Tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Bernardirfan (talk | contribs) Clarification, Replacing {{chem}} with {{chem2}} |
Bernardirfan (talk | contribs) Missing links |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{More citations needed|date=April 2021}} |
{{More citations needed|date=April 2021}} |
||
'''Tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate''' is |
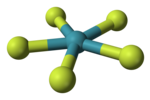
'''Tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate''' is a [[chemical compound]] with the [[chemical formula]] N(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>XeF<sub>5</sub>. The {{chem2|[XeF5]-}} ion it contains was the first example of a [[pentagonal planar molecular geometry]] [[VSEPR theory|AX<sub>5</sub>E<sub>2</sub>]] species.<ref name = "Christe">{{cite journal | title = The pentafluoroxenate(IV) anion, {{chem|XeF|5|−}}: the first example of a pentagonal planar AX<sub>5</sub> species | last1= Christe |first1=K. O. |last2=Curtis |first2=E. C. |last3=Dixon |first3=D. A. |last4=Mercier |first4=H. P. |last5=Sanders |first5=J. C. P. |last6=Schrobilgen |first6=G. J. | journal = [[Journal of the American Chemical Society]] | year = 1991 | volume = 113 | issue = 9 | pages = 3351–3361 | doi = 10.1021/ja00009a021}}</ref> It was prepared by the reaction of [[Tetramethylammonium fluoride|N(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>F]] with [[xenon tetrafluoride]], N(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>F being chosen because it can be prepared in anhydrous form and is readily soluble in organic solvents.<ref name = "Christe"/> The anion is planar, with the fluorine atoms in a slightly distorted pentagonal coordination (Xe–F bond lengths 197.9–203.4 pm, and F–X–F bond angles 71.5°–72.3°).<ref name = "Christe"/> Other salts have been prepared with sodium, cesium and rubidium, and vibrational spectra show that these contain the same planar ion.<ref name = "Christe"/> The isolated anion has the [[molecular symmetry|point group]] of ''D''<sub>5h</sub>.<ref name = "Christe"/> |
||
[[File:Pentafluoroxenate-ion-from-xtal-3D-balls.png|150px|Ball-and-stick model of the pentafluoroxenate ion]] [[File:Pentafluoroxenate-ion-2D.png|150px|Structural formula of the pentafluoroxenate ion]] |
[[File:Pentafluoroxenate-ion-from-xtal-3D-balls.png|150px|Ball-and-stick model of the pentafluoroxenate ion]] [[File:Pentafluoroxenate-ion-2D.png|150px|Structural formula of the pentafluoroxenate ion]] |
||
Revision as of 17:40, 9 February 2024

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetramethylammonium pentafluoridoxenonate(−)
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| N(CH3)4XeF5 | |||
| Molar mass | 300.4308 g/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2021) |
Tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula N(CH3)4XeF5. The [XeF5]− ion it contains was the first example of a pentagonal planar molecular geometry AX5E2 species.[1] It was prepared by the reaction of N(CH3)4F with xenon tetrafluoride, N(CH3)4F being chosen because it can be prepared in anhydrous form and is readily soluble in organic solvents.[1] The anion is planar, with the fluorine atoms in a slightly distorted pentagonal coordination (Xe–F bond lengths 197.9–203.4 pm, and F–X–F bond angles 71.5°–72.3°).[1] Other salts have been prepared with sodium, cesium and rubidium, and vibrational spectra show that these contain the same planar ion.[1] The isolated anion has the point group of D5h.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d e Christe, K. O.; Curtis, E. C.; Dixon, D. A.; Mercier, H. P.; Sanders, J. C. P.; Schrobilgen, G. J. (1991). "The pentafluoroxenate(IV) anion, XeF−
5: the first example of a pentagonal planar AX5 species". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 113 (9): 3351–3361. doi:10.1021/ja00009a021.