Government of the Grand National Assembly: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
The executive ministers were elected by the assembly so it was a directorial system. Tag: Reverted |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| official_languages = [[Ottoman Turkish|Turkish]]<ref name=anayasa>[https://www.anayasa.gov.tr/tr/mevzuat/onceki-anayasalar/1921-anayasasi/] TEŞKİLÂTI ESASİYE KANUNU</ref> |
| official_languages = [[Ottoman Turkish|Turkish]]<ref name=anayasa>[https://www.anayasa.gov.tr/tr/mevzuat/onceki-anayasalar/1921-anayasasi/] TEŞKİLÂTI ESASİYE KANUNU</ref> |
||
| religion = [[Islam]] (official)<ref name=anayasa></ref> |
| religion = [[Islam]] (official)<ref name=anayasa></ref> |
||
| government_type = {{nowrap|[[Provisional government]]}} under a [[ |
| government_type = {{nowrap|[[Provisional government]]}} under a [[directorial system]] |
||
| title_leader = [[Speaker of the Parliament of Turkey|Speaker]] |
| title_leader = [[Speaker of the Parliament of Turkey|Speaker]] |
||
| leader1 = [[Mustafa Kemal Atatürk|Mustafa Kemal]]{{ref|a|a}}{{ref|b|b}} |
| leader1 = [[Mustafa Kemal Atatürk|Mustafa Kemal]]{{ref|a|a}}{{ref|b|b}} |
||
Revision as of 23:22, 26 November 2023
State of Turkey Türkiye Devleti | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1920–1923 | |||||||||||||||||
| Motto: Ya istiklâl ya ölüm! "Independence or death!" | |||||||||||||||||
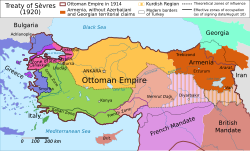 De Jure Situation in the Ottoman Empire following the Treaty of Sèvres. | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Ankara (de facto) | ||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | Turkish[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Islam (official)[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Provisional government under a directorial system | ||||||||||||||||
| Speaker | |||||||||||||||||
• 1920–1923 | Mustafa Kemalab | ||||||||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||||||||
• 1920–1921 | Mustafa Kemal | ||||||||||||||||
• 1921–1922 | Mustafa Fevzi | ||||||||||||||||
• 1922–1923 | Hüseyin Rauf | ||||||||||||||||
• 1923 | Ali Fethi | ||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Grand National Assembly | ||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | War of Independence | ||||||||||||||||
| 23 April 1920 | |||||||||||||||||
| 3 May 1920 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20 January 1921 | |||||||||||||||||
| 11 October 1922 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 November 1922 | |||||||||||||||||
| 24 July 1923 | |||||||||||||||||
| 29 October 1923 | |||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||
• | 6–7 million[2] | ||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Ottoman lira | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | Turkey | ||||||||||||||||
The Government of the Grand National Assembly (Template:Lang-tr), self-identified as the State of Turkey (Türkiye Devleti) or Turkey (Türkiye),[3] commonly known as the Ankara Government (Ankara Hükûmeti),[4][5][6][7][8][9] or archaically the Angora Government, was the provisional and revolutionary Turkish government based in Ankara (then known as Angora) during the Turkish War of Independence (1919–1923) and during the final years of the Ottoman Empire. It was led by the Turkish National Movement, as opposed to the crumbling Constantinople Government, which was led by the Ottoman Sultan.
During the War of Independence, the Government of the Grand National Assembly commanded the army known as Kuva-yi Milliye ("National Forces"). After the war and victory over the monarchist Constantinople Government, the republican Ankara Government declared the end of the Ottoman Empire and the creation of the Republic of Turkey from its ashes in 1923. The Grand National Assembly is today the parliamentary body of Turkey.
Background
At the time the Ankara Government was proclaimed, there existed another Turkish government in the Allied-occupied Constantinople (now Istanbul), namely the Imperial Ottoman Government, often known as the "Constantinople Government" (as opposed to the nationalist Ankara Government). Once the Grand National Assembly was established, on 23 April 1920, without rejecting at first the legitimacy of the Ottoman Sultanate, the new parliament in Ankara formed its own government within the Assembly. The Ministers were called "Vekil" (Acting) instead of the conventional "Nazır", to keep with the provisional nature of the government.
