Hemispheres of Earth: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
MetricMaster (talk | contribs) Article cleanup Tags: references removed Visual edit |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[File:Map of the World.jpg|thumb|300x300px|Map roughly depicting the [[Eastern hemisphere|Eastern]] and [[Western hemisphere]]s]] |
[[File:Map of the World.jpg|thumb|300x300px|Map roughly depicting the [[Eastern hemisphere|Eastern]] and [[Western hemisphere]]s]] |
||
In [[geography]] and [[cartography]], '''hemispheres of Earth''' are any division of [[Earth|the globe]] into two [[Sphere#Plane sections|hemispheres]] |
In [[geography]] and [[cartography]], '''hemispheres of Earth''' are any division of [[Earth|the globe]] into two equal halves ([[Sphere#Plane sections|hemispheres]]) usually as divided into northern and southern halves by the equator, or into western and eastern halves by an imaginary line passing through the poles. <ref>{{Cite web |title=hemisphere {{!}} Etymology, origin and meaning of hemisphere by etymonline |url=https://www.etymonline.com/word/hemisphere |access-date=2022-12-03 |website=www.etymonline.com |language=en}}</ref> |
||
== Geographical Hemispheres == |
== Geographical Hemispheres == |
||
The primary hemispherical split geographically is made by [[latitude|latitudinal]] (north/south) and [[longitude|longitudinal]] (east-west)<ref> |
The primary hemispherical split geographically is made by [[latitude|latitudinal]] (north/south) and [[longitude|longitudinal]] (east-west) markers:<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/hemisphere/ | title=Hemisphere| date=2011-03-22}}</ref><ref name="ngs">{{Cite web |title=hemisphere {{!}} National Geographic Society |url=https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/hemisphere |access-date=2022-08-27 |website=education.nationalgeographic.org}}</ref> |
||
* North–South |
|||
* North–South<ref name=ngs>{{Cite web |title=hemisphere {{!}} National Geographic Society |url=https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/hemisphere |access-date=2022-08-27 |website=education.nationalgeographic.org}}</ref> |
|||
** [[Northern Hemisphere]], the half that lies north of the [[Equator]] |
** [[Northern Hemisphere]], the half that lies north of the [[Equator]] |
||
** [[Southern Hemisphere]], the half that lies south of the Equator |
** [[Southern Hemisphere]], the half that lies south of the Equator |
||
* East–West |
* East–West |
||
** [[Eastern Hemisphere]], the half that lies east of the [[prime meridian]] and west of the [[180th meridian]] |
** [[Eastern Hemisphere]], the half that lies east of the [[prime meridian]] and west of the [[180th meridian]] |
||
** [[Western Hemisphere]], the half that lies west of the prime meridian and east of the 180th meridian |
** [[Western Hemisphere]], the half that lies west of the prime meridian and east of the 180th meridian |
||
== Alternative Hemispheres == |
== Alternative Hemispheres == |
||
| ⚫ | Alternative Earth Hemispheres can divide the earth along cultural and religious lines, or to maximise the preponderance of geographic features, for example land and water.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Boggs |first1=S. W. |year=1945 |title=This Hemisphere |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00221344508986498 |journal=Journal of Geography |volume=44 |issue=9 |pages=345–355 |doi=10.1080/00221344508986498}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Land-water hemispheres === |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{multiple image |
{{multiple image |
||
| Line 56: | Line 60: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{See also|Land and water hemispheres}} |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[Antarctica]] |
|||
** [[South Pole]] |
|||
* [[Arctic Ocean]] |
|||
** [[North Pole]] |
|||
* [[Geographical centre of Earth|Earth's geographical centre]] |
* [[Geographical centre of Earth|Earth's geographical centre]] |
||
* [[Eastern Hemisphere]] |
|||
* [[Global North and Global South]] |
* [[Global North and Global South]] |
||
* [[Land and water hemispheres]] |
* [[Land and water hemispheres]] |
||
* [[Northern Hemisphere]] |
|||
* [[Southern Hemisphere]] |
|||
* [[Western Hemisphere]] |
|||
* [[East–West dichotomy]] |
* [[East–West dichotomy]] |
||
Revision as of 06:54, 8 March 2023


In geography and cartography, hemispheres of Earth are any division of the globe into two equal halves (hemispheres) usually as divided into northern and southern halves by the equator, or into western and eastern halves by an imaginary line passing through the poles. [1]
Geographical Hemispheres
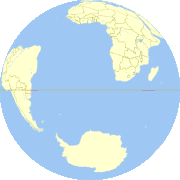
The primary hemispherical split geographically is made by latitudinal (north/south) and longitudinal (east-west) markers:[2][3]
- North–South
- Northern Hemisphere, the half that lies north of the Equator
- Southern Hemisphere, the half that lies south of the Equator
- East–West
- Eastern Hemisphere, the half that lies east of the prime meridian and west of the 180th meridian
- Western Hemisphere, the half that lies west of the prime meridian and east of the 180th meridian
Alternative Hemispheres
Alternative Earth Hemispheres can divide the earth along cultural and religious lines, or to maximise the preponderance of geographic features, for example land and water.[4]
The East–West division can also be seen in a cultural and religious sense, as a division into two cultural and religious hemispheres.
An alternative geographical hemisphere splits the earth at 20° west and 160° east so that Africa and Europe are not divided[3], and the Earth may also be split into hemispheres of day and night by the terrestrial terminator.
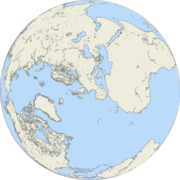
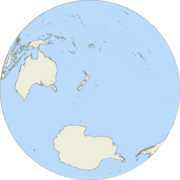
Land-water hemispheres
Alternative hemispheres schemes have sought to divide the planet in a way that maximises the preponderance of one geographic feature or another in each division, for example the land-water division:
- Land Hemisphere, the hemisphere on Earth containing the largest possible area of land
- Water Hemisphere, the hemisphere on Earth containing the largest possible area of water
See also
- Earth's geographical centre
- Global North and Global South
- Land and water hemispheres
- East–West dichotomy
References
- ^ "hemisphere | Etymology, origin and meaning of hemisphere by etymonline". www.etymonline.com. Retrieved 2022-12-03.
- ^ "Hemisphere". 2011-03-22.
- ^ a b "hemisphere | National Geographic Society". education.nationalgeographic.org. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- ^ Boggs, S. W. (1945). "This Hemisphere". Journal of Geography. 44 (9): 345–355. doi:10.1080/00221344508986498.
External links
![]() Media related to Earth's hemispheres at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Earth's hemispheres at Wikimedia Commons