
return "Render a button in a Linux style"
class WindowsButton(Button):
def paint(self):
return "Render a button in a Windows style"
class MacOSButton(Button):
def paint(self):
return "Render a button in a MacOS style"
class GUIFactory(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def create_button(self):
pass
class LinuxFactory(GUIFactory):
def create_button(self):
return LinuxButton()
class WindowsFactory(GUIFactory):
def create_button(self):
return WindowsButton()
class MacOSFactory(GUIFactory):
def create_button(self):
return MacOSButton()
if platform == "linux":
factory = LinuxFactory()
elif platform == "darwin":
factory = MacOSFactory()
elif platform == "win32":
factory = WindowsFactory()
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Not implemented for your platform: {platform}")
button = factory.create_button()
result = button.paint()
print(result)
Alternative implementation using the classes themselves as factories:
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from sys import platform
class Button(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def paint(self):
pass
class LinuxButton(Button):
def paint(self):
return "Render a button in a Linux style"
class WindowsButton(Button):
def paint(self):
return "Render a button in a Windows style"
class MacOSButton(Button):
def paint(self):
return "Render a button in a MacOS style"
if platform == "linux":
factory = LinuxButton
elif platform == "darwin":
factory = MacOSButton
elif platform == "win32":
factory = WindowsButton
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Not implemented for your platform: {platform}")
button = factory()
result = button.paint()
print(result)
See also
References
- ^ a b Freeman, Eric; Robson, Elisabeth; Sierra, Kathy; Bates, Bert (2004). Hendrickson, Mike; Loukides, Mike (eds.). Head First Design Patterns (paperback). Vol. 1. O'REILLY. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-596-00712-6. Retrieved 2012-09-12.
- ^ a b Freeman, Eric; Robson, Elisabeth; Sierra, Kathy; Bates, Bert (2004). Hendrickson, Mike; Loukides, Mike (eds.). Head First Design Patterns (paperback). Vol. 1. O'REILLY. p. 162. ISBN 978-0-596-00712-6. Retrieved 2012-09-12.
- ^ "The Abstract Factory design pattern - Problem, Solution, and Applicability". w3sDesign.com. Retrieved 2017-08-11.
- ^ Gamma, Erich; Richard Helm; Ralph Johnson; John M. Vlissides (2009-10-23). "Design Patterns: Abstract Factory". informIT. Archived from the original on 2009-10-23. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
Object Creational: Abstract Factory: Intent: Provide an interface for creating families of related or dependent objects without specifying their concrete classes.
- ^ Veeneman, David (2009-10-23). "Object Design for the Perplexed". The Code Project. Archived from the original on 2011-09-18. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
The factory insulates the client from changes to the product or how it is created, and it can provide this insulation across objects derived from very different abstract interfaces.
- ^ a b "Abstract Factory: Implementation". OODesign.com. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "The Abstract Factory design pattern - Structure and Collaboration". w3sDesign.com. Retrieved 2017-08-12.
External links
- Abstract Factory implementation in Java
 Media related to Abstract factory at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Abstract factory at Wikimedia Commons- Abstract Factory UML diagram + formal specification in LePUS3 and Class-Z (a Design Description Language)
- Abstract Factory Abstract Factory implementation example

