Bacitracin: Difference between revisions
Rescuing 4 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.3 |
→Controversies: Added content Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
=== Controversies === |
=== Controversies === |
||
Some have claimed that bacitracin is a [[protein disulfide isomerase]] inhibitor, but this is disputed by ''in vitro'' studies.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Karala AR, Ruddock LW | title = Bacitracin is not a specific inhibitor of protein disulfide isomerase | journal = The FEBS Journal | volume = 277 | issue = 11 | pages = 2454–62 | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20477872 | doi = 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07660.x | s2cid = 37519169 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Weston BS, Wahab NA, Roberts T, Mason RM | title = Bacitracin inhibits fibronectin matrix assembly by mesangial cells in high glucose | journal = Kidney International | volume = 60 | issue = 5 | pages = 1756–64 | date = November 2001 | pmid = 11703593 | doi = 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00991.x | doi-access = free | title-link = doi }}</ref> |
Some have claimed that bacitracin is a [[protein disulfide isomerase]] inhibitor, but this is disputed by ''in vitro'' studies.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Karala AR, Ruddock LW | title = Bacitracin is not a specific inhibitor of protein disulfide isomerase | journal = The FEBS Journal | volume = 277 | issue = 11 | pages = 2454–62 | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20477872 | doi = 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07660.x | s2cid = 37519169 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Weston BS, Wahab NA, Roberts T, Mason RM | title = Bacitracin inhibits fibronectin matrix assembly by mesangial cells in high glucose | journal = Kidney International | volume = 60 | issue = 5 | pages = 1756–64 | date = November 2001 | pmid = 11703593 | doi = 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00991.x | doi-access = free | title-link = doi }}</ref> |
||
=== Big Hero 6 === |
|||
“You are not allergic to bacitracin.” |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 02:41, 22 April 2023
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Baciguent, Baciim, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical, intramuscular, Ophthalmic drug administration |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
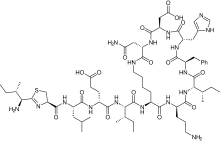
| Formula | C66H103N17O16S |
| Molar mass | 1422.71 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bacitracin[1] is a polypeptide antibiotic. It is a mixture of related cyclic peptides produced by Bacillus licheniformis bacteria, that was first isolated from the variety "Tracy I" (ATCC 10716) in 1945.[2] These peptides disrupt gram-positive bacteria by interfering with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis.
Bacitracin is primarily used as a topical preparation, as it can cause kidney damage when used internally.[3] It is generally safe when used topically, but in rare cases may cause hypersensitivity, allergic or anaphylactic reactions, especially in people allergic to neomycin.[4][5]
Medical uses

Bacitracin is used in human medicine as a polypeptide antibiotic and is "approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in chickens and turkeys," though use in animals contributes to antibiotic resistance.[6]
As bacitracin zinc salt, in combination with other topical antibiotics (usually polymyxin B and neomycin) as an ointment ("triple antibiotic ointment," with the brand name Neosporin), it is used for topical treatment of a variety of localized skin and eye infections, as well as for the prevention of wound infections. A non-ointment form of ophthalmic solution is also available for eye infections.[7]

Spectrum of activity and susceptibility data
Bacitracin is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. It targets gram-positive bacteria, especially those that cause skin infections. The following represents susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.[8]
- Staphylococcus aureus – ≤0.03 μg/mL – 700 μg/mL
- Staphylococcus epidermidis – 0.25 μg/mL – >16 μg/mL
- Streptococcus pyogenes – 0.5 μg/mL – >16 μg/mL
Mechanism of action
Bacitracin interferes with the dephosphorylation of C55-isoprenyl pyrophosphate, and a related molecule known as bactoprenol pyrophosphate; both of these lipids function as membrane carrier molecules that transport the building-blocks of the peptidoglycan bacterial cell wall outside of the inner membrane.[9]
History
Bacitracin was isolated by Balbina Johnson, a bacteriologist at the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons.[10] Its name derives from the fact that a compound produced by a microbe in young Margaret Treacy's (1936–1994)[11] leg injury showed antibacterial activity.[12]
One strain isolated from tissue debrided from a compound fracture of the tibia was particularly active. We named this growth-antagonistic strain for the patient, "Tracy I." When cell-free filtrates of broth cultures of this bacillus proved to possess strong antibiotic activity and to be non-toxic, further study seemed warranted. We have called this active principle "Bacitracin.[10]
Bacitracin was approved by the US FDA in 1948.[13]
Synthesis
This section is missing information about commercial strain improvement by mutagenesis: these strains themselves have names like UV-MN-HN-6; enzyme functions. (February 2022) |
Bacitracin is synthesised via nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), which means that ribosomes are not directly involved in its synthesis. The three-enzyme operon is called BacABC, not to be confused with BacABCDE of bacilycin synthesis.[14]
Composition
Bacitracin is composed of a mixture of related compounds with varying degrees of antibacterial activity. Notable fractions include bacitracin A, A1, B, B1, B2, C, D, E, F, G, and X.[15] Bacitracin A has been found to have the most antibacterial activity. Bacitracin B1 and B2 have similar potencies and are approximately 90% as active as bacitracin A.[16]
Society and culture
Controversies
Some have claimed that bacitracin is a protein disulfide isomerase inhibitor, but this is disputed by in vitro studies.[17][18]
Big Hero 6
“You are not allergic to bacitracin.”
