Wilhelm Cornides: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Misc citation tidying. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | #UCB_CommandLine |
HeyElliott (talk | contribs) Adding local short description: "Wehrmacht sergeant in World War II", overriding Wikidata description "German writer" |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Wehrmacht sergeant in World War II}} |
|||
{{Infobox person |
{{Infobox person |
||
| name = Wilhelm Cornides |
| name = Wilhelm Cornides |
||
Revision as of 21:40, 24 January 2024
Wilhelm Cornides | |
|---|---|
 Wilhelm Cornides, magazine print | |
| Born | 20 July 1920 München, Germany |
| Died | 15 July 1966 (aged 45) |
| Occupation | Publisher |
Wilhelm Cornides (20 July 1920 – 15 July 1966) was a Wehrmacht sergeant in World War II, serving in the General Government territory. He was the author of the Cornides Report, which contains his account of the extermination of Jews at Belzec during the Holocaust. In December 1946 Cornides became the founder of Europa-Archiv (renamed Internationale Politik in 1995), the first post-war magazine in Allied-occupied Germany. In 1955 he was instrumental along with Theodor Steltzer, Minister-President of Schleswig Holstein and former member of the dissident Kreisau Circle, in founding the German Council on Foreign Relations (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Auswärtige Politik, DGAP). Through his mother Cäcilie (Cilla) von Oldenbourg, Cornides was a member of the Oldenbourg family, owners of Oldenbourg Verlag publishers; a German publishing house founded in 1858 by Rudolf Oldenbourg.[1]
Holocaust witness

On 30 August 1942, during the occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany, Cornides was in Rzeszów (renamed Reichshof), on his way to the city of Chełm (Cholm) by train. He wrote a private journal to pass the time, recording things he would not want to talk about with anyone else. He wrote what a German railway policeman told him, that the area would soon be free of Jews (Judenfrei), since every day freight trains packed with Jews from the Generalgouvernement passed through the railway yard, and come back in the evening empty and swept clean. The policeman said he had seen 6,000 Jews from Jarosław (Jaroslau) recently killed in one day.[2] Cornides made also several entries about what he had seen himself. His observations surfaced in 1959, typewritten on three letter size sheets.[3] They were published in July 1959 by historian Hans Rothfels in the German quarterly Journal of Contemporary History (Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte).[1] By that time, the much more revealing Gerstein Report which featured shocking details about the extermination process at Belzec was already well known in Germany.[4][5]
Diary entries
Cornides took a regular German passenger train from Rzeszów to Chełm and spoke with the other passengers. He arrived at Rawa Ruska junction around noon on 31 August 1942 and made further entries in his journal later that day.[2]
At ten minutes past noon I saw a transport train run into the station. On the roof and running boards sat guards with rifles. One could see from a distance that the cars were jammed full of people. I turned and walked along the whole train: it consisted of 35 cattle cars and one passenger car. In each of the cars there were at least 60 Jews – in the case of the enlisted men's or prisoner transports these wagons would hold 40 men; however, the benches had been removed and one could see that those who were locked in here had to stand pressed together. Some of the doors were opened a crack, the windows criss-crossed with barbed wire. Among the locked-in people there were a few men and most of those were old; everything else was women, girls and children. Many children crowded at the windows and the narrow door openings. The youngest were surely not more than two years old.[2]

I talked to a policeman on duty at the railway station. Upon my question as to where the Jews actually came from, he answered: "Those are probably the last ones from Lvow [i.e. the Lwów Ghetto]. That has been going on now for three weeks uninterruptedly. In Jarosław they only let eight remain, no one knows why." I asked: "How far are they going?" Then he said: "To Belzec." "And then?" "Poison." I asked: "Gas?" He shrugged his shoulders. Then he said only: "At the beginning they always shot them I believe."[6][7]
Cornides lounged at the Deutsches Haus in Rawa Ruska before he boarded the connecting train to Chełm the same evening. In the next hour, he made three separate entries in his diary. The first, written at 5.30 pm, stated that what he had learned was extraordinary.[2]
When we boarded at 4:40 pm an inbound transport had just arrived. I walked along the train twice and counted 56 cars. On the doors had been written in chalk: '60', '70', once '90', occasionally '40' – obviously the number of Jews inside the cattle cars. In my compartment I spoke with a railway policeman’s wife who was visiting her husband here. She says these transports are now passing through daily, sometimes also with the German Jews. Yesterday six children’s bodies were found along the track.[2]
Belzec camp
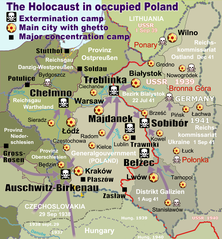


