Skaergaard intrusion: Difference between revisions
m Duplicate word removed |
→External links: recovered categories |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* [http://www.skaergaard.org/ ''The (virtual) Skaergaard Intrusion''] |
* [http://www.skaergaard.org/ ''The (virtual) Skaergaard Intrusion''] |
||
[[Category:Geology of Greenland]] |
|||
[[Category:Arctic research]] |
|||
[[Category:Layered intrusions]] |
|||
{{regional-geology-stub}} |
|||
[[Category:Paleogene magmatism]] |
|||
Revision as of 19:13, 29 November 2023
68°10′06″N 31°43′01″W / 68.1683°N 31.7169°W The Skaergaard intrusion is a layered igneous intrusion in the Kangerlussuaq area of East Greenland and is comprised of various rocks and minerals including gabbro, olivine, apatite, and basalt.[1]
History and background
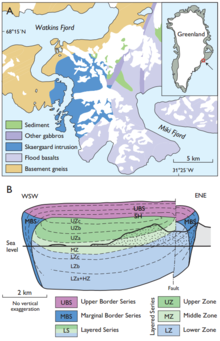

The Skaergaard intrusion was formed 56 million years ago during the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean.[1] The intrusion was emplaced beneath the preexisting rock in the region, including plateau basalt and gneiss.[1][2] The intrusion has a general oval shape, which is atypical in igneous emplacement.[1] Due to the tectonic activity in East Greenland, the intrusion is now slightly tilted towards the sea.[1] Specifically, the lower parts of the intrusion are exposed to the north while sections of the roof are conserved to the south.[1]
Discovery and early studies
The Skaergaard intrusion was first discovered by Lawrence Wager on his Arctic Air-Route Expedition in 1930.[1] In 1933, the first aerial photography of the region was taken in order to create a topographic map of the area.[1] The first scientific expedition to the intrusion took place in 1935 and 1936 and lasted over 13 months.[1] This expedition was led by Wager accompanied by a small team, including geologist William Alexander Deer.[1] Through this mission, the team studied the intrusion through reconnaissance mapping.[1]
Geologic characteristics
The intrusion is made up of three separate geologic sequences which formed at the floor, roof, and walls, with the formation at the floor being much thicker than that of the other two sequences.[1] The rocks of these sequences are further divided into three categories: the lower zone, middle zone, and upper zone.[1] The zone categorization is based on the occurrence of specific minerals such as augite, Fe-Ti oxides, rounded grains of olivine, apatite, and ferrobustamite.[1]
The intrusion formed from the crystallization of a convecting body of magma which resulted in the lineation, layering, cross bedding, and channel structures within the rocks.[1] These features result from sedimentary formations created by grain re-arrangement via magmatic currents.[1]
Within the solid rocks of the formation, the crystals are classified into two categories: primary precipitate crystals and interprecipitate crystals.[1] Primary precipitate crystals form in conditions of high presence of liquids while interprecipitate crystals form from interprecipitate liquid, liquid in the spaces between grains which solidify them together.[1]
This data was developed from the 1939 memoir written by Lawrence Wager and William Alexander Deer from their 1935 expedition.[1]
Scientific significance
Data acquired from researching the Skaergaard intrusion can be used to model the how the intrusion was originally formed and how magma fractional crystallization takes place.[2] Multiple models of magmatic assimilation and recharge have been developed from the Skaergaard intrusion including the continuous replenishment model, intermittent recharge model, end-member replenishment model, and pulse recharge model.[2]
The Skaergaard intrusion also exhibits the formation of one of the largest basaltic magmatic regions in the world.[2]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Holness, Marian B.; Nielsen, Troels F.D.; Tegner, Christian (2017-12-01). "The Skaergaard Intrusion of East Greenland: Paradigms, Problems and New Perspectives". Elements. 13 (6): 391–396. doi:10.2138/gselements.13.6.391. ISSN 1811-5217.
- ^ a b c d Stewart, Brian W.; DePaolo, Donald J. (1990). "Isotopic studies of processes in mafic magma chambers: II. The Skaergaard Intrusion, East Greenland". Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology. 104 (2): 125–141. doi:10.1007/bf00306438. ISSN 0010-7999.
