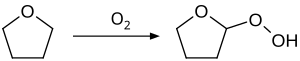Hydroperoxide: Difference between revisions
Alfa-ketosav (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
m cite repair; |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Properties== |
==Properties== |
||
The O−O [[bond length]] in peroxides is about 1.45 [[Ångström|Å]], and the R−O−O angles (R = H, C) are about 110° (water-like). Characteristically, the C−O−O−H dihedral angles are about 120°. The O−O bond is relatively weak, with a [[bond dissociation energy]] of {{convert|45–50|kcal/mol|abbr=on}}, less than half the strengths of C−C, C−H, and C−O bonds.<ref>{{cite journal|title=A Reassessment of the Bond Dissociation Energies of Peroxides. An ''ab Initio'' Study|first1=Robert D.|last1=Bach|first2=Philippe Y.|last2=Ayala|first3=H. B.|last3=Schlegel|journal=[[J. Am. Chem. Soc.]]|date=1996|volume=118|issue=50|pages=12758–12765|doi=10.1021/ja961838i}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups|chapter=Stereochemical and conformational aspects of peroxy compounds|pages=85–96|year=1983|author=Otto Exner|editor=Saul Patai|publisher=Wiley|doi=10.1002/9780470771730.ch2|isbn=9780470771730}}</ref> |
The O−O [[bond length]] in peroxides is about 1.45 [[Ångström|Å]], and the R−O−O angles (R = H, C) are about 110° (water-like). Characteristically, the C−O−O−H dihedral angles are about 120°. The O−O bond is relatively weak, with a [[bond dissociation energy]] of {{convert|45–50|kcal/mol|abbr=on}}, less than half the strengths of C−C, C−H, and C−O bonds.<ref>{{cite journal|title=A Reassessment of the Bond Dissociation Energies of Peroxides. An ''ab Initio'' Study|first1=Robert D.|last1=Bach|first2=Philippe Y.|last2=Ayala|first3=H. B.|last3=Schlegel|journal=[[J. Am. Chem. Soc.]]|date=1996|volume=118|issue=50|pages=12758–12765|doi=10.1021/ja961838i}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups|chapter=Stereochemical and conformational aspects of peroxy compounds|pages=85–96|year=1983|author=Otto Exner|editor=Saul Patai|publisher=Wiley|doi=10.1002/9780470771730.ch2|isbn={{Format ISBN|9780470771730}}}}</ref> |
||
Hydroperoxides are typically more volatile than the corresponding alcohols: |
Hydroperoxides are typically more volatile than the corresponding alcohols: |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Hydroperoxides can be reduced to [[Alcohol (chemistry)|alcohol]]s with [[lithium aluminium hydride]], as described in this idealized equation: |
Hydroperoxides can be reduced to [[Alcohol (chemistry)|alcohol]]s with [[lithium aluminium hydride]], as described in this idealized equation: |
||
:4 ROOH + LiAlH<sub>4</sub> → LiAlO<sub>2</sub> + 2 H<sub>2</sub>O + 4 ROH |
:4 ROOH + LiAlH<sub>4</sub> → LiAlO<sub>2</sub> + 2 H<sub>2</sub>O + 4 ROH |
||
This reaction is the basis of methods for analysis of organic peroxides.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Higuchi|first1=T.|last2=Zuck|first2=Donald Anton|title=Behaviors of Several Compounds as Indicators in Lithium Aluminum Hydride Titration of Functional Groups|journal=Journal of the American Chemical Society|volume=73| |
This reaction is the basis of methods for analysis of organic peroxides.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Higuchi|first1=T.|last2=Zuck|first2=Donald Anton|title=Behaviors of Several Compounds as Indicators in Lithium Aluminum Hydride Titration of Functional Groups|journal=Journal of the American Chemical Society|volume=73|page=2676|year=1951|doi=10.1021/ja01150a073|issue=6}}</ref> Another way to evaluate the content of peracids and peroxides is the volumetric titration with [[alkoxide]]s such as [[sodium ethoxide]].<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Martin|first1=A. J.|title=Potentiometric titration of hydroperoxide and peracid in Anhydrous Ethylenediamine|journal=Analytical Chemistry|volume=29|pages=79–81|year=1957|doi=10.1021/ac60121a022}}</ref> |
||
The [[phosphite ester]]s and tertiary phosphines also effect reduction: |
The [[phosphite ester]]s and tertiary phosphines also effect reduction: |
||
:ROOH + PR<sub>3</sub> → OPR<sub>3</sub> + ROH |
:ROOH + PR<sub>3</sub> → OPR<sub>3</sub> + ROH |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
