Chenzhou: Difference between revisions
| Line 208: | Line 208: | ||
|Nov humidity = 77 |
|Nov humidity = 77 |
||
|Dec humidity = 77 |
|Dec humidity = 77 |
||
|unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm |
|unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm |
||
|Jan precipitation days = |
|Jan precipitation days = 16.4 |
||
|Feb precipitation days = 16. |
|Feb precipitation days = 16.1 |
||
|Mar precipitation days = 19. |
|Mar precipitation days = 19.4 |
||
|Apr precipitation days = |
|Apr precipitation days = 16.5 |
||
|May precipitation days = |
|May precipitation days = 17.4 |
||
|Jun precipitation days = 15. |
|Jun precipitation days = 15.8 |
||
|Jul precipitation days = |
|Jul precipitation days = 10.3 |
||
|Aug precipitation days = 14. |
|Aug precipitation days = 14.6 |
||
|Sep precipitation days = |
|Sep precipitation days = 11.7 |
||
|Oct precipitation days = |
|Oct precipitation days = 10.7 |
||
|Nov precipitation days = 11. |
|Nov precipitation days = 11.7 |
||
|Dec precipitation days = |
|Dec precipitation days = 12.0 |
||
|year precipitation days = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|Jan sun = 53.5 |
|||
| url = http://data.cma.cn/data/weatherBk.html |
|||
|Feb sun = 53.4 |
|||
|script-title=zh:中国地面气候标准值月值(1981-2010) |
|||
|Mar sun = 59.5 |
|||
| publisher = China Meteorological Data Service Center |
|||
| |
|Apr sun = 91.2 |
||
|May sun = 111.9 |
|||
| access-date = 20 October 2018}}</ref> |
|||
|Jun sun = 127.7 |
|||
| source 2 = Weather China (precipitation days 1971–2000)<ref name = Clim>{{cite web |
|||
|Jul sun = 219.0 |
|||
|Aug sun = 162.3 |
|||
|Sep sun = 121.1 |
|||
|Oct sun = 118.0 |
|||
|Nov sun = 100.0 |
|||
|Dec sun = 84.4 |
|||
|year sun = |
|||
| Jan percentsun = 16 |
|||
| Feb percentsun = 17 |
|||
| Mar percentsun = 16 |
|||
| Apr percentsun = 24 |
|||
| May percentsun = 27 |
|||
| Jun percentsun = 31 |
|||
| Jul percentsun = 52 |
|||
| Aug percentsun = 40 |
|||
| Sep percentsun = 33 |
|||
| Oct percentsun = 33 |
|||
| Nov percentsun = 31 |
|||
| Dec percentsun = 26 |
|||
| year percentsun = |
|||
|Jan snow days = 3.5 |
|||
|Feb snow days = 1.7 |
|||
|Mar snow days = 0.3 |
|||
|Apr snow days = 0 |
|||
|May snow days = 0 |
|||
|Jun snow days = 0 |
|||
|Jul snow days = 0 |
|||
|Aug snow days = 0 |
|||
|Sep snow days = 0 |
|||
|Oct snow days = 0 |
|||
|Nov snow days = 0 |
|||
|Dec snow days = 0.8 |
|||
|year snow days = |
|||
|source 1 = [[China Meteorological Administration]] (precipitation days, snow days, sunshine 1991–2015)<ref name="cma graphical">{{cite web |url=http://data.cma.cn/data/weatherBk.html |script-title=zh:中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data |publisher=[[China Meteorological Administration]] |language = zh-hans |access-date=11 June 2023}}</ref><ref> |
|||
{{cite web|url=https://experience.arcgis.com/template/e724038fda394e9d9b7921f10fd1aa55/page/%E7%BA%AF%E8%A1%A8%E6%A0%BC%E7%BB%9F%E8%AE%A1-(%E5%AF%B9%E6%AF%948110%E5%8F%98%E5%8C%96)/?org=UQmaps |script-title=zh:中国气象数据网|publisher=[[China Meteorological Administration]] |language = zh-hans | access-date =28 May 2023}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| url = http://www.weather.com.cn/cityintro/101250501.shtml? |
| url = http://www.weather.com.cn/cityintro/101250501.shtml? |
||
