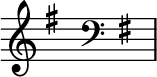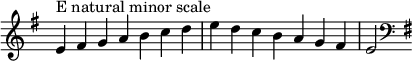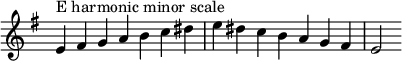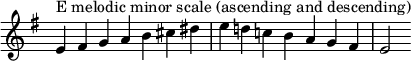E minor: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Barr Epstein (talk | contribs) |
Ethanman6969 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''E minor''' is a [[minor scale]] based on [[E (musical note)|E]], consisting of the pitches E, [[F♯ (musical note)|F{{Music|sharp}}]], [[G (musical note)|G]], [[A (musical note)|A]], [[B (musical note)|B]], [[C (musical note)|C]], and [[D (musical note)|D]]. Its [[key signature]] has one [[sharp (music)|sharp]]. Its [[relative key|relative major]] is [[G major]] and its [[parallel key|parallel major]] is [[E major]].<ref>[https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z6ch8xs/revision/4 "Notation"] ''BBC Bitesize''. Retrieved 2023-06-14.</ref> |
'''E minor''' is a [[minor scale]] based on [[E (musical note)|E]], consisting of the pitches E, [[F♯ (musical note)|F{{Music|sharp}}]], [[G (musical note)|G]], [[A (musical note)|A]], [[B (musical note)|B]], [[C (musical note)|C]], and [[D (musical note)|D]]. Its [[key signature]] has one [[sharp (music)|sharp]]. Its [[relative key|relative major]] is [[G major]] and its [[parallel key|parallel major]] is [[E major]].<ref>[https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z6ch8xs/revision/4 "Notation"] ''BBC Bitesize''. Retrieved 2023-06-14.</ref> |
||
== Scale Degree Chords == |
|||
* [[Tonic (music)|'''Tonic''']] - E minor |
|||
* '''[[Supertonic]]''' - [[Diminished triad|F-sharp diminished]] |
|||
* '''[[Mediant]]''' - [[G major]] |
|||
* '''[[Subdominant]]''' - [[A minor]] |
|||
* [[Dominant (music)|'''Dominant''']] - [[B minor]] |
|||
* '''[[Submediant]]''' - [[C major]] |
|||
* '''[[Subtonic]]''' - [[D major]] |
|||
The E [[natural minor scale]] is: |
The E [[natural minor scale]] is: |
||
Revision as of 11:36, 22 September 2023
| Relative key | G major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | E major |
| Dominant key | B minor |
| Subdominant | A minor |
| Component pitches | |
| E, F♯, G, A, B, C, D | |
E minor is a minor scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F♯, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature has one sharp. Its relative major is G major and its parallel major is E major.[1]
Scale Degree Chords
- Tonic - E minor
- Supertonic - F-sharp diminished
- Mediant - G major
- Subdominant - A minor
- Dominant - B minor
- Submediant - C major
- Subtonic - D major
The E natural minor scale is:
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The E harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are:
Much of the classical guitar repertoire is in E minor, as this is a very natural key for the instrument. In standard tuning (E A D G B E), four of the instrument's six open (unfretted) strings are part of the tonic chord. The key of E minor is also popular in heavy metal music, as its tonic is the lowest note on a standard-tuned guitar.
Notable compositions
- George Frideric Handel
- Messiah (overture)
- Joseph Haydn
- Symphony No. 44 (Trauer)
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
- Ludwig van Beethoven
- Carl Maria von Weber
- Franz Danzi
- Niccolò Paganini
- Felix Mendelssohn
- Frédéric Chopin
- Charles-Valentin Alkan
- Le festin d'Ésope, Op. 39, No. 12, from 12 etudes in all the minor keys
- Johannes Brahms
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
- Antonín Dvořák
- Symphony No. 9 (From the New World)[2]
- Piano Trio Op. 90
- Slavonic Dance No. 2, Op. 46
- Slavonic Dance No. 2, Op. 72
- Edvard Grieg
- Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
- Giuseppe Verdi
- Edward Elgar
- Jean Sibelius
- Symphony No. 1, Op. 39
- Ralph Vaughan Williams
- Sergei Rachmaninoff
- Moments musicaux, Op. 16, No. 4
- Symphony No. 2
- Vocalise, Op. 34, No. 14
- Maurice Ravel
- Sergei Prokofiev
- Dmitri Shostakovich
- Johann Sebastian Bach
- Bedřich Smetana
See also
References
- ^ "Notation" BBC Bitesize. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
- ^ "Symphony No. 9 in E minor, 'From the New World’ – Largo by Antonín Dvořák" BBC. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
External links
 Media related to E minor at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to E minor at Wikimedia Commons