Western Togoland: Difference between revisions
Wowzers122 (talk | contribs) no source for the 11 million figure no source for French being a widely spoken language |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| largest_settlement_type = <!--Type of settlement if largest settlement not a city--> |
| largest_settlement_type = <!--Type of settlement if largest settlement not a city--> |
||
| official_languages = [[English language|English]] |
| official_languages = [[English language|English]] |
||
| national_languages = [[French language|French]] |
|||
| regional_languages = [[Ewe language|Ewe]], [[Dangme]], [[Avatime language|Avatime]], [[Nyangbo-Tafi language|Tafi]], [[Logba language|Logba]] |
| regional_languages = [[Ewe language|Ewe]], [[Dangme]], [[Avatime language|Avatime]], [[Nyangbo-Tafi language|Tafi]], [[Logba language|Logba]] |
||
| languages_type = <!--Use to specify a further type of language, if not official, national or regional--> |
| languages_type = <!--Use to specify a further type of language, if not official, national or regional--> |
||
| Line 67: | Line 66: | ||
| area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> |
| area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> |
||
| area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> |
| area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> |
||
| population_estimate = |
| population_estimate = 4,000,000 |
||
| population_census = |
| population_census = |
||
| population_estimate_year = |
| population_estimate_year = 2017 |
||
| population_estimate_rank = |
| population_estimate_rank = |
||
| population_census_year = |
| population_census_year = |
||
| Line 126: | Line 125: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
The German Empire established the [[Togoland|Togoland protectorate]] in 1884. Under German administration, the [[protectorate]] was regarded as a model colony or ''Musterkolonie'' and experienced a [[Golden age (metaphor)|golden age]].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JDIranayvgUC&q=togoland+reputation+musterkolonie&pg=PA173|title=Alabama in Africa: Booker T. Washington, the German Empire, and the Globalization of the New South|last=Zimmerman|first=Andrew|date=2012-05-27|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-15586-9|language=en}}</ref> During the [[First World War]] in 1914, Britain and France invaded the protectorate. After the German defeat and the signing of the [[Treaty of Versailles]], the western part of Togoland became a British mandate, [[British Togoland]], and the eastern part became [[French Togoland]]. After the [[Second World War]] British Togoland became a [[United Nations Trust Territory]] that was under British administration. In the [[1956 British Togoland status plebiscite]], 58% of the western Togolese voted to integrate into what would in 1957 become independent [[Ghana]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://unpo.org/members/20425|title=UNPO: Western Togoland|website=unpo.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Ghana - THE COLONIAL ERA: BRITISH RULE OF THE GOLD COAST|url=http://countrystudies.us/ghana/8.htm|access-date=2020-07-24|website=countrystudies.us}}</ref> |
The German Empire established the [[Togoland|Togoland protectorate]] in 1884. Under German administration, the [[protectorate]] was regarded as a model colony or ''Musterkolonie'' and experienced a [[Golden age (metaphor)|golden age]].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JDIranayvgUC&q=togoland+reputation+musterkolonie&pg=PA173|title=Alabama in Africa: Booker T. Washington, the German Empire, and the Globalization of the New South|last=Zimmerman|first=Andrew|date=2012-05-27|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-15586-9|language=en}}</ref> During the [[First World War]] in 1914, Britain and France invaded the protectorate. After the German defeat and the signing of the [[Treaty of Versailles]], the western part of Togoland became a British mandate, [[British Togoland]], and the eastern part became [[French Togoland]]. After the [[Second World War]] British Togoland became a [[United Nations Trust Territory]] that was under British administration. In the [[1956 British Togoland status plebiscite]], 58% of the western Togolese voted to integrate into what would in 1957 become independent [[Ghana]].<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://unpo.org/members/20425|title=UNPO: Western Togoland|website=unpo.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Ghana - THE COLONIAL ERA: BRITISH RULE OF THE GOLD COAST|url=http://countrystudies.us/ghana/8.htm|access-date=2020-07-24|website=countrystudies.us}}</ref> |
||
On May 9, 2017, the [[Homeland Study Group Foundation]] ({{lang-fr|Fondation du Groupe d'étude de la Patrie}}) unsuccessfully tried to declare the independence of Western Togoland. On May 7, 2019, the national executive of the Volta separatist group, Homeland Study Group Foundation (HSGF/FGEP), Emmanuel Agbavor has rejected claims that the group had a [[militia]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://citinewsroom.com/2019/05/07/we-have-no-militia-western-togoland-independence-fighters/|title=We have no militia - Western Togoland independence 'fighters'|date=2019-05-07|website=Citi Newsroom|language=en-US|access-date=2019-05-08}}</ref> |
On May 9, 2017, the [[Homeland Study Group Foundation]] ({{lang-fr|Fondation du Groupe d'étude de la Patrie}}) unsuccessfully tried to declare the independence of Western Togoland. On May 7, 2019, the national executive of the Volta separatist group, Homeland Study Group Foundation (HSGF/FGEP), Emmanuel Agbavor has rejected claims that the group had a [[militia]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://citinewsroom.com/2019/05/07/we-have-no-militia-western-togoland-independence-fighters/|title=We have no militia - Western Togoland independence 'fighters'|date=2019-05-07|website=Citi Newsroom|language=en-US|access-date=2019-05-08}}</ref> |
||
| Line 134: | Line 133: | ||
==Demographics== |
==Demographics== |
||
About |