In his train compartment, Cornides talked to a German woman who had witnessed the round-up of Jews at Chełm and the shooting of those who tried to escape. The railway policeman said: "In the railway documents these trains run under the name of resettlement transports," and added that after the murder of Reinhard Heydrich by Czech resistance members, several trains filled with Czech Jews had passed through. Camp Belzec was located on the railway line. The woman promised to point it out to Cornides when they passed it. The entry in his diary reads:[2][8]
6:20 p.m. We passed Camp Belzec. Before then, we traveled for some time through a tall pine forest. When the woman called: "Now it comes," one could see a high hedge of fir trees. A strong sweetish odour could be made out distinctly. "But they are stinking already," says the woman. "Oh nonsense, it is only the gas," the railway policeman said, laughing. Meanwhile – we had gone on about 200 meters – the sweetish odour was transformed into a strong smell of something burning. "That is from the crematory," said the policeman. A short distance further on, the fence stopped. In front of it, one could see a guard house with an SS post. A double track led into the camp. One track branched off from the main line, the other ran over a turntable from the camp to a row of sheds some 250 meters away. A freight car happened to stand on the turntable. Several Jews were busy turning the disk. SS guards, rifles under their arms, stood by. One of the sheds was open; one could distinctly see that it was filled to the ceiling with bundles of clothes. As we went on, I looked back one more time. The fence was too high to see anything at all.[2]
In his typewritten pages, Cornides also summarized conversations with other Germans he met during his stopover in the Deutsches Haus at Rawa Ruska, as well as statements he remembered from Chełm upon his arrival there.
A policeman in the townhall restaurant at Cholm (Chełm) on 1 September 1942 said: "The policemen who guard the Jewish transports are not allowed inside the camp, only the SS and the Ukrainian Sonderdienst – a police formation consisting of Ukrainian auxiliaries – do so [see Trawniki men for more historical background]. Thereby, they have created a good business. Recently a Ukrainian was here who had a great wad of notes, clocks and gold – everything imaginable. They find all of this when they gather and ship the clothing." In answer to the question: "In which way were the Jews killed?" the policeman answered: "Someone tells them that they must be deloused. Then they undress and enter a room into which at first a heatwave is let in, and thereby they already have received one small dose of gas. It is enough to act as a local anaesthetic. The rest then follows and then they are immediately burned."[2]
See also
- Special Prosecution Book-Poland, 1937–1939
- Jäger Report, 1941
- Einsatzgruppen reports, 1941–1942
- Riegner Telegram, 1942
- Höfle Telegram, 1943
- Katzmann Report, 1943
- Korherr Report, 1943
- Gerstein Report, 1945
References
- ^ a b Gilles Karmasyn (2014). "Lire l'introduction sur Wilhelm Cornides". Wilhelm Cornides notes sur Belzec - août-septembre 1942. Pratique de l'histoire et dévoiements négationnistes PHDN: depuis 1996. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h S.J.; H.E.A.R.T (2007). "Cornides report". Belzec Death Camp. Holocaust Research Project.org. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
Sources: Martin Gilbert, Peter Longerich, Max Freiherr Du Prel.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gilles Karmasyn & PHDN (2009), Facsimiles of Cornides notes with the French introduction. Featuring photocopy of 3 typewritten pages (not the original diary), stamped by Institut fur Zeitgeschichte (ED-81).
- ^ Florent Brayard (2000), An Early Report by Kurt Gerstein (with introduction), Bulletin du Centre de recherche français à Jérusalem, 6 / 2000.
- ^ Gerstein Report (in English translation) ARC 2006. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ^ Martin Gilbert (1979), Final Journey. The fate of the Jews in Nazi Europe Publisher: New York, New York Mayflower Books, ASIN: B0027U6TUQ.
- ^ Peter Longerich, Die Ermordung der europäischen Juden. Eine umfassende Dokumentation des Holocaust, Piper, Munich, 1989 (contains reproduction of Cornides notes).
- ^ Martin Gilbert (1997). Holocaust Journey: Travelling in Search of the Past. Columbia University Press. pp. 211–212. ISBN 9780231109642. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
External links
- Deportations to Belzec Arad, pp. 383-389 Table with exact dates and numbers (Internet Archive). Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- The German Council on Foreign Relations (DGAP) from its beginnings Wayback Machine
- International Politik, English version homepage.
