Nuclear–cytoplasmic ratio: Difference between revisions
Kj cheetham (talk | contribs) Importing Wikidata short description: "Measurement used in cell biology" |
Kj cheetham (talk | contribs) Added {{More footnotes needed}} tag |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Measurement used in cell biology}} |
{{Short description|Measurement used in cell biology}} |
||
{{correct title|reason=namespace|edit=omission|title=N:C ratio}} |
{{correct title|reason=namespace|edit=omission|title=N:C ratio}} |
||
{{More footnotes needed|date=January 2024}} |
|||
[[File:Nuclear-to-cytoplasm ratios.png|thumb|260px|Nuclear-cytoplasmic ratios.]] |
[[File:Nuclear-to-cytoplasm ratios.png|thumb|260px|Nuclear-cytoplasmic ratios.]] |
||
The '''nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio''' (also variously known as the '''nucleus:cytoplasm ratio''', '''nucleus-cytoplasm ratio''', '''N:C ratio''', or '''N/C''') is a measurement used in [[cell biology]]. It is a ratio of the size (i.e., volume) of the [[cell nucleus|nucleus]] of a cell to the size of the [[cytoplasm]] of that cell.<ref name="Turgeon">{{cite book | author = Turgeon, Mary Louise | title = Clinical hematology: theory and procedures | publisher = Lippincott Williams & Wilkins | location = Hagerstwon, MD | year = 2005 | pages = 67 | isbn = 0-7817-5007-5 }}</ref> |
The '''nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio''' (also variously known as the '''nucleus:cytoplasm ratio''', '''nucleus-cytoplasm ratio''', '''N:C ratio''', or '''N/C''') is a measurement used in [[cell biology]]. It is a ratio of the size (i.e., volume) of the [[cell nucleus|nucleus]] of a cell to the size of the [[cytoplasm]] of that cell.<ref name="Turgeon">{{cite book | author = Turgeon, Mary Louise | title = Clinical hematology: theory and procedures | publisher = Lippincott Williams & Wilkins | location = Hagerstwon, MD | year = 2005 | pages = 67 | isbn = 0-7817-5007-5 }}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 20:15, 16 January 2024
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (January 2024) |
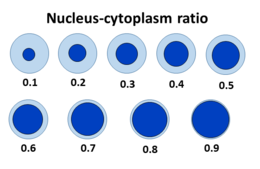
The nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio (also variously known as the nucleus:cytoplasm ratio, nucleus-cytoplasm ratio, N:C ratio, or N/C) is a measurement used in cell biology. It is a ratio of the size (i.e., volume) of the nucleus of a cell to the size of the cytoplasm of that cell.[1]
The N:C ratio indicates the maturity of a cell, because as a cell matures the size of its nucleus generally decreases. For example, "blast" forms of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and megakaryocytes start with an N:C ratio of 4:1, which decreases as they mature to 2:1 or even 1:1 (with exceptions for mature thrombocytes and erythrocytes, which are anuclear cells, and mature lymphocytes, which only decrease to a 3:1 ratio and often retain the original 4:1 ratio).[1]
An increased N:C ratio is commonly associated with precancerous dysplasia as well as with malignant cells.
See also
References
- ^ a b Turgeon, Mary Louise (2005). Clinical hematology: theory and procedures. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 67. ISBN 0-7817-5007-5.
Further reading
- Herbert E. Nieburgs (1967). "Nuclear/Cytoplasmic Ratio (N/C) and Nuclear Chromatin". Diagnostic cell pathology in tissue and smears. New York & London: Grune & Stratton. pp. 15–16.
- Takahashi, Masayoshi (1981). Color atlas of cancer cytology (2nd ed.). New York: Igaku-Shoin. pp. 32–34, 50. ISBN 0-89640-050-6.
- John D. Bancroft; Alan Stevens (1982). Theory and practice of histological techniques (2nd ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 438–439.