| script-title=zh:郴州 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 |
| script-title=zh:郴州 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 |
||
Revision as of 21:22, 10 June 2023
Chenzhou
郴州市 | |
|---|---|
 Chen River and the residential on the river bank in Chenzhou City | |
 Chenzhou's administrative area in Hunan | |
| Coordinates (Chenzhou municipal government): 25°46′12″N 113°00′58″E / 25.770°N 113.016°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Hunan |
| Municipal seat | Beihu District |
| Area | |
| 19,317 km2 (7,458 sq mi) | |
| • Urban (2017)[1] | 580.00 km2 (223.94 sq mi) |
| Population (2010 census) | |
| 4,581,778 | |
| • Density | 240/km2 (610/sq mi) |
| • Urban (2020)[1] | 960,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 423000 |
| Area code | 0735 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HN-10 |
| License plate prefixes | 湘L |
| GDP(2015) | CNY 201.21 billion |
| Website | en |
Chenzhou (Chinese: 郴州; pinyin: Chēnzhōu) is a prefecture-level city located in the south of Hunan province, China, bordering the provinces of Jiangxi to the east and Guangdong to the south. Its administrative area covers 19,317 square kilometres (7,458 sq mi), 9.2% of the provincial area, and its total population reached 4,581,779 in the 2010 census, 26% of them living in urban areas, 74% of them live in rural areas.[2]
History
Chenzhou is a historical city dating back from the Qin Dynasty. The area was historically named Guiyang (simplified Chinese: 桂阳; traditional Chinese: 桂陽; pinyin: Guìyáng) Commandery before being renamed to the current name in the year 735 during the Tang Dynasty. The Chinese character 郴, meaning "City in the Forest", uniquely refers to only the area. Known to be popular among the literacy circle of the Tang courts, poets such as Wang Changling, Du Fu, Han Yu, Liu Yuxi and Qin Guan have visited and wrote poems to the natural beauty of the area.
According to unsourced claims from Jung Chang and Jon Halliday in their book Mao: The Unknown Story, Chenzhou, along with neighboring Leiyang city was razed in 1928 by troops (Chinese Red Army) under the command of Zhu De, who was following directives which originated in Moscow and passed on by higher officials of the Chinese Communist Party. The strategy was to leave large numbers of peasants from the cities with no option but to join communist uprisings. [citation needed]
Chenzhou was the site of a large investigation when its municipal government and party committee, led by Secretary Li Dalun, was charged on multiple counts of corruption in June 2006. [citation needed]
Geography
Chenzhou is situated at the juncture of Hunan and Guangdong provinces at the foot of small Qitian Mountains of the Nanling Mountain Range. Places of interest, natural scenic spots, ancient relics and buildings make for over 100 tourism spots in the city. The major ones are the Suxian Hill, the Wanhuayan, the Dongjiang Lake, and the Wugai Mountain Hunting Field.
Climate
Chenzhou has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfa), with four distinct seasons. Spring is subject to heavy rainfall, while the summers are long, hot, and humid with lesser rainfall, and autumn is comfortable and rather dry. Winter is rather brief, but cold snaps occur with temperatures occasionally dropping below freezing, and while not heavy, rain can be frequent.