"The single most important synthetic application of alkyl hydroperoxides is without doubt the metal-catalysed epoxidation of alkenes." In the [[Halcon process]] [[tert-butyl hydroperoxide]] (TBHP) is employed for the production of [[propylene oxide]].<ref name=Patai>{{cite book |title= Syntheses and Uses of Hydroperoxides and Dialkylperoxides |editor1-first= Saul |editor1-last= Patai | author= Roger A. Sheldon |year= 1983 |publisher= John Wiley & Sons |doi= 10.1002/9780470771730.ch6|series=PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups}}</ref> |
"The single most important synthetic application of alkyl hydroperoxides is without doubt the metal-catalysed epoxidation of alkenes." In the [[Halcon process]] [[tert-butyl hydroperoxide]] (TBHP) is employed for the production of [[propylene oxide]].<ref name=Patai>{{cite book |title= Syntheses and Uses of Hydroperoxides and Dialkylperoxides |editor1-first= Saul |editor1-last= Patai | author= Roger A. Sheldon |year= 1983 |publisher= John Wiley & Sons |doi= 10.1002/9780470771730.ch6|series=PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups}}</ref> |
||
Of specialized interest, chiral [[epoxide]]s are prepared using hydroperoxides as reagents in the [[Sharpless epoxidation]].<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Hill, J. G. |author2=[[K. Barry Sharpless|Sharpless, K. B.]] |author3=Exon, C. M. |author4=Regenye, R. |journal=[[Org. Synth.]]|volume=63| |
Of specialized interest, chiral [[epoxide]]s are prepared using hydroperoxides as reagents in the [[Sharpless epoxidation]].<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Hill, J. G. |author2=[[K. Barry Sharpless|Sharpless, K. B.]] |author3=Exon, C. M. |author4=Regenye, R. |journal=[[Org. Synth.]]|volume=63|page=66|year=1985|doi=10.15227/orgsyn.063.0066| |
||
title=Enantioselective Epoxidation Of Allylic Alcohols: (2s,3s)-3-propyloxiranemethanol}}</ref> |
title=Enantioselective Epoxidation Of Allylic Alcohols: (2s,3s)-3-propyloxiranemethanol}}</ref> |
||
[[Image:Sharpless epoxidation DE.svg|center|400px|The Sharpless epoxidation]] |
[[Image:Sharpless epoxidation DE.svg|center|400px|The Sharpless epoxidation]] |
||
===Production of cyclohexanone and caprolactone=== |
===Production of cyclohexanone and caprolactone=== |
||
Hydroperoxides are intermediates in the production of many organic compounds in industry. For example, the cobalt catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexane to [[cyclohexanone]]:<ref name=Ullmann1>{{Ullmann| |
Hydroperoxides are intermediates in the production of many organic compounds in industry. For example, the cobalt catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexane to [[cyclohexanone]]:<ref name=Ullmann1>{{Ullmann|author=Michael T. Musser|title=Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone|year=2005|doi=10.1002/14356007.a08_217}}</ref> |
||
:C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> → (CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>CO + H<sub>2</sub>O |
:C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> → (CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>CO + H<sub>2</sub>O |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
====Hock processes==== |
====Hock processes==== |
||
[[File:Hock-Phenol.png|thumb|250px|Synthesis of cumene hydroperoxide]] |
[[File:Hock-Phenol.png|thumb|250px|Synthesis of cumene hydroperoxide]] |
||
Compounds with [[allyl]]ic and [[benzyl]]ic C−H bonds are especially susceptible to oxygenation.<ref>{{cite journal| first1 = H. B. | last1 = Knight | first2 = Daniel | last2 = Swern | journal=Org. Synth.|title = Tetralin Hydroperoxide | volume = 34 | |
Compounds with [[allyl]]ic and [[benzyl]]ic C−H bonds are especially susceptible to oxygenation.<ref>{{cite journal| first1 = H. B. | last1 = Knight | first2 = Daniel | last2 = Swern | journal=Org. Synth.|title = Tetralin Hydroperoxide | volume = 34 | page = 90| year = 1954 | doi= 10.15227/orgsyn.034.0090}}.</ref> Such reactivity is exploited industrially on a large scale for the production of [[phenol]] by the [[Cumene process]] or Hock process for its [[cumene]] and [[cumene hydroperoxide]] intermediates.<ref>Brückner, R. ''Reaktionsmechanismen: organische Reaktionen, Stereochemie, moderne Synthesemethoden'', pp. 41–42, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Munich, 2004, {{ISBN|3-8274-1579-9}} (in German)</ref> Such reactions rely on [[radical initiator]]s that reacts with oxygen to form an intermediate that abstracts a hydrogen atom from a weak C-H bond. The resulting radical binds O<sub>2</sub>, to give hydroperoxyl (ROO<sup>.</sup>), which then continues the cycle of H-atom abstraction.<ref name=org206>Heinz G. O. Becker ''Organikum'', Wiley-VCH, 2001, {{ISBN|3-527-29985-8}} pp. 206–207</ref> |
