Flag of the German Empire: Difference between revisions
Tags: Reverted references removed |
m Reverted edits by 210.3.50.94 (talk) (HG) (3.4.12) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
The Weimar Republic did not use it as a national flag though it did see use within the {{lang|de|[[Reichswehr]]}} and by many [[Weimar paramilitary groups|paramilitary organizations]] including the [[Freikorps]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Zama|first=Sarah|date=2021-05-16|title=Reichswehr|url=https://neverwasmag.com/2021/05/reichswehr/|access-date=2021-08-25|website=Never Was|language=en-US}}</ref> It would see usage by [[Right-wing politics|right-wing]] [[Conservatism in Germany|conservative]] and [[Liberalism in Germany|liberal]] political parties, including the [[German National People's Party]] and the [[German People's Party]]. Immediately after the electoral victory of the [[Nazi Party]] in March 1933, German President [[Paul von Hindenburg]] reinstated the flag by decree as the co-official [[flag of Germany]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://alex.onb.ac.at/cgi-content/alex?apm=0&aid=dra&datum=19330004&zoom=2&seite=00000103&x=18&y=10 |website=Österreichische Nationalbibliothek |access-date=14 November 2021|title=ÖNB-ALEX – Deutsches Reichsgesetzblatt Teil I 1867–1945 }}</ref> In 1935, a year after Hindenburg's death, the Imperial Flag was banned from use as the national flag in favour of the black-red-white [[Flag of Nazi Germany|swastika flag]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://alex.onb.ac.at/cgi-content/alex?apm=0&aid=dra&datum=19350004&zoom=2&seite=00001145&x=10&y=7 |website=Österreichische Nationalbibliothek|title=ÖNB-ALEX – Deutsches Reichsgesetzblatt Teil I 1867–1945}}</ref> |
The Weimar Republic did not use it as a national flag though it did see use within the {{lang|de|[[Reichswehr]]}} and by many [[Weimar paramilitary groups|paramilitary organizations]] including the [[Freikorps]].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Zama|first=Sarah|date=2021-05-16|title=Reichswehr|url=https://neverwasmag.com/2021/05/reichswehr/|access-date=2021-08-25|website=Never Was|language=en-US}}</ref> It would see usage by [[Right-wing politics|right-wing]] [[Conservatism in Germany|conservative]] and [[Liberalism in Germany|liberal]] political parties, including the [[German National People's Party]] and the [[German People's Party]]. Immediately after the electoral victory of the [[Nazi Party]] in March 1933, German President [[Paul von Hindenburg]] reinstated the flag by decree as the co-official [[flag of Germany]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://alex.onb.ac.at/cgi-content/alex?apm=0&aid=dra&datum=19330004&zoom=2&seite=00000103&x=18&y=10 |website=Österreichische Nationalbibliothek |access-date=14 November 2021|title=ÖNB-ALEX – Deutsches Reichsgesetzblatt Teil I 1867–1945 }}</ref> In 1935, a year after Hindenburg's death, the Imperial Flag was banned from use as the national flag in favour of the black-red-white [[Flag of Nazi Germany|swastika flag]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://alex.onb.ac.at/cgi-content/alex?apm=0&aid=dra&datum=19350004&zoom=2&seite=00001145&x=10&y=7 |website=Österreichische Nationalbibliothek|title=ÖNB-ALEX – Deutsches Reichsgesetzblatt Teil I 1867–1945}}</ref> |
||
=== World War |
=== World War II === |
||
[[File:NKFD armband.jpg|thumb|left|A variation of armband design used by the [[National Committee for a Free Germany]]]] |
[[File:NKFD armband.jpg|thumb|left|A variation of armband design used by the [[National Committee for a Free Germany]]]] |
||
During [[World War |
During [[World War II]], German prisoners of war who had defected to the [[Soviet Union]] and German exiles in the Soviet Union, mainly the members of the [[Communist Party of Germany]], formed the [[National Committee for a Free Germany]], an anti-fascist military and political organization which sought to overthrow the Nazi regime and aided the Red Army in various ways, including the combat against the ''Wehrmacht'', and adopted the black-white red flag as their symbol and as a flag for a possible democratic German state after the overthrow of Hitler. The main reason for the choice was the rejection of the Weimar Republic by the organization, since the prisoners of war who constituted the majority of the organization were highly critical of the Weimar Germany and said that initially they supported the Nazis only because of their disgust or hatred towards the "weakness" of the Weimar Republic, and the Communists agreed with them. The manifesto of the organization included criticisms of the "powerless" Weimar Republic and contrasted it to the future democratic state, a "truly popular" democratic government strong enough to crush the remains of the Nazi regime. The other reason was that the KPD leaders wanted to reassure its majority that the NKFD was not a Communist outfit but a union with all kind of views opposed to Nazism. The black-white-red flag became the flag of the organization and was used in its propaganda materials and on the armbands worn by the members of the organization.<ref>{{cite book|author=Kai Schoenhals|title=The Free Germany Movement: A Case of Patriotism Or Treason?|year=1989|isbn=9780313263903|pages=|publisher=Bloomsbury Academic |url=https://archive.org/details/freegermanymovem0000scho}}</ref> |