The Ankara Government was founded to represent Turkey because the de jure capital, Constantinople, was under occupation. The president of the GNA (renamed the Grand National Assembly of Turkey after 8 February 1921) and later of the Republic of Turkey, was Mustafa Kemal Pasha. Once the Armistice of Mudanya was signed, replacing the Armistice of Mundros (signed by the Ottoman Empire in 1918 at the end of World War I) and ending the Turkish War of Independence, the GNA abolished the imperial Sultanate, which was accused of collaborating with the Allies during the occupation of Turkey.

The Angora Government and its Claims
The Kemalists or Nationalists control more or less effectively the area shaded. They have been driven away from the Aegean by the Greeks, but claim Thrace, Smyrna, Armenia, and all Mesopotamia down to the Persian Gulf
The Constantinople Government, representing the Ottoman sultanate and the old imperial and monarchical order, initially refused to recognize the Turkish national movement and the Government of the Grand National Assembly in Ankara, holding that it alone was the legitimate government of the Ottoman Empire. It attempted to militarily defeat the Ankara Government using its Kuva-yi Inzibatiye, i.e. the "Forces of Order", commonly known as the "Army of the Caliphate" (as opposed to the GNA's forces, the Kuva-yi Milliye, the "Army of the Nation"), but failed to do so. In 1921, diplomatic teams from both the monarchist Constantinople Government and the republican Ankara Government appeared at the Conference of London. In a surprising move, however, the Ottoman diplomatic team led by Ahmet Tevfik Pasha gave in and allowed the Turkish diplomatic team led by Bekir Sami Kunduh to be the sole representatives of the country at the conference. The Treaty of Lausanne was signed on 24 July 1923, between the representatives of the Allies and of Ankara, thus officially recognizing the government of Ankara as the legitimate Turkish government.
On 29 October, the Republic of Turkey was proclaimed by the Grand National Assembly of Turkey.
The governments
The governments prior to the Republic were used to be called "Executive ministers of Turkey." They were:
- 1st cabinet of the Executive Ministers of Turkey
- 2nd cabinet of the Executive Ministers of Turkey
- 3rd cabinet of the Executive Ministers of Turkey
- 4th cabinet of the Executive Ministers of Turkey
- 5th cabinet of the Executive Ministers of Turkey
See also
- Turkish National Movement
- Armistice of Mudanya
- Turkish War of Independence
- Abolition of the Ottoman sultanate
References
- ^ a b [1] TEŞKİLÂTI ESASİYE KANUNU
- ^ Belgelerle Türk tarihi dergisi, Edition 18, Menteş Kitabevi, 1986, page 72. (in Turkish)
- ^ Ryan Gingeras (2019). Eternal Dawn: Turkey in the Age of Atatürk. p. 86.
- ^ Esra Yakut: Şeyhülislâmlık: yenileşme döneminde devlet ve din, Kitap Yayınevi Ltd., 2005, ISBN 9789758704941, page 198,199. (in Turkish)
- ^ Pars Tuğlacı: Çağdaş Türkiye, Cem Yayınevi, 1987, Turkey page 358. (in Turkish)
- ^ Hakan Alan, Avni Alan: İstanbul Şehir Rehberi, ASBOOK, 2007, ISBN 9750114701, page 12. (in Turkish)
- ^ Yahya Kemal: Eğil Dağlar, Kubbealtı Publishing, 1966, ISBN 9757618519, pages 13, 92-93, 138, 155, 170, 188, 204-205, 232, 302, 338. (in Turkish)
- ^ William Hale: Turkish Foreign Policy, 1774-2000, Routledge, 2012, ISBN 0415599865, pages 36, 37, 38, 50, 265.
- ^ Kemal Kirişci, Gareth M. Winrow: The Kurdish Question and Turkey: An Example of a Trans-State Ethnic Conflict, Routledge, 1997, ISBN 0714647462, pages 71-75, 77-79, 80, 82-84.
External links
- History of the Grand National Assembly Archived 2022-01-12 at the Wayback Machine