||
[[File:Schenk-En-Reaktion.png|thumb|230px|Synthesis of hydroperoxides of alkene and singlet oxygen in an [[ene reaction]]]] |
[[File:Schenk-En-Reaktion.png|thumb|230px|Synthesis of hydroperoxides of alkene and singlet oxygen in an [[ene reaction]]]] |
||
Revision as of 12:34, 1 October 2023

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds of the form ROOH, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group (–OOH). The hydroperoxide anion (HOO−) and the neutral hydroperoxyl radical (HOO·) consist of an unbond hydroperoxy group. When R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.[1]
Properties
The O−O bond length in peroxides is about 1.45 Å, and the R−O−O angles (R = H, C) are about 110° (water-like). Characteristically, the C−O−O−H dihedral angles are about 120°. The O−O bond is relatively weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 45–50 kcal/mol (190–210 kJ/mol), less than half the strengths of C−C, C−H, and C−O bonds.[2][3]
Hydroperoxides are typically more volatile than the corresponding alcohols:
- tert-BuOOH (b.p. 36 °C) vs tert-BuOH (b.p. 82-83 °C)
- CH3OOH (b.p. 46 °C) vs CH3OH (b.p. 65 °C)
- cumene hydroperoxide (b.p. 153 °C) vs cumyl alcohol (b.p. 202 °C)
Miscellaneous reactions
Hydroperoxides are mildly acidic. The range is indicated by 11.5 for CH3OOH to 13.1 for Ph3COOH.[4]
Hydroperoxides can be reduced to alcohols with lithium aluminium hydride, as described in this idealized equation:
- 4 ROOH + LiAlH4 → LiAlO2 + 2 H2O + 4 ROH
This reaction is the basis of methods for analysis of organic peroxides.[5] Another way to evaluate the content of peracids and peroxides is the volumetric titration with alkoxides such as sodium ethoxide.[6] The phosphite esters and tertiary phosphines also effect reduction:
- ROOH + PR3 → OPR3 + ROH
Uses
Precursors to epoxides
"The single most important synthetic application of alkyl hydroperoxides is without doubt the metal-catalysed epoxidation of alkenes." In the Halcon process tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) is employed for the production of propylene oxide.[7]
Of specialized interest, chiral epoxides are prepared using hydroperoxides as reagents in the Sharpless epoxidation.[8]

Production of cyclohexanone and caprolactone
Hydroperoxides are intermediates in the production of many organic compounds in industry. For example, the cobalt catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexanone:[9]
- C6H12 + O2 → (CH2)5CO + H2O
Drying oils, as found in many paints and varnishes, function via the formation of hydroperoxides.
Hock processes
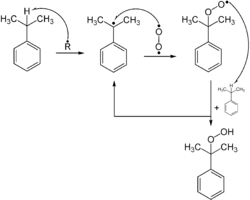
Compounds with allylic and benzylic C−H bonds are especially susceptible to oxygenation.[10] Such reactivity is exploited industrially on a large scale for the production of phenol by the Cumene process or Hock process for its cumene and cumene hydroperoxide intermediates.[11] Such reactions rely on radical initiators that reacts with oxygen to form an intermediate that abstracts a hydrogen atom from a weak C-H bond. The resulting radical binds O2, to give hydroperoxyl (ROO.), which then continues the cycle of H-atom abstraction.[12]

Formation
By autoxidation
The most important (in a commercial sense) peroxides are produced by autoxidation, the direct reaction of O2 with a hydrocarbon. Autoxidation is a radical reaction that begins with the abstraction of an H atom from a relatively weak C-H bond. Important compounds made in this way include tert-butyl hydroperoxide, cumene hydroperoxide and ethylbenzene hydroperoxide:[7]
- R-H + O2 → ROOH
Auto-oxidation reaction is also observed with common ethers, such as diethyl ether, diisopropyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, and 1,4-dioxane. An illustrative product is diethyl ether peroxide. Such compounds can result in a serious explosion when distilled.[12] To minimize this problem, commercial samples of THF are often inhibited with butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT). Distillation of THF to dryness is avoided because the explosive peroxides concentrate in the residue.