||
The Germany change the name(Alfred Kingdom)and kill Russia ,China and be friend with USA.It thinks Taiwan is real China. At last Germany be the bigger winner in World War III |
|||
Many members of this organization would play a role in the [[Soviet occupation zone in Germany|Soviet occupation]] and organization of the [[East Germany|East German government]]. Due to this, after World War II, by those who saw the Imperial flag as a symbol of [[German resistance to Nazism]] and by those that saw the black-red-gold flag as a symbol of the failed [[Weimar Republic|Weimar republic]]. It was proposed that East Germany adopted the Imperial Flag as their [[national flag]]. In the end, the East Germany decided to adopt the [[Flag of East Germany|black-red-gold flag]] as its national flag with the addition of its [[coat of arms of East Germany|coat of arms]].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2017-09-06 |title=Finding the last emblems of the German Democratic Republic in Berlin |url=https://digitalcosmonaut.com/national-emblem-german-democratic-republic/ |access-date=2023-12-18 |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Lowenfeld |first=Andreas F. |date=1952 |title=The Free Germany Committee. An Historical Study |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/1404896 |journal=The Review of Politics |volume=14 |issue=3 |pages=346–366 |doi=10.1017/S0034670500003478 |jstor=1404896 |s2cid=146241771 |issn=0034-6705}}</ref> |
|||
> |
|||
=== After German Reunification === |
=== After German Reunification === |
||
Revision as of 04:00, 21 October 2024
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (May 2022) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
 | |
| Use | State flag, civil and state ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 (3:5 in 1933–1935) |
| Adopted |
|
| Relinquished |
|
| Design | A horizontal tricolour of black, white, and red |
The black-white-red flag[1] (Schwarz-Weiß-Rot),[2] also known as the flag of the German Empire, the Imperial Flag or the Realm Flag (Reichsflagge), is a combination between the flag of Prussia and the flag of the Hanseatic League. Starting as the national flag of the North German Confederation, it would go on to be commonly used officially and unofficially under the nation-state of the German Reich, which existed from 1871 to 1945. After 1918, it was used as a political symbol by various organizations.
History
Unification of Germany
The flag was first proposed and adopted under the leadership of Otto von Bismarck, where it would be used as the flag of the North German Confederation which was formed in 1867.[3] During the Franco-Prussian War, the German Empire was founded (i.e., the South German states joined the Confederation). Germany would continue using it until the German Revolution of 1918–1919, which resulted in the founding of the Weimar Republic.[4]
Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany

The Weimar Republic did not use it as a national flag though it did see use within the Reichswehr and by many paramilitary organizations including the Freikorps.[5] It would see usage by right-wing conservative and liberal political parties, including the German National People's Party and the German People's Party. Immediately after the electoral victory of the Nazi Party in March 1933, German President Paul von Hindenburg reinstated the flag by decree as the co-official flag of Germany.[6] In 1935, a year after Hindenburg's death, the Imperial Flag was banned from use as the national flag in favour of the black-red-white swastika flag.[7]
World War II