| Climate data for Chenzhou (1981–2010 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.0 (80.6) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.6 (96.1) |
36.2 (97.2) |
38.0 (100.4) |
40.3 (104.5) |
40.5 (104.9) |
38.6 (101.5) |
36.4 (97.5) |
33.5 (92.3) |
27.4 (81.3) |
40.5 (104.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.7 (62.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
27.8 (82.0) |
31.1 (88.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
33.2 (91.8) |
29.1 (84.4) |
24.1 (75.4) |
18.8 (65.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.4 (43.5) |
8.6 (47.5) |
12.6 (54.7) |
18.7 (65.7) |
23.3 (73.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
29.6 (85.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.6 (76.3) |
19.4 (66.9) |
13.9 (57.0) |
8.5 (47.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
9.6 (49.3) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
23.5 (74.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
10.4 (50.7) |
5.1 (41.2) |
15.1 (59.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.9 (21.4) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
2.9 (37.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.4 (56.1) |
18.6 (65.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.2 (55.8) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 80.1 (3.15) |
116.2 (4.57) |
155.4 (6.12) |
190.3 (7.49) |
186.6 (7.35) |
191.9 (7.56) |
123.0 (4.84) |
170.6 (6.72) |
96.1 (3.78) |
77.5 (3.05) |
67.9 (2.67) |
47.9 (1.89) |
1,503.5 (59.19) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 16.4 | 16.1 | 19.4 | 16.5 | 17.4 | 15.8 | 10.3 | 14.6 | 11.7 | 10.7 | 11.7 | 12.0 | 172.6 |
| Average snowy days | 3.5 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 6.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82 | 82 | 81 | 79 | 77 | 75 | 67 | 73 | 77 | 78 | 77 | 77 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 53.5 | 53.4 | 59.5 | 91.2 | 111.9 | 127.7 | 219.0 | 162.3 | 121.1 | 118.0 | 100.0 | 84.4 | 1,302 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 16 | 17 | 16 | 24 | 27 | 31 | 52 | 40 | 33 | 33 | 31 | 26 | 29 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration (precipitation days, snow days, sunshine 1991–2015)[3][4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[5] | |||||||||||||
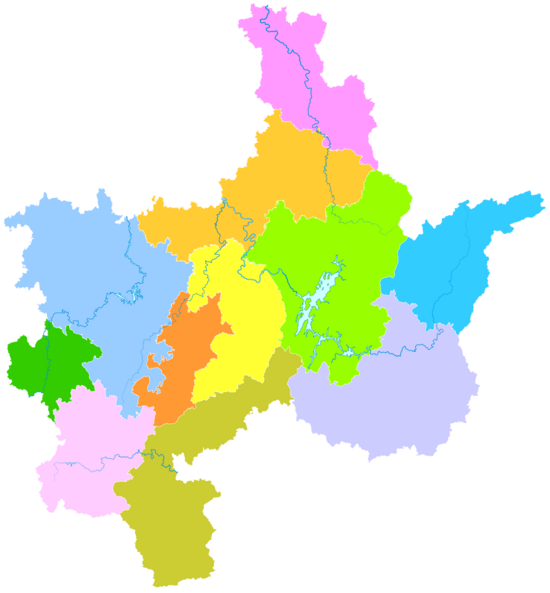
Administrative divisions

- Beihu District (北湖区), 815 km2 (315 sq mi). Population: 300,000 (2003).
- Suxian District (苏仙区), 1,342 km2 (518 sq mi). Population: 249,900
- Zixing City (资兴市) 2,716 km2 (1,049 sq mi). Population: 360,000
- Guiyang County (桂阳县), 2,954 km2 (1,141 sq mi). Population: 790,000
- Yongxing County (永兴县), 1,979 km2 (764 sq mi). Population: 630,000
- Yizhang County (宜章县), 2,086 km2 (805 sq mi). Population: 560,000
- Jiahe County (嘉禾县), 696 km2 (269 sq mi). Population: 340,000
- Linwu County (临武县), 1,375 km2 (531 sq mi). Population: 310,000
- Rucheng County (汝城县), 2,424 km2 (936 sq mi). Population: 360,000
- Guidong County (桂东县), 1,453 km2 (561 sq mi). Population: 170,000
- Anren County (安仁县), 1,461 km2 (564 sq mi). Population: 390,000
| Map |
|---|
Economy
Major deposits of tungsten, bismuth and molybdenum make Chenzhou a production base for non-ferrous metals.
Colleges and universities
Notable people
- Duan Yixuan, a singer and actress
- Long Yang, a hostess in CCTV
- Ouyang Jingling, a paralympic athlete
- Xue Yiwei, Chinese writer living in Montreal[6]
- Li Xingxue (李星学), Chinese botanist and member of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Government
The current CPC Party Secretary of Chenzhou is Yi Pengfei and the current Mayor is Liu Zhiren.
Tourism
The areas of interest in Chenzhou include: Wanhua Rock (万华岩), Wugai Mountain Hunting Field, Suxian Hill and Dongjiang Lake. The city is served by Chenzhou Beihu Airport.
References
- ^ a b Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 68. Archived from the original on 18 June 2019. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ (in Chinese) Demographics of Chenzhou Archived May 11, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Official website of Chenzhou Government, August 28, 2007.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ^ 郴州 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ "The Fate of a Novel Amid China's Reform". University of California Los Angeles. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
External links
- Chenzhou News Website, run by Chenzhou Government
- Official website of Chenzhou Government