Although ether hydroperoxide often form adventitiously (i.e. autoxidation), they can be prepared in high yield by the acid-catalyzed addition of hydrogen peroxide to vinyl ethers:[13]
- C2H5OCH=CH2 + H2O2 → C2H5OCH(OOH)CH3
From hydrogen peroxide
Many industrial peroxides are produced using hydrogen peroxide. Reactions with aldehydes and ketones yield a series of compounds depending on conditions. Specific reactions include addition of hydrogen peroxide across the C=O double bond:
- R2C=O + H2O2 → R2C(OH)OOH
In some cases, these hydroperoxides convert to give cyclic diperoxides:
- [R2C(O2H)]2O2 → [R2C]2(O2)2 + 2 H2O
Addition of this initial adduct to a second equivalent of the carbonyl:
- R2C=O + R2C(OH)OOH → [R2C(OH)]2O2
Further replacement of alcohol groups:
- [R2C(OH)]2O2 + 2 H2O2 → [R2C(O2H)]2O2 + 2 H2O
Triphenylmethanol reacts with hydrogen peroxide gives the unusually stable hydroperoxide, Ph3COOH.[14]
Naturally occurring hydroperoxides
Many hydroperoxides are derived from fatty acids, steroids, and terpenes. The biosynthesis of these species is affected extensively by enzymes.

References
- ^ Klenk, Herbert; Götz, Peter H.; Siegmeier, Rainer; Mayr, Wilfried. "Peroxy Compounds, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_199. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Bach, Robert D.; Ayala, Philippe Y.; Schlegel, H. B. (1996). "A Reassessment of the Bond Dissociation Energies of Peroxides. An ab Initio Study". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (50): 12758–12765. doi:10.1021/ja961838i.
- ^ Otto Exner (1983). "Stereochemical and conformational aspects of peroxy compounds". In Saul Patai (ed.). PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. Wiley. pp. 85–96. doi:10.1002/9780470771730.ch2. ISBN 978-0-470-77173-0.
- ^ Klenk, Herbert; Götz, Peter H.; Siegmeier, Rainer; Mayr, Wilfried. "Peroxy Compounds, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_199. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Higuchi, T.; Zuck, Donald Anton (1951). "Behaviors of Several Compounds as Indicators in Lithium Aluminum Hydride Titration of Functional Groups". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 73 (6): 2676. doi:10.1021/ja01150a073.
- ^ Martin, A. J. (1957). "Potentiometric titration of hydroperoxide and peracid in Anhydrous Ethylenediamine". Analytical Chemistry. 29: 79–81. doi:10.1021/ac60121a022.
- ^ a b Roger A. Sheldon (1983). Patai, Saul (ed.). Syntheses and Uses of Hydroperoxides and Dialkylperoxides. PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470771730.ch6.
- ^ Hill, J. G.; Sharpless, K. B.; Exon, C. M.; Regenye, R. (1985). "Enantioselective Epoxidation Of Allylic Alcohols: (2s,3s)-3-propyloxiranemethanol". Org. Synth. 63: 66. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.063.0066.
- ^ Michael T. Musser (2005). "Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_217. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Knight, H. B.; Swern, Daniel (1954). "Tetralin Hydroperoxide". Org. Synth. 34: 90. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.034.0090..
- ^ Brückner, R. Reaktionsmechanismen: organische Reaktionen, Stereochemie, moderne Synthesemethoden, pp. 41–42, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Munich, 2004, ISBN 3-8274-1579-9 (in German)
- ^ a b Heinz G. O. Becker Organikum, Wiley-VCH, 2001, ISBN 3-527-29985-8 pp. 206–207
- ^ Milas, Nicholas A.; Peeler, Robert L.; Mageli, Orville L. (1954). "Organic Peroxides. XIX. α-Hydroperoxyethers and Related Peroxides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (9): 2322–2325. doi:10.1021/ja01638a012.
- ^ Bryant E. Rossiter and Michael O. Frederick "Triphenylmethyl Hydroperoxide" E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2013. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt363m.pub2
- ^ Matsui K (2006). "Green leaf volatiles: hydroperoxide lyase pathway of oxylipin metabolism". Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 9 (3): 274–80. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2006.03.002. PMID 16595187.