Tarsal tunnel: Difference between revisions
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.8.8) (Ost316 - 10417 |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: encyclopedia, authors 1-1. Removed parameters. Some additions/deletions were parameter name changes. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Corvus florensis | #UCB_webform 718/3499 |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Structure== |
==Structure== |
||
The roof of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the [[Flexor retinaculum of foot|flexor retinaculum of the foot]].<ref name=":1">{{Citation| |
The roof of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the [[Flexor retinaculum of foot|flexor retinaculum of the foot]].<ref name=":1">{{Citation|last1=Lowe|first1=Whitney|title=Chapter 6 - Foot, ankle, and lower leg|date=2009-01-01|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780443068126000064|work=Orthopedic Massage (Second Edition)|pages=77–115|editor-last=Lowe|editor-first=Whitney|place=Edinburgh|publisher=Mosby|language=en|doi=10.1016/b978-0-443-06812-6.00006-4|isbn=978-0-443-06812-6|access-date=2021-03-02|last2=Chaitow|first2=Leon|editor2-last=Chaitow|editor2-first=Leon}}</ref> The floor of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the [[medial malleolus]] and the [[calcaneus]].<ref name=":1" /> |
||
===Contents=== |
===Contents=== |
||
The [[tibial nerve]], [[posterior tibial artery]], [[posterior tibial vein]], and flexor tendons travel in a bundle along this pathway through the tarsal tunnel, in the following order from anteromedial to posterolateral: |
The [[tibial nerve]], [[posterior tibial artery]], [[posterior tibial vein]], and flexor tendons travel in a bundle along this pathway through the tarsal tunnel, in the following order from anteromedial to posterolateral: |
||
* [[Tibialis posterior muscle|Tibialis posterior tendon]].<ref name=":0">{{Citation| |
* [[Tibialis posterior muscle|Tibialis posterior tendon]].<ref name=":0">{{Citation|last1=Minieka|first1=Michael|title=Chapter 54 - Entrapment Neuropathies|date=2005-01-01|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780443066511500587|work=Essentials of Pain Medicine and Regional Anesthesia (Second Edition)|pages=426–432|editor-last=Benzon|editor-first=Honorio T.|place=Philadelphia|publisher=Churchill Livingstone|language=en|doi=10.1016/b978-0-443-06651-1.50058-7|isbn=978-0-443-06651-1|access-date=2021-02-21|last2=Nishida|first2=Takashi|editor2-last=Raja|editor2-first=Srinivasa N.|editor3-last=Molloy|editor3-first=Robert E.|editor4-last=Liu|editor4-first=Spencer S.}}</ref> |
||
* [[Flexor digitorum longus muscle|Flexor digitorum longus tendon]].<ref name=":0" /> |
* [[Flexor digitorum longus muscle|Flexor digitorum longus tendon]].<ref name=":0" /> |
||
* [[Posterior tibial artery]].<ref name=":0" /> |
* [[Posterior tibial artery]].<ref name=":0" /> |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* [[Flexor hallucis longus muscle|Flexor hallucis longus tendon]].<ref name=":0" /> |
* [[Flexor hallucis longus muscle|Flexor hallucis longus tendon]].<ref name=":0" /> |
||
In the tunnel, the tibial nerve splits into three different paths.<ref name=":2">{{Citation|last=Kaufmann|first=Petra|title=Tibial Nerve|date=2003-01-01|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122268709020542| |
In the tunnel, the tibial nerve splits into three different paths.<ref name=":2">{{Citation|last=Kaufmann|first=Petra|title=Tibial Nerve|date=2003-01-01|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122268709020542|encyclopedia=Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences|pages=537–539|editor-last=Aminoff|editor-first=Michael J.|place=New York|publisher=Academic Press|language=en|doi=10.1016/b0-12-226870-9/02054-2|isbn=978-0-12-226870-0|access-date=2021-03-02|editor2-last=Daroff|editor2-first=Robert B.}}</ref> The [[medial calcaneal branches of the tibial nerve]] continues to the heel, while the [[medial plantar nerve]] and the [[lateral plantar nerve]] continue on to the bottom of the [[foot]].<ref name=":2" /> |
||
==Clinical significance== |
==Clinical significance== |
||
Revision as of 07:31, 20 February 2023
| Tarsal tunnel | |
|---|---|
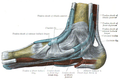
 Medial view of the ankle. The structures within the tarsal tunnel are depicted. | |
Dissection video (1 min 55 s) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Canalis tarsi |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The tarsal tunnel is a passage found along the inner leg underneath the medial malleolus of the ankle.
Structure
The roof of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the flexor retinaculum of the foot.[1] The floor of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the medial malleolus and the calcaneus.[1]
Contents
The tibial nerve, posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial vein, and flexor tendons travel in a bundle along this pathway through the tarsal tunnel, in the following order from anteromedial to posterolateral:
- Tibialis posterior tendon.[2]
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon.[2]
- Posterior tibial artery.[2]
- Posterior tibial vein.[1]
- Tibial nerve.[2]
- Flexor hallucis longus tendon.[2]
In the tunnel, the tibial nerve splits into three different paths.[3] The medial calcaneal branches of the tibial nerve continues to the heel, while the medial plantar nerve and the lateral plantar nerve continue on to the bottom of the foot.[3]
Clinical significance
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is the most commonly reported nerve entrapment of the ankle. It is analogous to carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist. It is caused by compression of the tibial nerve underneath the flexor retinaculum of the foot.[1] People with tarsal tunnel syndrome have pain in the plantar aspect of the foot mostly at night. Weight bearing increases pain and weakness is found on intrinsic foot muscles with positive Tinel sign at the tunnel. There is no tenderness present on the plantar foot, though this is typically the primary site of complaint.
Additional images
-
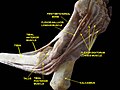
The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Medial aspect. The flexor retinaculum is labelled as laciniate lig.
-
Dissection image. Around the medial malleolus seeing from below.
-
Dissection video (41 s)
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Lowe, Whitney; Chaitow, Leon (2009-01-01), Lowe, Whitney; Chaitow, Leon (eds.), "Chapter 6 - Foot, ankle, and lower leg", Orthopedic Massage (Second Edition), Edinburgh: Mosby, pp. 77–115, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06812-6.00006-4, ISBN 978-0-443-06812-6, retrieved 2021-03-02
- ^ a b c d e Minieka, Michael; Nishida, Takashi (2005-01-01), Benzon, Honorio T.; Raja, Srinivasa N.; Molloy, Robert E.; Liu, Spencer S. (eds.), "Chapter 54 - Entrapment Neuropathies", Essentials of Pain Medicine and Regional Anesthesia (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 426–432, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06651-1.50058-7, ISBN 978-0-443-06651-1, retrieved 2021-02-21
- ^ a b Kaufmann, Petra (2003-01-01), "Tibial Nerve", in Aminoff, Michael J.; Daroff, Robert B. (eds.), Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences, New York: Academic Press, pp. 537–539, doi:10.1016/b0-12-226870-9/02054-2, ISBN 978-0-12-226870-0, retrieved 2021-03-02