During World War II, German prisoners of war who had defected to the Soviet Union and German exiles in the Soviet Union, mainly the members of the Communist Party of Germany, formed the National Committee for a Free Germany, an anti-fascist military and political organization which sought to overthrow the Nazi regime and aided the Red Army in various ways, including the combat against the Wehrmacht, and adopted the black-white red flag as their symbol and as a flag for a possible democratic German state after the overthrow of Hitler. The main reason for the choice was the rejection of the Weimar Republic by the organization, since the prisoners of war who constituted the majority of the organization were highly critical of the Weimar Germany and said that initially they supported the Nazis only because of their disgust or hatred towards the "weakness" of the Weimar Republic, and the Communists agreed with them. The manifesto of the organization included criticisms of the "powerless" Weimar Republic and contrasted it to the future democratic state, a "truly popular" democratic government strong enough to crush the remains of the Nazi regime. The other reason was that the KPD leaders wanted to reassure its majority that the NKFD was not a Communist outfit but a union with all kind of views opposed to Nazism. The black-white-red flag became the flag of the organization and was used in its propaganda materials and on the armbands worn by the members of the organization.[8]
Many members of this organization would play a role in the Soviet occupation and organization of the East German government. Due to this, after World War II, by those who saw the Imperial flag as a symbol of German resistance to Nazism and by those that saw the black-red-gold flag as a symbol of the failed Weimar republic. It was proposed that East Germany adopted the Imperial Flag as their national flag. In the end, the East Germany decided to adopt the black-red-gold flag as its national flag with the addition of its coat of arms.[9][10]
After German Reunification

After the reunification of Germany, the Reichsflagge remained as a symbol among right-wing monarchist organizations and the far-right in Germany. Due to the ban on Nazi swastika flag in modern Germany, many German Neo-Nazis instead adopted the Imperial Flag. However, the flag never originally had any racist or anti-Semitic meaning, despite its brief use in Nazi Germany. Among the right-wing the flag typically represents a rejection of the Federal Republic.[11][12]
Gallery
War ensigns and jacks
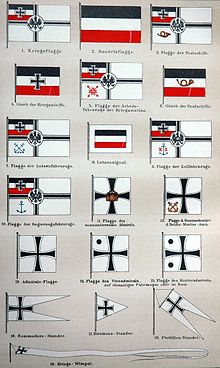
-
War Ensign of Germany (1867–1892)
-
War Ensign of Germany (1903–1919)
-
War Ensign of Germany (1903–1919) - Variant
-
Proposed war ensign (1919-1921) - never officially used
-
War Ensign of Germany (1921–1933)
-
Jack of North German Confederation and German Empire (1866–1903)
-
Jack of North German Confederation and German Empire (1866–1903) - 3:5 Variant
National flags
-
Flag of the North German Confederation and German Empire (1867–1918)
-
Flag of Nazi Germany (1933–1935)
Service flags and other
-
Flag of the Imperial Colonial Office (1907–1919)
-
Command symbol of the supreme commander in China (1900–1901)
-
Service flag of the Reich authorities at sea (1921–1926)
-
Service Flag of the Reich (1933–1935)
-
Reich service flag of the Imperial Navy
-
Flag of the mail ships (German Empire, 1892–1918)
-
Service flag for the “Other administrative branches of the Reich”, (1893–1919)
-
Merchant flag of the German Empire with the Iron Cross, (1896–1918)
Groups that use the Imperial flag
Historical
- National Socialist German Workers Party
- National Committee for a Free Germany
- German National People's Party
- German People's Party
- German Empire Party
- German Party (1947)
- The Black Channel
- Anti-Fascist Committee for a Free Germany
Modern day
- National Democratic Party of Germany
- Reichsbürger movement
- Several neo-Nazi groups and parties
See also
- German Reich
- State of the Teutonic Order
- German conservatism
- Freikorps
- Flag of Egypt
- Flag of Iraq
- Flag of Sudan
- Flag of Syria
- Flag of Upper Volta
- Flag of Yemen
References
- ^ A Third Reich, as I See It": Politics, Society, and Private Life in the Diaries of Nazi Germany, 1933-1939. Indiana University Press. 4 April 2023. ISBN 978-0-253-06534-6.
- ^ https://www.google.com/books/edition/Landsknechte_auf_dem_Weg_ins_Dritte_Reic
- ^ "North German Confederation* – Countries – Office of the Historian". history.state.gov. Retrieved 2021-04-10.
- ^ "Weimar Republic". HISTORY. Retrieved 2021-04-10.
- ^ Zama, Sarah (2021-05-16). "Reichswehr". Never Was. Retrieved 2021-08-25.
- ^ "ÖNB-ALEX – Deutsches Reichsgesetzblatt Teil I 1867–1945". Österreichische Nationalbibliothek. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ "ÖNB-ALEX – Deutsches Reichsgesetzblatt Teil I 1867–1945". Österreichische Nationalbibliothek.
- ^ Kai Schoenhals (1989). The Free Germany Movement: A Case of Patriotism Or Treason?. Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 9780313263903.
- ^ "Finding the last emblems of the German Democratic Republic in Berlin". 2017-09-06. Retrieved 2023-12-18.
- ^ Lowenfeld, Andreas F. (1952). "The Free Germany Committee. An Historical Study". The Review of Politics. 14 (3): 346–366. doi:10.1017/S0034670500003478. ISSN 0034-6705. JSTOR 1404896. S2CID 146241771.
- ^ Leffers, Jochen (2020-09-04). "Why right-wing demonstrators wave Imperial and Wirmer flags". Der Spiegel (in German). ISSN 2195-1349. Retrieved 2024-06-17.
- ^ "Imperial German Flag".

