References
- ^ J. Elks; C. R. Ganellin (1990). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 119–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Originally grouped under B. subtilis, but nomenclature has since changed. See Podstawka, Adam. "Bacillus licheniformis Tracy I | DSM 603, ATCC 10716, CCM 2181, IFO 12199, NBRC 12199, NCIB 8874, FDA BT1 | BacDiveID:686". bacdive.dsmz.de. Archived from the original on 2022-02-07. Retrieved 2022-02-07.
- ^ Zintel, H. A.; Ma, R. A.; Nichols, Anna C.; Ellis, Helen (1949). "The Absorption, Distribution, Excretion and Toxicity of Bacitracin in Man". American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 218 (4): 439–445. doi:10.1097/00000441-194910000-00012. PMID 18140540. S2CID 2371497.
- ^ Spann CT, Taylor SC, Weinberg JM (July 2004). "Topical antimicrobial agents in dermatology". Disease-a-Month. 50 (7): 407–21. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2004.05.011. PMID 15280871.
- ^ Trookman NS, Rizer RL, Weber T (March 2011). "Treatment of minor wounds from dermatologic procedures: a comparison of three topical wound care ointments using a laser wound model". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 64 (3 Suppl): S8-15. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.11.011. PMID 21247665.
- ^ Pearl MC (12 September 2007). "Antibiotic use on the farm hurts people—and doesn't help the bottom line". Discover Magazine. Archived from the original on 2007-09-25.
- ^ "Healthgrades > Find a Doctor > Doctor Reviews > Hospital Ratings". Archived from the original on 2011-05-23.
- ^ "Bacitracin Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data" (PDF). TOKU-E. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-12-22. Retrieved 2013-08-12.
- ^ Stone KJ, Strominger JL (December 1971). "Mechanism of action of bacitracin: complexation with metal ion and C 55 -isoprenyl pyrophosphate". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 68 (12): 3223–7. Bibcode:1971PNAS...68.3223S. doi:10.1073/pnas.68.12.3223. PMC 389626. PMID 4332017.
- ^ a b Johnson BA, Anker H, Meleney FL (October 1945). "Bacitracin: a new antibiotic produced by a member of the B. subtilis group". Science. 102 (2650): 376–7. Bibcode:1945Sci...102..376J. doi:10.1126/science.102.2650.376. PMID 17770204. S2CID 51066.
- ^ "Margaret Tracy & Balbina Johnson: The Women Behind Bacitracin". Archived from the original on 2014-04-28. Retrieved 2014-09-30.
- ^ "NewYork-Presbyterian | the Discovery of Bacitracin". 7 February 2017. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021. Retrieved 9 April 2020.
- ^ "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 2021-07-27. Retrieved 2021-09-17.
- ^ Konz, Dirk; Klens, Andrea; Schörgendorfer, Kurt; Marahiel, Mohamed A. (December 1997). "The bacitracin biosynthesis operon of Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 10716: molecular characterization of three multi-modular peptide synthetases". Chemistry & Biology. 4 (12): 927–937. doi:10.1016/s1074-5521(97)90301-x. PMID 9427658.
- ^ "Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products Bacitracin." Ema.europa.eu. The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, June 1998. Web. 18 Jan. 2013
- ^ Bell RG (January 1992). "Preparative high-performance liquid chromatographic separation and isolation of bacitracin components and their relationship to microbiological activity". Journal of Chromatography. 590 (1): 163–8. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(92)87018-4. PMID 1601975.
- ^ Karala AR, Ruddock LW (June 2010). "Bacitracin is not a specific inhibitor of protein disulfide isomerase". The FEBS Journal. 277 (11): 2454–62. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07660.x. PMID 20477872. S2CID 37519169.
- ^ Weston BS, Wahab NA, Roberts T, Mason RM (November 2001). "Bacitracin inhibits fibronectin matrix assembly by mesangial cells in high glucose". Kidney International. 60 (5): 1756–64. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00991.x. PMID 11703593.