About 4 million people live in Western Togoland. Languages of Western Togoland include [[English language|English]], [[Ewe language|Ewe]], [[Dangme]], [[Avatime language|Avatime]], and several others. The main religions are [[Christianity]], [[Islam]], and [[West African Vodun|Voodoo]]. The majority of the people in this region are ethnic [[Ewe people|Ewé]]s.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
== Reactions == |
== Reactions == |
||
Revision as of 00:32, 21 July 2024
Western Togoland[1] Togoland de l'Ouest | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Que Dieu bénisse notre Ouest Togoland" (French) (Template:Lang-en) | |
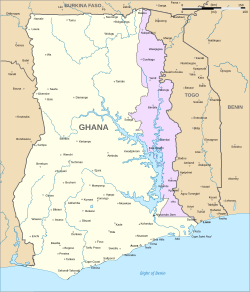 Western Togoland (purple) within Ghana | |
| Status | Unrecognised State |
| Capital | Ho |
| Official languages | English |
| Recognised regional languages | Ewe, Dangme, Avatime, Tafi, Logba |
| Religion | Christianity Islam West African Vodun |
| Demonym(s) | Western Togolese |
| Government | |
| Togbe Yesu Kwabla Edudzi (de facto) | |
| Unrecognized | |
• Independence from Ghana declared | 25 September 2020 |
| Area | |
• | 20,550 km2 (7,930 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2017 estimate | 4,000,000 |
Western Togoland (Template:Lang-fr) is a self-proclaimed state which is considered by the international community to be part of Ghana. It claims five of the Volta and Oti Regions. On 25 September 2020 separatists in Western Togoland declared independence from the Republic of Ghana.[2][3] Western Togoland has been a member state of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO) since 2017.[4]
History
The German Empire established the Togoland protectorate in 1884. Under German administration, the protectorate was regarded as a model colony or Musterkolonie and experienced a golden age.[5] During the First World War in 1914, Britain and France invaded the protectorate. After the German defeat and the signing of the Treaty of Versailles, the western part of Togoland became a British mandate, British Togoland, and the eastern part became French Togoland. After the Second World War British Togoland became a United Nations Trust Territory that was under British administration. In the 1956 British Togoland status plebiscite, 58% of the western Togolese voted to integrate into what would in 1957 become independent Ghana.[6][7]
On May 9, 2017, the Homeland Study Group Foundation (Template:Lang-fr) unsuccessfully tried to declare the independence of Western Togoland. On May 7, 2019, the national executive of the Volta separatist group, Homeland Study Group Foundation (HSGF/FGEP), Emmanuel Agbavor has rejected claims that the group had a militia.[8]
Independence
On September 25, 2020, secessionists demanded that Ghanaian Security forces leave the Volta Region after attacking several police stations in the North Tongu District of the Volta Region. In a press statement declaring their secession from Ghana, the Homeland Study Group Foundation under the leadership of Charles Kormi Kudzordz declared sovereignty over the area.[9][10] The Government of Ghana did not take the declaration seriously, viewing it as a "joke", although prominent security expert Adib Sani urged the government to treat the issue as a national security risk.[10] There have been injuries and deaths in the clashes following the declaration of independence[11] though the Republic of Ghana claims to have gained intel on those clashes before they occurred.[12] Ghana sources claim the secessionist group heading the independence movement, the Homeland Study Group, is under control.[13] However, the secessionists took over arms and set up road blockades.[2] The president of the Republic of Ghana has denied negotiating with the secessionists.[14]
Demographics
About 4 million people live in Western Togoland. Languages of Western Togoland include English, Ewe, Dangme, Avatime, and several others. The main religions are Christianity, Islam, and Voodoo. The majority of the people in this region are ethnic Ewés.[6]
Reactions
Ghana and other nations consider this movement could lead to an undesired adverse reaction. The WTRF could follow in the wake of other secessionist movements in the region such as those in Anglophone Cameroon, which quickly turned into an open armed conflict with the Cameroonian government. This risk could be combined with others, such as the expansion of Jihadist movements.
See also
References
- ^ "The State of Western Togoland". Peoples' Liberation Council of Western Togoland. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- ^ a b Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. "Ghana's Western Togoland region declares sovereignty | DW | 25.09.2020". DW.COM. Retrieved 2020-10-01.
- ^ "Western Togoland suspected separatists fresh attack for Ghana". BBC News Pidgin. Retrieved 2020-10-01.
- ^ "UNPO - Members". unpo.org. Retrieved 2020-10-04.
- ^ Zimmerman, Andrew (2012-05-27). Alabama in Africa: Booker T. Washington, the German Empire, and the Globalization of the New South. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-15586-9.
- ^ a b "UNPO: Western Togoland". unpo.org.
- ^ "Ghana - THE COLONIAL ERA: BRITISH RULE OF THE GOLD COAST". countrystudies.us. Retrieved 2020-07-24.
- ^ "We have no militia - Western Togoland independence 'fighters'". Citi Newsroom. 2019-05-07. Retrieved 2019-05-08.
- ^ "Western Togoland: Secessionists order Ghana Security forces out of Volta Region". My Joy Online. 2020-09-25. Retrieved 2020-09-08.
- ^ a b "98.9FMWhy Ghana must not laugh off Western Togoland secessionist movement - Security Expert reveals". Ghana Web. 29 September 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ "One dead, two injured after 'Western Togolanders' capture of Juapong". www.ghanaweb.com. 2020-09-25. Retrieved 2020-10-04.
- ^ "Government's intelligence claim on Volta separatist attack false – Security Analyst". www.ghanaweb.com. 2020-09-29. Retrieved 2020-10-04.
- ^ emmakd (2020-09-26). "One dead, three injured in Volta Region secessionist disturbance". Ghana Business News. Retrieved 2020-10-04.
- ^ "Secessionists Attacks: Government will not negotiate with criminals - Bawumia". MyJoyOnline.com. 2020-09-30. Retrieved 2020-10-04.



